What is Bacterial Cell wall?
Bacterial cell wall is a strong, protective outer layer that surrounds the bacterial cell. It gives the cell its shape, protects it from bursting, and helps the bacteria survive in different environments. Bacterial cell wall is made of peptidoglycan, a polymer made of sugars and amino acids that provides structural strength. In Gram-positive bacteria, the wall consists of many layers of peptidoglycan and teichoic acids, while Gram-negative bacteria have a thinner peptidoglycan layer surrounded by an outer membrane containing lipopolysaccharides.
Summary of Bacterial Cell wall
- Provides Shape and Strength: The bacterial cell wall maintains the cell’s shape and offers structural support.
- Prevents Bursting: It protects the cell from bursting due to internal pressure by counteracting osmotic forces.
- Varies Among Bacteria: The composition differs between Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, influencing their staining properties and antibiotic susceptibility.
Table of Contents
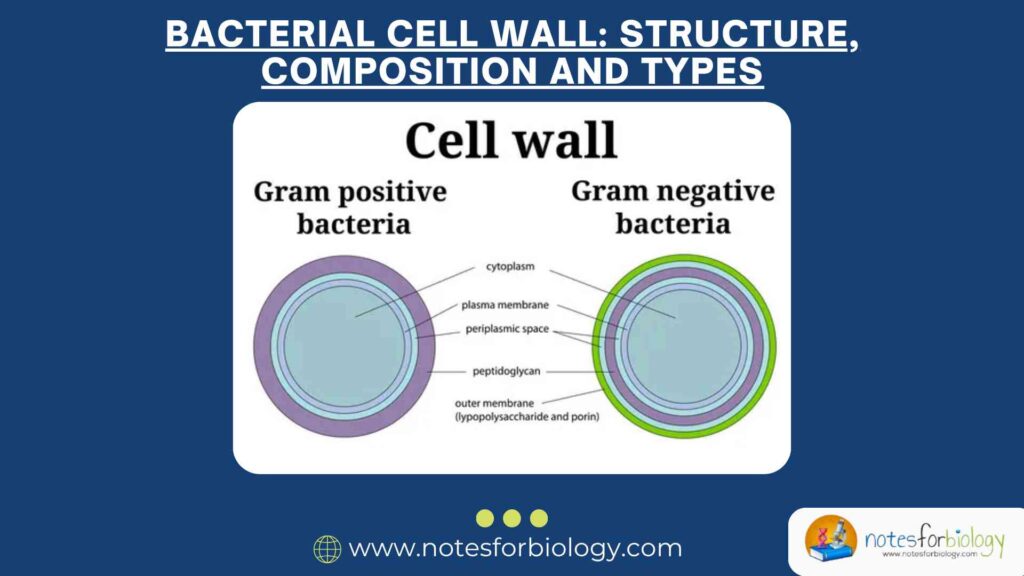
Bacterial cell wall diagram
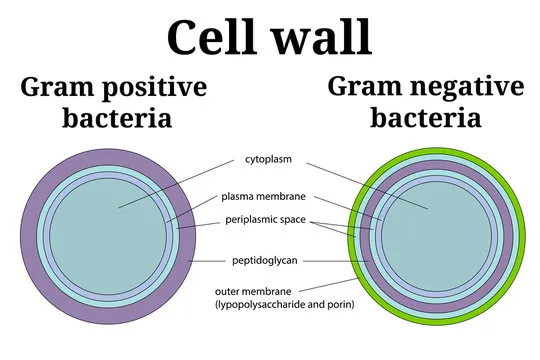
Structure of Bacterial Cell wall
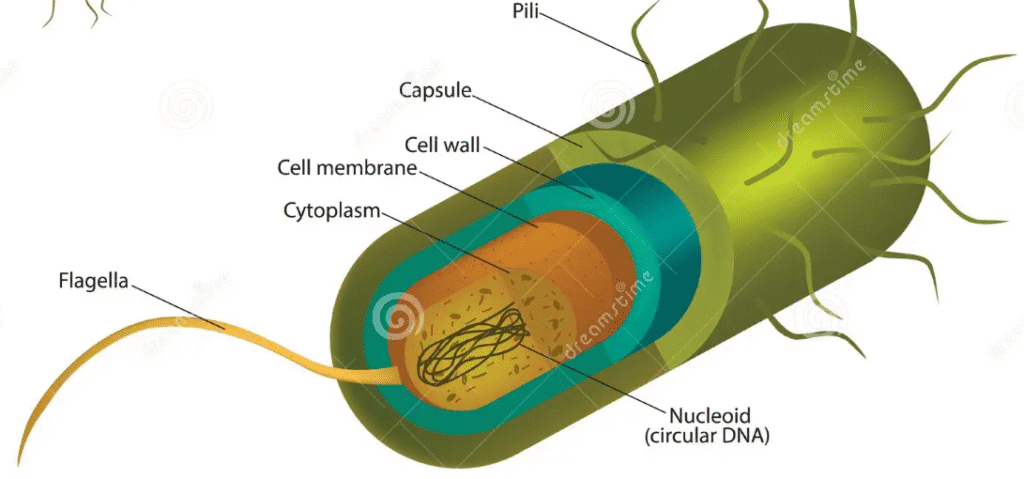
The bacterial cell wall is like a strong, protective shell that wraps around a bacterium, giving it shape and keeping it from bursting. Think of it as a bacteria’s exoskeleton just like how a turtle has a hard shell, bacteria have their own armor.
1. Peptidoglycan Layer (Murein)
This is the main component of bacterial cell walls. It is made of sugar chains (NAG & NAM) linked by peptide bonds, forming a strong mesh-like structure. This layer provides rigidity and prevents the cell from bursting.
2. Gram-Positive Cell Wall
- Has a thick, strong layer made of peptidoglycan (like a brick wall).
- Contains teichoic acids (help bacteria stick to surfaces).
- Stains purple in lab tests.
- Easier to kill with common antibiotics (like penicillin).
- Example: Staphylococcus (causes skin infections).
2. Gram-Negative Cell Wall
- Has a thin peptidoglycan layer (like a chain-link fence).
- Covered by an extra outer membrane (like a slippery raincoat).
- This membrane has toxic LPS (triggers fevers).
- Contains porins (tiny gates for food/air).
- Stains pink in lab tests.
- Harder to treat (many antibiotics can’t get through).
- Example: E. coli (causes food poisoning).
4. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) Layer
Found in Gram-negative bacteria, this layer helps bacteria resist antibiotics and protects them from harmful substances. It also plays a role in bacterial infections.
5. Periplasmic Space
This is the gap between the inner membrane and the peptidoglycan layer in Gram-negative bacteria. It contains enzymes that help bacteria break down nutrients.
6. Capsule (Optional)
Some bacteria have an extra protective layer called a capsule. It helps bacteria avoid being destroyed by the immune system and makes them more resistant to harsh conditions.
Composition of Bacterial Cell wall
The bacterial cell wall is a protective outer layer that maintains the shape of the cell and prevents it from bursting due to internal pressure. Its composition varies between Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, which is important for their identification and treatment.
1. Peptidoglycan (Murein)
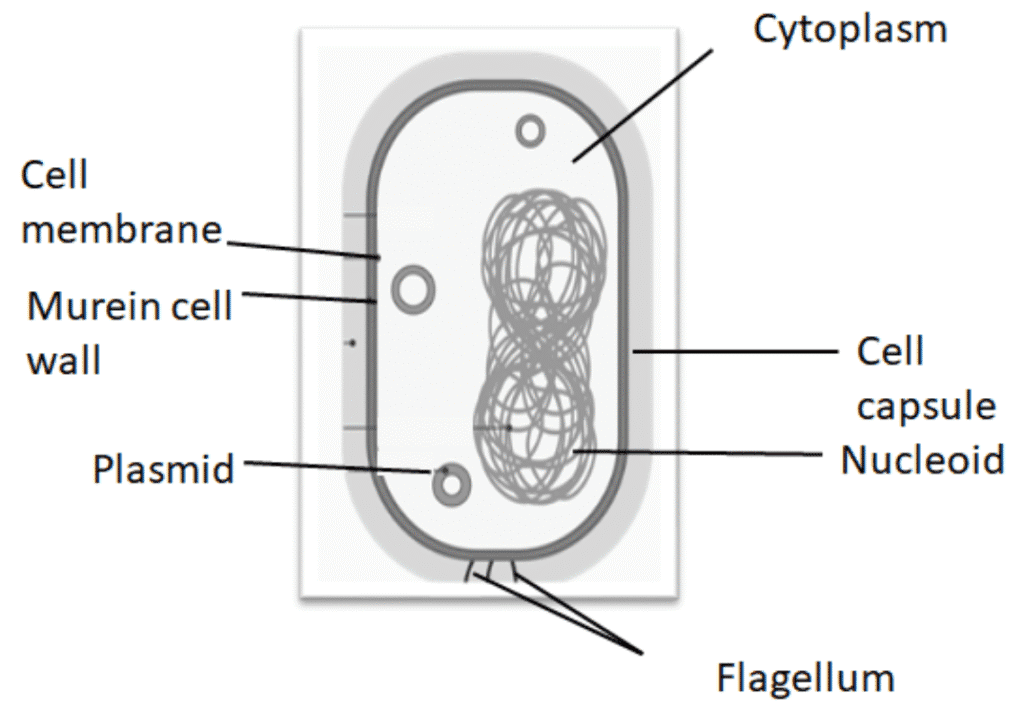
Peptidoglycan is the main component of the bacterial cell wall. It is a mesh-like polymer made of sugars and amino acids, forming a strong and flexible structure. This layer provides rigidity and protects the cell from osmotic pressure.
2. Teichoic and Lipoteichoic Acids (Gram-Positive Bacteria)
In Gram-positive bacteria, the cell wall contains teichoic acids, which are polymers that provide structural support and contribute to the cell’s negative charge. Lipoteichoic acids are anchored in the cell membrane and play roles in cell wall maintenance and ion transport.
3. Outer Membrane and Lipopolysaccharides (Gram-Negative Bacteria)
Gram-negative bacteria have an outer membrane external to the peptidoglycan layer. This membrane contains lipopolysaccharides (LPS), which protect the bacteria from certain chemicals and can trigger immune responses in humans.
4. Periplasmic Space (Gram-Negative Bacteria)
Between the inner cytoplasmic membrane and the outer membrane in Gram-negative bacteria lies the periplasmic space. This gel-like area contains enzymes and proteins involved in nutrient processing and cell wall assembly.
5. Proteins and Enzymes
Both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria have proteins and enzymes in their cell walls that assist in various functions, including nutrient transport and defense mechanisms. These components are essential for the bacteria’s survival and can be targets for antibiotics.
The bacterial cell wall is primarily composed of peptidoglycan, providing structural strength and shape. Gram-positive bacteria have a thick peptidoglycan layer with teichoic acids, while Gram-negative bacteria feature a thin peptidoglycan layer and an outer membrane containing lipopolysaccharides. Understanding these differences is crucial for developing targeted antibiotics and treating bacterial infections effectively.
Types of Bacterial Cell wall
1. Gram-Positive Cell Wall
- Has a thick, strong layer made of peptidoglycan (like a brick wall).
- Contains teichoic acids (help bacteria stick to surfaces).
- Stains purple in lab tests.
- Easier to kill with common antibiotics (like penicillin).
- Example: Staphylococcus (causes skin infections).
2. Gram-Negative Cell Wall
- Has a thin peptidoglycan layer (like a chain-link fence).
- Covered by an extra outer membrane (like a slippery raincoat).
- This membrane has toxic LPS (triggers fevers).
- Contains porins (tiny gates for food/air).
- Stains pink in lab tests.
- Harder to treat (many antibiotics can’t get through).
- Example: E. coli (causes food poisoning).
3. Acid-Fast Bacteria (Special Type)
- Has a thick, waxy coating (like a grease shield).
- Resists most stains and drugs.
- Needs a special acid-fast test to detect.
- Example: Mycobacterium tuberculosis (causes TB).
4. Mycoplasma (No Cell Wall!)
- Lacks a cell wall (only has a soft membrane).
- Can’t be killed by penicillin (since it targets walls).
- Example: Mycoplasma pneumoniae (causes “walking pneumonia”).
Conclusion
Bacterial cell walls are essential structures that provide shape, protection, and support to bacterial cells. The two main types Gram-positive and Gram-negative differ in their composition and structure, which influences their staining characteristics and susceptibility to antibiotics. Additionally, some bacteria naturally lack a cell wall, like Mycoplasma, or can lose it under certain conditions, forming L-forms, protoplasts, or spheroplasts.
Understanding these variations is crucial in microbiology, as it aids in the identification of bacteria and informs the selection of appropriate treatments. Recognizing the differences in cell wall types helps healthcare professionals and researchers develop effective strategies to combat bacterial infections.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the functions of Bacterial cell wall?
The bacterial cell wall is a crucial structure that provides shape, strength, and protection to the cell. It prevents the cell from bursting due to internal pressure, acts as a barrier against harmful substances, and, in some bacteria, contributes to their ability to cause disease.
What is the bacterial cell wall made of?
It is primarily composed of peptidoglycan, a mesh-like polymer of sugars and amino acids unique to bacteria.
How does the bacterial cell wall contribute to disease?
In some bacteria, components of the cell wall can interact with the host’s immune system, aiding in the bacterium’s ability to cause disease.
Related Articles