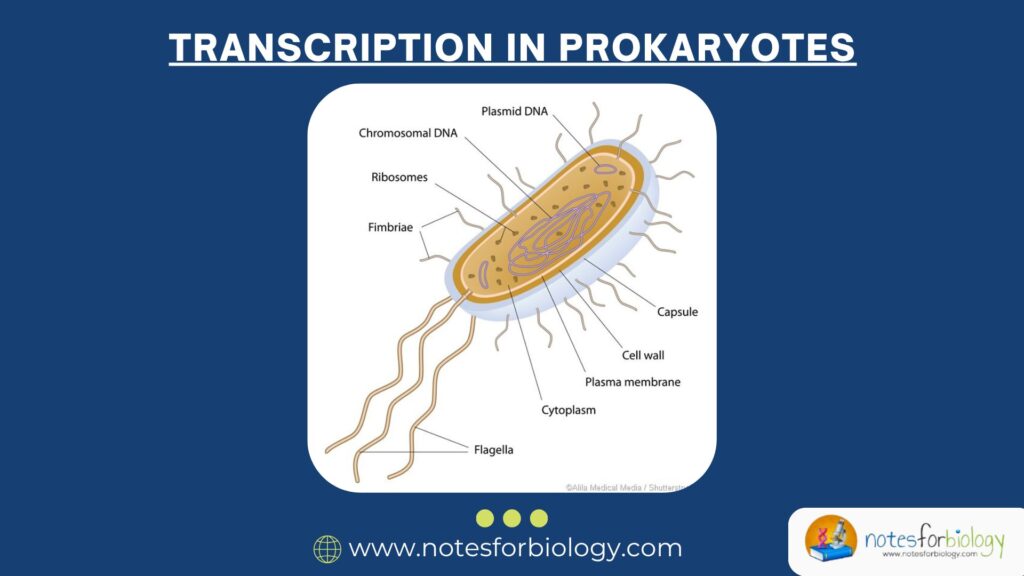
A prokaryote is a type of simple, single-celled organism that does not have a nucleus or other membrane-bound organelles inside its cell. In prokaryotes (like bacteria), this entire process is beautifully simple yet incredibly efficient. In this explanation, we’ll take a friendly walk through everything you need to know about transcription in prokaryotes — using simple language, real-life analogies, and clear examples.
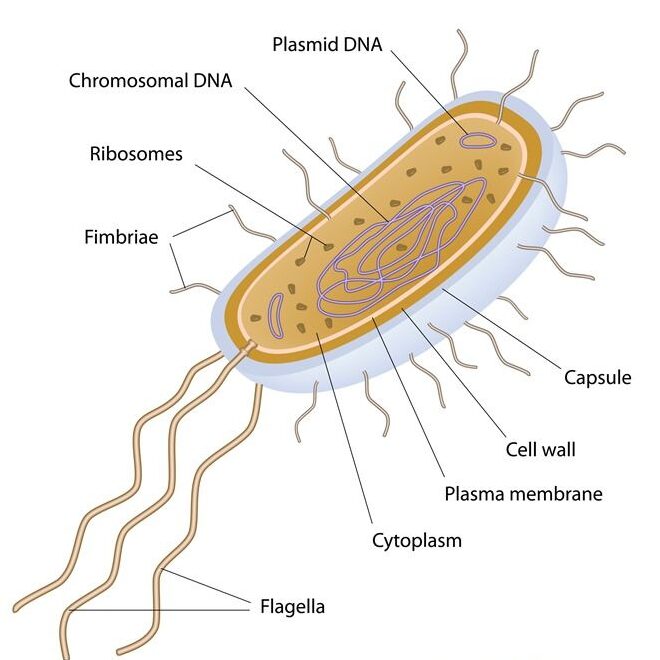
Table of Contents
What Is Transcription?
Transcription is the process of making an RNA copy of a gene’s DNA sequence. This RNA copy (called messenger RNA or mRNA) carries the instructions needed to make proteins — the actual machines and structures of the cell.
So, in short:
DNA → mRNA → Protein
Transcription is the first step in this chain.
Where Does Transcription Happen in Prokaryotes?
In prokaryotic cells, transcription happens directly in the cytoplasm, because they don’t have a nucleus. As soon as the mRNA is made, ribosomes can start reading it to build proteins — kind of like printing a recipe and immediately handing it to the cook.
Key Players in Transcription
Before we dive into the steps, let’s meet the main “characters” involved in transcription:
1. DNA
- Holds the genetic code — the instructions for building proteins.
2. RNA Polymerase
- The main enzyme responsible for reading DNA and making RNA.
- In prokaryotes, there is only one type of RNA polymerase.
3. Sigma Factor (σ)
- A helper protein that guides RNA polymerase to the right starting point on the DNA (like a GPS).
4. Promoter Region
- A specific sequence on the DNA that tells RNA polymerase where to start transcription.
- Common ones include the -10 region (TATAAT) and -35 region (TTGACA).
5. Terminator
A special DNA sequence that tells RNA polymerase where to stop.
The Three Main Stages of Transcription
Just like writing a letter, transcription happens in three steps: Initiation, Elongation, and Termination.
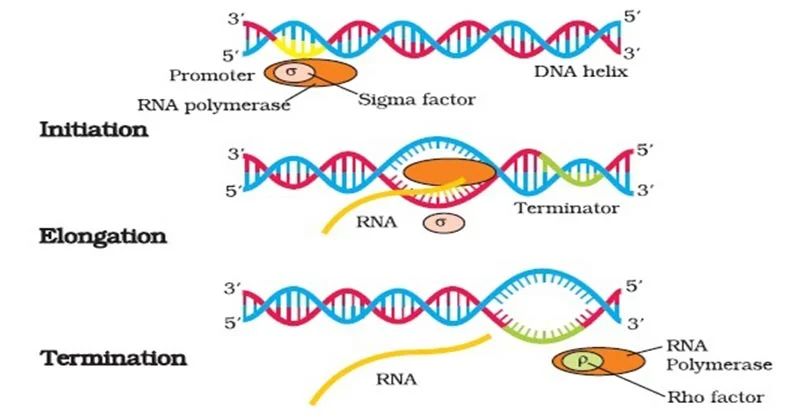
1. Initiation — “Starting the Engine”
This is where everything begins.
a. Finding the Start Line
The sigma factor binds to RNA polymerase and leads it to a promoter — a sequence of DNA that marks the start of a gene. You can think of the promoter as a green traffic light telling RNA polymerase, “Go! Start here!”
b. Opening the DNA
Once RNA polymerase reaches the promoter, it unwinds a small portion of the DNA to expose the template strand. This unwound section is called the transcription bubble.
c. First Letters Written
RNA polymerase starts putting together the first few RNA nucleotides (A, U, G, C) based on the DNA template. In RNA, uracil (U) replaces thymine (T).When everything is stable and ready, the sigma factor detaches, and RNA polymerase continues on its own.
2. Elongation — “Writing the Message”
RNA polymerase moves along the DNA template, adding RNA nucleotides one by one. It reads the DNA strand from 3’ to 5’ and makes RNA in the 5’ to 3’ direction.
Think of RNA polymerase as a train riding along the tracks (DNA), laying down a ribbon (RNA) behind it.
Here’s what happens:
- The DNA behind is rewound.
- The DNA ahead is unwound.
- A growing RNA strand comes out the back.
Important: This RNA is complementary to the DNA template. For example:
- If DNA has A, RNA adds U
- If DNA has T, RNA adds A
- If DNA has C, RNA adds G
- If DNA has G, RNA adds C
This continues until the enzyme hits the “stop sign.”
3. Termination — “Finishing the Job”
Eventually, RNA polymerase reaches a terminator sequence, and transcription ends.
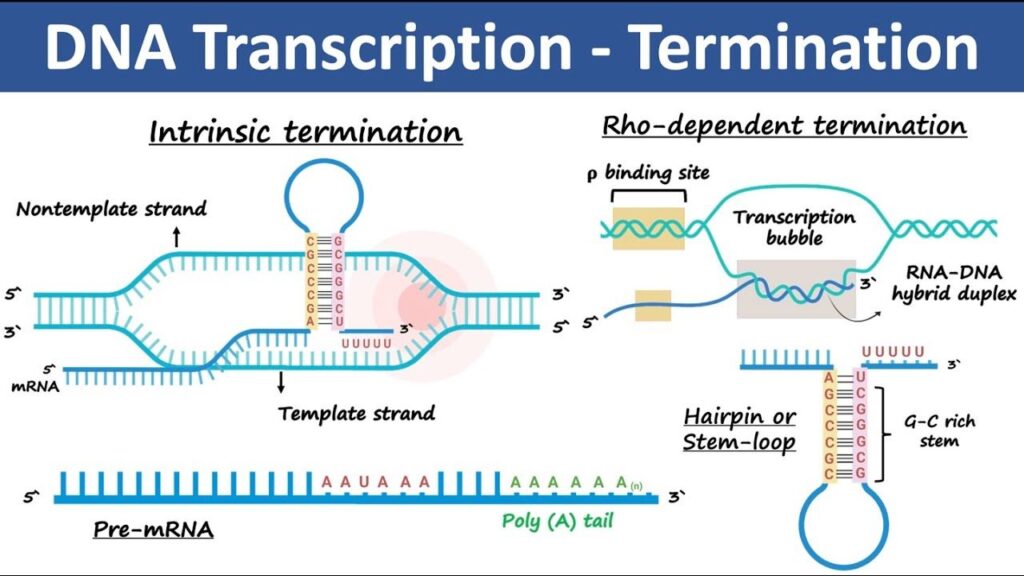
There are two types of termination mechanisms in prokaryotes:
a. Rho-Independent Termination
Also known as intrinsic termination.
- The DNA has a GC-rich region followed by a string of A’s.
- This causes the RNA to fold into a hairpin loop, followed by a weak A-U stretch.
- The hairpin causes RNA polymerase to pause, and the weak A-U bonds break easily. The RNA falls off. Job done!
b. Rho-Dependent Termination
- Requires a protein called Rho.
- Rho attaches to the RNA and chases RNA polymerase.
- When RNA polymerase pauses at a stop signal, Rho catches up and knocks it off the DNA.
- Transcription ends.
A Special Note on Coupled Transcription and Translation
In prokaryotes, something amazing happens: transcription and translation are coupled.
That means:
- As soon as the RNA starts coming out of RNA polymerase, ribosomes immediately attach and start building proteins.
- This can only happen because there’s no nuclear membrane separating the DNA and ribosomes.
It’s like writing a recipe and having a chef cook it before you’ve even finished typing it!
Why Is Transcription So Important?
Transcription is the first step in gene expression. If a cell needs a protein, it first needs the mRNA blueprint for that protein. Without transcription, the genetic code in DNA would be useless.
It also allows cells to respond to changes quickly. For example:
- When bacteria sense lactose, they start transcribing genes to digest it.
- When nutrients are scarce, they stop transcribing certain genes to conserve energy.
- In short, transcription gives cells flexibility, speed, and control.
Regulation of Transcription in Prokaryotes
Prokaryotes must save energy by only transcribing what they need. This is managed through gene regulation.
One famous example is the lac operon in E. coli:
- When lactose is absent, a repressor protein binds to the DNA and blocks transcription.
- When lactose is present, it binds to the repressor and removes it.
- This allows RNA polymerase to transcribe the genes needed to break down lactose.
It’s like a smart thermostat — turning on heating only when it’s cold.
Fun Facts About Transcription in Prokaryotes
- Fast and efficient: Bacterial RNA polymerase can make RNA at about 40-50 nucleotides per second.
- Multiple copies at once: Many RNA polymerase enzymes can transcribe the same gene at the same time — like a team of copywriters working on different sections of a book.
- Polycistronic mRNA: In prokaryotes, one mRNA can code for several proteins. This is rare in eukaryotes.
- One RNA polymerase does it all: Unlike eukaryotes (which have RNA polymerases I, II, and III), prokaryotes use just one type of RNA polymerase for all kinds of RNA.
Recap Table: Transcription in Prokaryotes
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Initiation | RNA polymerase (with sigma factor) binds to promoter and starts RNA synthesis |
| Elongation | RNA polymerase moves along DNA, adding RNA nucleotides |
| Termination | Transcription ends when RNA polymerase reaches a stop signal |
| Key Enzyme | RNA polymerase |
| Location | Cytoplasm |
| Speed | ~40-50 nucleotides per second |
| Coupling | Transcription and translation happen simultaneously |
| Regulation | Operons like lac operon control when genes are transcribed |
CONCLUSION
Transcription in prokaryotes might seem like a tiny process, but it is absolutely essential for life. It’s how bacteria sense their environment, survive stress, and reproduce. The beauty lies in its simplicity and speed — a streamlined system that allows these tiny organisms to adapt in real time.
In the grand orchestra of life, transcription is like the sheet music — turning genetic information into instructions, making sure that each cell knows what to do, and when to do it. In prokaryotes, this process is not only fast and efficient, but also a great example of nature’s genius in keeping things simple yet powerful.
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
What is prokaryotes?
A prokaryote is a type of simple, single-celled organism that does not have a nucleus or other membrane-bound organelles inside its cell.
What is Transcription ?
Transcription is the process of making an RNA copy of a gene’s DNA sequence. This RNA copy (called messenger RNA or mRNA) carries the instructions needed to make proteins — the actual machines and structures of the cell.
What are the stages of Transcription in prokaryotes ?
The stages of transcription in prokaryotes are initiation, where RNA polymerase binds to the promoter and starts RNA synthesis; elongation, where it moves along the DNA and builds the RNA strand; and termination, where it stops transcription and releases the RNA molecule.
Related Articles