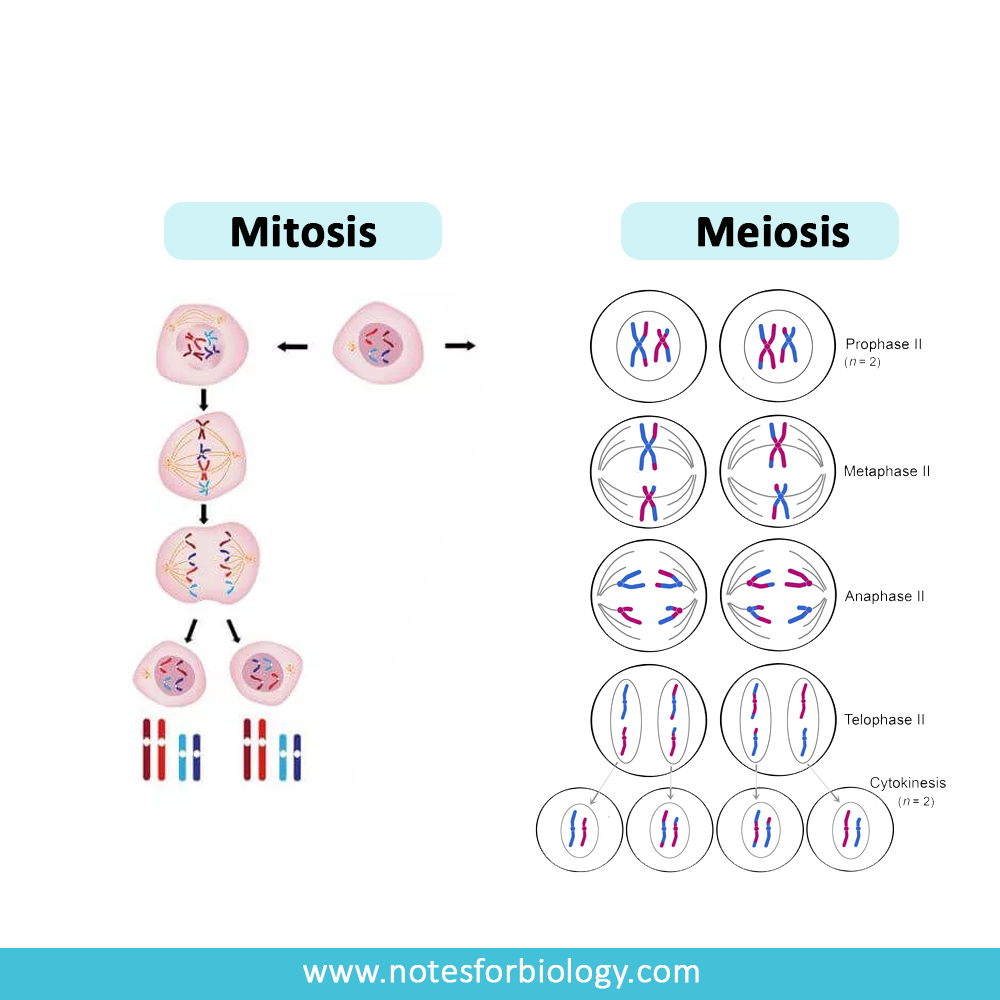
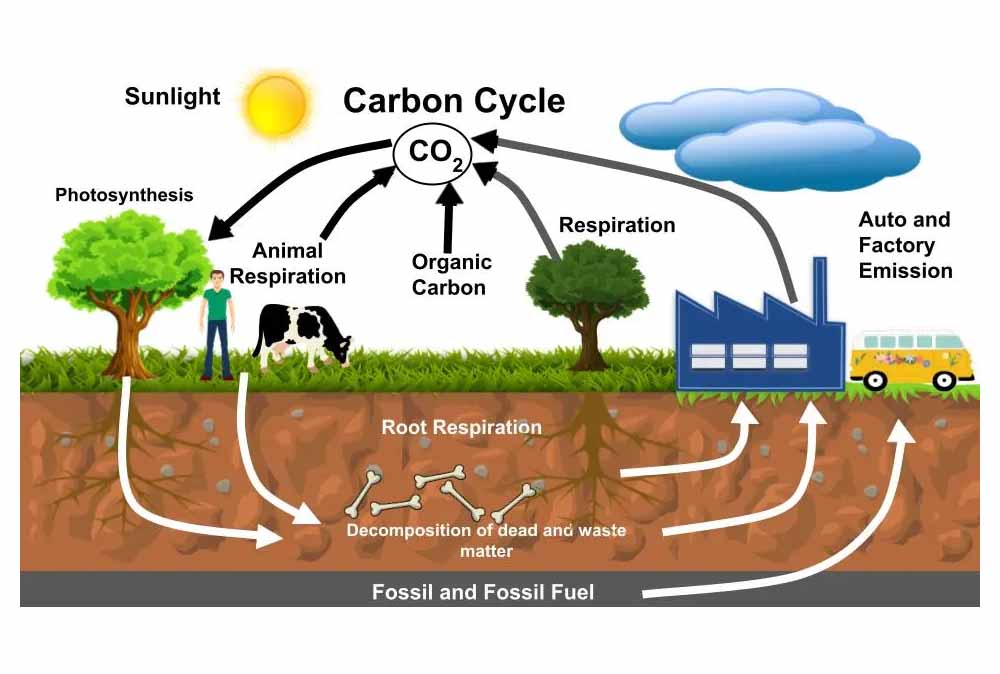
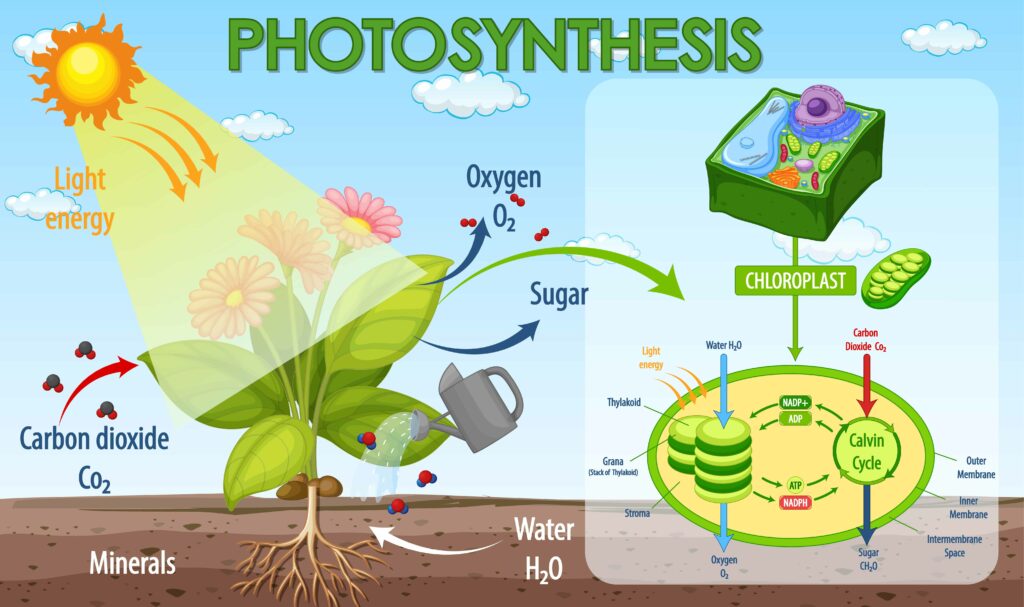
List of 5 Important Biology Topics
Today, we will discuss the list of 5 Important biology topics. Biology plays an important role in the preparation for many competitive examinations. Here, we have a tendency to area unit providing an inventory of some necessary topics in Biology to hurry up the preparation. The topics mentioned below are unit elementary in nature and […]
List of 5 Important Biology Topics Read More »