The phenylalanine deaminase test is a biochemical test used to identify bacteria that possess the enzyme phenylalanine deaminase. This enzyme plays a crucial role in bacterial metabolism, allowing them to break down the amino acid phenylalanine into phenylpyruvic acid and ammonia.
Table of Contents
Principle of the Phenylalanine deaminase test
The PDA test leverages the specific enzymatic activity of phenylalanine deaminase. When bacteria possessing this enzyme are exposed to a medium containing phenylalanine, they convert it into phenylpyruvic acid. This acid reacts with ferric chloride, a chemical reagent added to the medium, to produce a green-colored compound. The presence of this green color indicates a positive PDA test, signifying that the bacterium in question can break down phenylalanine.
Requirements for the Phenylalanine deaminase test
Phenylalanine Agar: This is a specially formulated agar medium containing phenylalanine as the key ingredient. It provides a suitable environment for bacterial growth and facilitates the deamination process.
Ferric Chloride Solution: This reagent is essential for visualizing the phenylpyruvic acid produced during deamination. When added to the medium, it reacts with phenylpyruvic acid to generate the green-colored complex, which signifies a positive result.
Bacterial Culture: A pure culture of the bacterium to be tested is required. This ensures that the observed results are specific to the organism being examined.
Incubator: An incubator is needed to provide the appropriate temperature for bacterial growth. The incubation temperature for the PDA test is usually 35-37°C.
Sterile Inoculating Loop or Needle: These tools are used to transfer the bacterial culture to the PDA agar.
Test Tubes or Petri Dishes: These containers are used to hold the PDA agar and the bacterial culture.
Procedure of the Phenylalanine deaminase test
Preparation: A small amount of the bacterial culture is inoculated onto the surface of the PDA agar slant using a sterile inoculating loop or needle. Ensure that the streak is relatively thin and uniform.
Incubation: The inoculated PDA agar slant is then incubated at 35-37°C for 18-24 hours. This incubation period allows the bacteria to grow and produce phenylpyruvic acid if they possess the enzyme phenylalanine deaminase.
Observation: After incubation, the PDA agar slant is carefully observed for any color change. If the slant exhibits a green color, it signifies a positive result. This indicates that the bacteria in question can break down phenylalanine and produce phenylpyruvic acid. If the slant remains its original color, the result is negative, indicating the absence of phenylalanine deaminase activity.
Confirmation: For further confirmation, a few drops of ferric chloride solution are added to the slant. If the green color intensifies, it confirms the presence of phenylpyruvic acid and thus, the positive PDA test result.
Results Interpretation
Positive Phenylalanine deaminase test
A green color develops on the PDA agar slant after the addition of ferric chloride solution. This indicates that the bacterium possesses the enzyme phenylalanine deaminase and can break down phenylalanine.
Negative Phenylalanine deaminase test
No green color develops on the PDA agar slant after the addition of ferric chloride solution. This suggests that the bacterium lacks the enzyme phenylalanine deaminase and cannot break down phenylalanine.
Clinical Significance of the Phenylalanine deaminase test
The PDA test is a valuable tool in the identification and differentiation of various bacterial species. It is particularly useful in identifying the following:
Proteus spp.
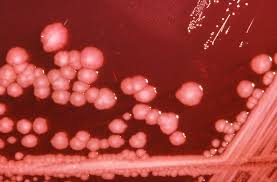
Most species of Proteus are known to be positive for the PDA test. This information helps differentiate them from other bacteria that lack this enzyme.
Enterobacter spp.
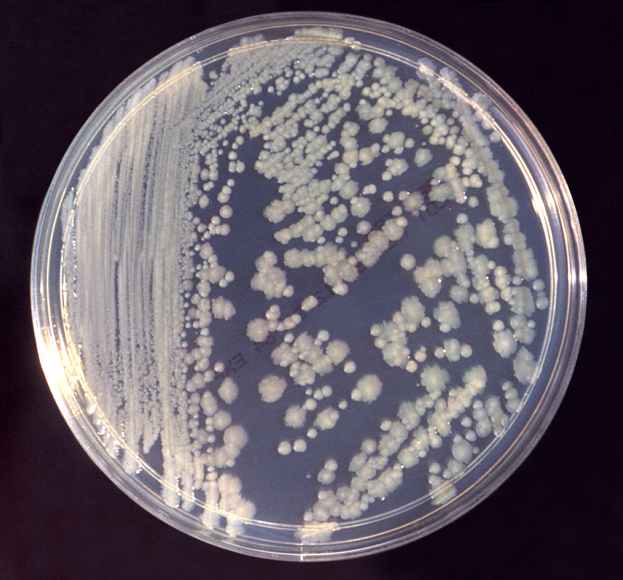
Some Enterobacter species are also known to be positive for the PDA test, further aiding in their identification.
Other bacterial species
While not as common, certain other bacteria may also possess the phenylalanine deaminase enzyme.
Overall, the PDA test serves as a crucial step in identifying bacterial species based on their metabolic capabilities. By observing the presence or absence of phenylalanine deaminase activity, we can gain valuable insights into the biochemical characteristics of various bacteria, paving the way for accurate diagnosis and treatment of bacterial infections.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQ)
Define Phenylalanine?
Since phenylalanine is an important amino acid—one that our systems cannot make on their own—we must obtain it through diet.
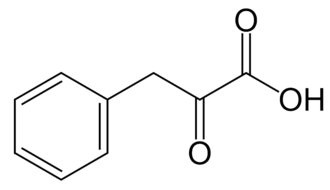
What is Phenylpyruvic acid?
Phenylpyruvic acid is the organic compound with the formula C6H5CH2C(O)CO2H. It is a keto acid.
Related Articles