What do you mean by Tinea pedis?
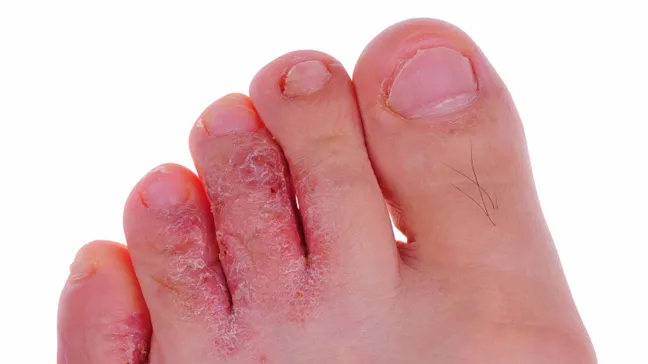
Athlete’s foot, or tinea pedis, is a common fungal infection of the foot’s epidermis.
Athlete’s foot, or tinea pedis, is a common fungal illness that affects the skin of the feet. It’s a bothersome issue that can lead to itchiness, discomfort, and potentially further bacterial infections. But, you may effectively manage this ailment if you are aware of its causes, symptoms, and course of therapy.
Table of Contents
Aetiology: The Enzymatic Offender
The fungi known as dermatophytes, which like warm, humid conditions, are the cause of tinea pedis. These fungi cause the typical symptoms by feeding on the keratin in your skin. The most frequent offenders are:
Rubrum Trichophyton
The majority of instances of tinea pedis, particularly the scaly, chronic form, are caused by this fungus.
Mentagrophytes Trichophyton
The acute, blistering form of the infection is frequently brought on by this fungus.
Phyton floccosum epidermis
Though less often, this fungus can also result in tinea pedis.
Clinical Signs and Symptoms: An Examination
Depending on the person and the type of infection, tinea pedis can have a variety of symptoms. Below is a summary of the typical forms:
Toe Web (interdigital) Tinea Pedis
This type is the most prevalent and is distinguished by:
itching: The primary symptom, which is usually severe and worse at night, is itching.
Scaling and cracking: The dry, scaly, and potentially cracked skin between the toes can cause pain and sometimes even bacterial infections.
Maceration (softening): Moisture trapped in the toe webs can cause the skin to become white and mushy.
Sneakers Tinea Pedis
This type resembles a moccasin and starts on the foot soles and progresses to the heels. It displays:
Scaling: Itchy, dry, and flaky skin.
Redness and inflammation: The skin may turn red and swollen, especially in the areas that are closest to the injury.
Skin thickening: The foot soles may get more robust and thicker.
Tinea Pedis with vesicles
This kind is less typical and includes:
Blisters: Blisters are tiny, fluid-filled blisters that can rupture and cause pain and discomfort.
Inflammation and redness: The afflicted area usually has redness and inflammation.
Scaling: There might be some scaling.
Ulcerative Tinea Pedis
Individuals with diabetes or compromised immune systems may have this severe variant. It includes:
Deep ulcers: Open sores that could hurt and bleed.
Swelling and inflammation: The skin around the injury gets puffy and red.
Drainage: Fluid or pus may come out of the ulcers.
Diagnosis: Fungus Identification
A doctor’s comprehensive physical examination is generally enough to diagnose tinea pedis. They will examine the afflicted area and search for the typical signs. To be sure of the diagnosis and pinpoint the precise fungus causing the infection, a culture could be required in certain situations. To identify the type of fungus, a sample of the afflicted skin must be taken and grown in a lab.
Treatment: Getting Rid of the Mould
The good news is that there are typically treatments for tinea pedis. Eliminating the fungus and preventing reinfection are the objectives of treatment. Among the choices are:
Medicines that fight fungus
Antifungal creams, ointments, or sprays for the skin
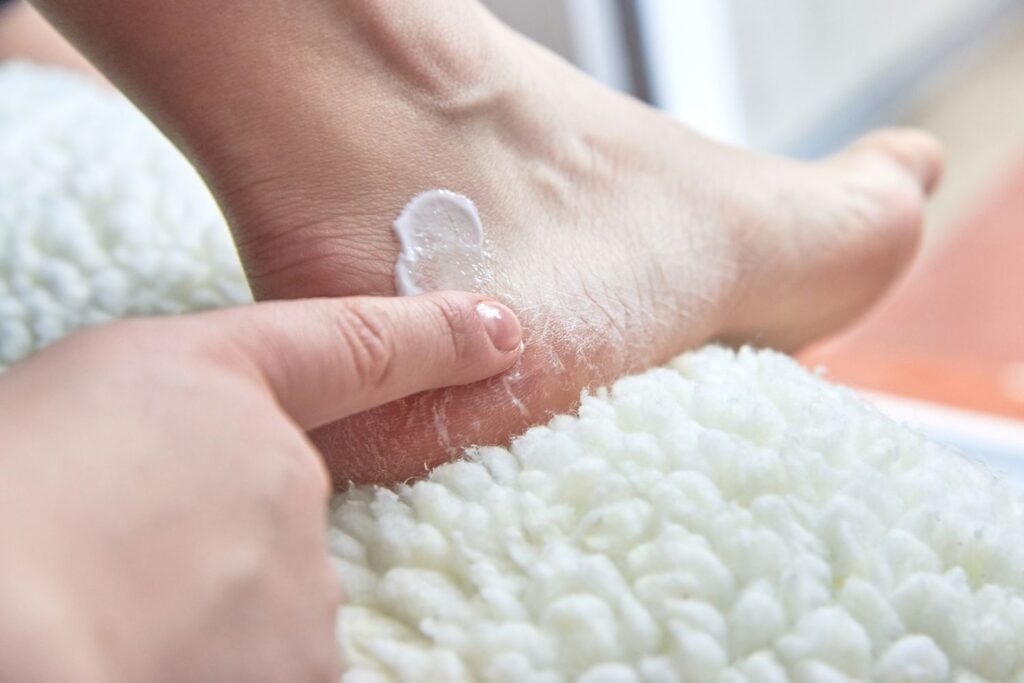

These are the first-line therapies and work well in most situations. Terbinafine, clotrimazole, miconazole, and ketoconazole are typical components.
Antifungal drugs taken orally
When topical therapies have failed to control an infection or in more severe situations, they are prescribed. Terbinafine, itraconazole, and fluconazole are typical examples.
Alternative Medical Interventions
Keeping the feet clean and dry: Maintaining dry and clean feet is essential to stopping the infection’s progress and accelerating healing. Every day, wash and thoroughly dry your feet, paying careful attention to the spaces between your toes.
Putting on breathable shoes: Steer clear of damp socks and shoes that are too tight. Choose shoes with mesh or leather uppers that allow for airflow.
Changing socks every day: Sweat is absorbed by socks, which also serve as a haven for fungi. Replace your socks on a regular basis, particularly if your feet perspire a lot.
Using antifungal powders or sprays: Applying powders or sprays with antifungal properties can help keep your feet dry and stop the growth of fungus.
Steer clear of public swimming pools and showers: These are common areas where fungal infections can spread.
Avoidance: Being Ahead of the Curve
It is imperative to prevent tinea pedis in order to minimise irritation and associated problems. Here are a few precautions to take:
Keep your feet clean and dry: Maintain clean and dry feet by giving them a regular wash and making sure they are completely dry, especially in between the toes.
Put on breathable shoes: Steer clear of tight-fitting shoes that retain moisture and instead choose shoes made of breathable fabrics.
Replace your socks every day: If you perspire a lot, especially, wear clean, fresh socks every day.
Don’t exchange towels or shoes: These objects may have fungus that propagate the illness.
Address any fungus infections right away: Treating tinea pedis can become more difficult if you neglect its early symptoms.
In summary, a persistent issue that is manageable
Although tinea pedis is a common and frequently resistant fungal illness, there is no need to be alarmed. Through knowledge of the condition’s causes, symptoms, and remedies, you can effectively manage it and maintain the comfort and health of your feet. See a physician for an accurate diagnosis and course of treatment if you think you might have tinea pedis. Recall that maintaining clean, dry, and well-ventilated feet is essential to avoiding this illness and having comfortable, healthy feet.
Frequnetly Asked Questions(FAQ)
What do you mean by Trichophyton?
A genus of fungi known as Trichophyton is the cause of the tinea, or ringworm, group of illnesses. These infections, which can harm the skin, hair, and nails, are widespread.
What do you mean by Antifungal drugs ?
Medications known as antifungal medicines are used to treat fungal infections. Fungi are microscopic organisms that can infect people with a wide range of illnesses.
Related Articles