What is Tinea unguium?
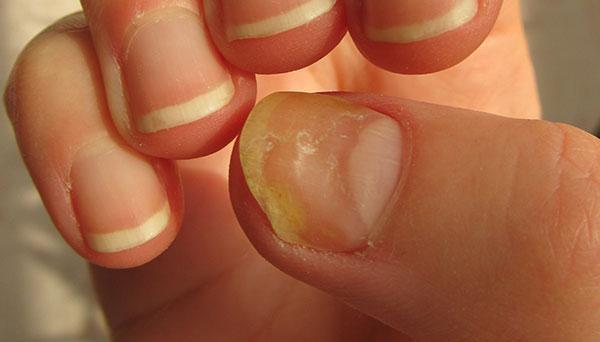
Onychomycosis, another name for tinea unguium, is a fungal infection of the nails. It’s a prevalent ailment that primarily affects toenails rather than fingernails. It’s not life-threatening, but it can be annoying, persistent, and occasionally even painful. Let’s examine this nail problem in more detail:
Table of Contents
Origin: The Internal Enemy
Different dermatophytes, a class of fungi that feed on keratin, the protein found in your nails, are the cause of tinea unguium. These fungi infiltrate the nail plate, interfering with its regular growth and leading to a host of issues.
The most frequent offenders consist of
Trichophyton rubrum: Accounting for around 90% of cases, this is the most common culprit.
Trichophyton mentagrophytes: One more frequently occurring cause is Trichophyton mentagrophytes, especially when athletes’ foot is involved.
Epidermophyton floccosum: Athlete’s foot is frequently brought on by the fungus Epidermophyton floccosum, which can also spread to the nails.
Clinical Symptoms: Indications of Overtake
A variety of visual signs, typically affecting the nail plate, are present with tinea unguium.
Thickness and distortion: The nail gets crumbly, brittle, and thicker; it also frequently lifts off the nail bed.
Discoloration: The nail could become yellow, brown, black, or white.
White patches: The nail plate may develop little white patches, usually near the base, which give the nail a “chalky” appearance.
Crunching of the nail: An infected nail may break and crumble readily, making trimming it challenging.
Subungual debris: Debris can build up in the subungual space—the area between the nail plate and the nail bed—appearing as a white or yellow deposit.
Diagnosis: Determining the Opponent
A combination of clinical examination and laboratory tests is used to diagnose tinea unguium:
Visual examination: The classic indications and symptoms of tinea unguium are typically recognized by a dermatologist.
Preparation of KOH: A small amount of scraped nail material is combined with potassium hydroxide (KOH). Under a microscope, the keratin is dissolved by this solution, revealing the fungal components.
Nail culture: To determine the precise kind of fungus causing the infection, a sample of nail debris is grown in a laboratory.
Therapy
Antifungal drugs are typically used to treat tinea unguium, and they can be given in a number of ways:
Topical antifungal agents
Topical antifungal medications are administered directly to the nail that is affected. They are available in several forms, such as lotions, creams, and nail lacquers. Butenafine, amorolfine, and ciclopirox olamine are typical examples.
Oral antifungal agents
These are administered orally and act systemically. When topical therapies are not working or for more severe instances, oral antifungals are usually employed. Terbinafine, itraconazole, and fluconazole are a few examples.
Laser therapy
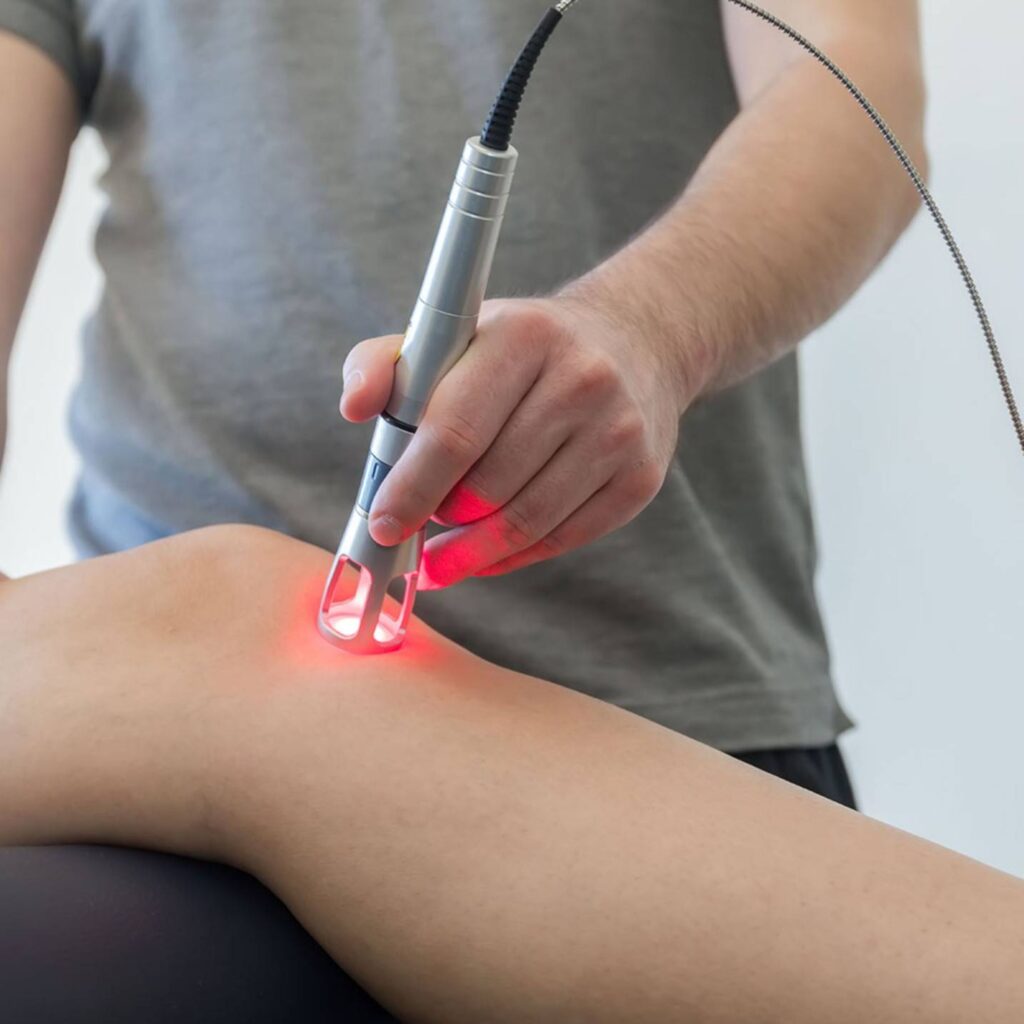
Using a laser, the fungal infection inside the nail plate is targeted and destroyed as part of laser therapy. Patients who have not responded to conventional therapy or those with severe cases are frequently candidates for it.
Crucial Points to Remember
Treatment duration: Even if the illness seems to go away sooner, it’s important to finish the entire course of medication. Recurrence is possible if treatment is not completed.
Removal of the nail: In certain circumstances, removing the infected nail may be necessary to allow the antifungal drug to penetrate the skin.
Recurrence: If the underlying cause (such as athlete’s foot) is not treated, tinea unguium may have a tendency to return.
Prevention: Always Be One Step Ahead
Always wash your hands: Maintaining proper hygiene and limiting exposure to the fungus are necessary to prevent tinea unguium,Always wash your hands,especially after coming into contact with hazardous objects or sick people.
Put on fresh shoes and socks: Wash your shoes on a regular basis and change your socks every day.
Refrain from sharing private items: Towels, shoes, and nail clippers are examples of this.
Maintain manicures: Fungi are less prone to grow under short nails.
Treat athlete’s foot promptly: In order to stop the infection from spreading to the nails, athlete’s foot should be treated right away.
Unguium can be a bothersome and enduring condition. However, the majority of instances can be successfully managed with the right diagnosis and care. Recall that in order to reduce the effects of this fungal invasion, early action is essential.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQ)
What do you mean by hazardous objects?
Waste classified as hazardous needs to be managed carefully in order to protect the environment and public health. Waste can be dangerous due to a variety of characteristics, such as toxicity, strong chemical reactions, or corrosiveness.
What do you mean by KOH?
Potassium hydroxide’s chemical formula is KOH.
Caustic potash is the common name for this potent basic.
Related Articles