What is Actinobacteria?
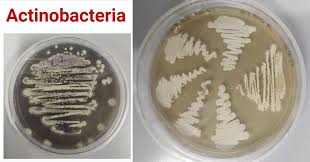
Actinobacteria is a phylum of Gram-positive bacteria notable for its varied metabolic capacities, unique branching filamentous shape, and high G+C concentration in their DNA are the actinobacteria. They can be found in many different types of environments, such as soil, water, and even some very harsh ones. In ecological processes including decomposition, nitrogen fixation, and nutrient cycling, actinobacteria are essential. They are particularly important to the pharmaceutical and biotechnological sectors because they produce large amounts of bioactive substances, including as antifungals, antibiotics, and anticancer medicines.
Table of Contents
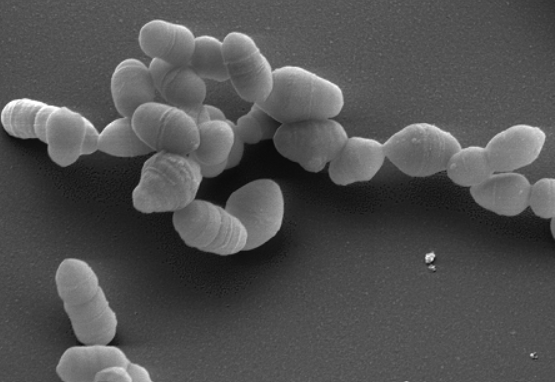
General characteristics of Actinobacteria
- rod-shaped, branching filamentous, or gram-positive.
- reproduction by the creation and breaking of spores.
- Aerial and substrate mycelium resembling fungi grow in vitro.
- pigmentation seen in the majority of animals.
- High percentage (between 55% and 75%) of G + C in DNA
- Ubiquitous distribution across various habitats (symbiotic, free-living, diverse temperature, pH, salinity, and oxygen conditions).
- Muramic acid and mucolic acid are found in cell walls and filaments.
- longer generation period than other types of bacteria.
- The majority of it lack both motility and capsulation1.
Actinobacteria Overview
A remarkable class of bacteria known for their varied metabolic capacities and unique filamentous appearance is known as the actinobacteria.
Taxonomy
One of the largest phyla of bacteria is Actinobacteria, which includes actinobacteria. These bacteria are Gram-positive and have DNA that contains a lot of G+C.
Morphology
They usually grow filamentous, producing hyphae that branch and resemble mushrooms. They are not the same as fungus, though, as they are prokaryotic creatures. Additionally, certain actinobacteria can be rods or cocci.
Ecology
They are found in many different types of environments, such as freshwater, soil, marine environments, and even harsh settings like arctic areas and hot springs. They are vital to the cycling of nutrients, the breakdown of organic matter, and the fertility of the soil.
Metabolic Diversity
They are well known for their adaptability in the metabolism and capacity to generate a wide range of bioactive substances. They produce a great deal of immunosuppressants, antifungals, anticancer drugs, and other pharmacologically active materials. One genus of Actinobacteria that is particularly well-known for producing antibiotics is Streptomyces.
Biotechnological Significance
They can produce bioactive chemicals with therapeutic potential, they are extremely significant in the pharmaceutical and biotechnological industries. Actinobacteria is the source of several pharmaceutically significant antibiotics, including vancomycin, erythromycin, and streptomycin.
Pathogenicity
They can be helpful or innocuous to humans, animals, and plants, but some species can be harmful to them. For instance, human tuberculosis is caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis, but diphtheria is caused by Coryne bacterium diphtheriae.
Research and Future Prospects
They are still the focus of a lot of research because of their wide range of biological activity and promise for bio technology. It is essential to comprehend the metabolism and genetics of Actinobacteria in order to find new antibiotics and other bioactive substances.
All things considered, actinobacteria are an intriguing class of bacteria with major implications for industry, medicine, and the environment. They are actively being studied and applied in science because to their metabolic diversity, biotechnological potential, and ecological responsibilities
Common Actino bacteria Genera
A well-known Genera are
- Streptomyces: Approximately 40% of soil isolates belong to this genus.
- Nocardia
- Micromonospora
- Actinomyces
- Frankia
- Actinoplanes
- Streptosporangium
- Arthrobacter
- Salinispora
And many more
Significance and Applications
They have a vital role in nature
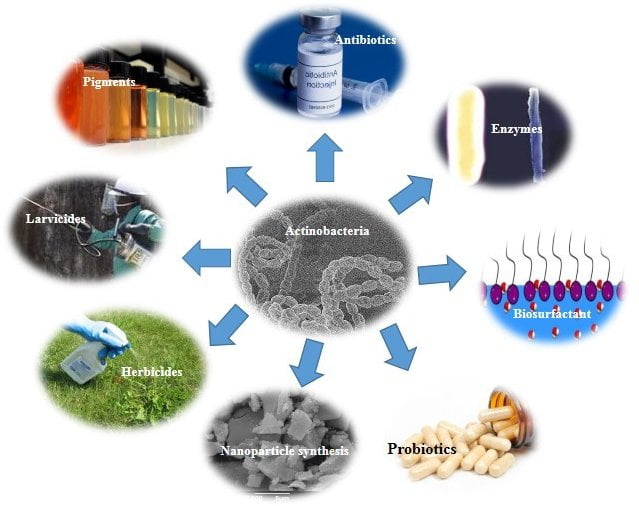
Biodegradation
They decompose intricate organic materials.
Bioremediation
They assist in bioremediation: the removal of contaminants.
Biocontrol
Certain types of them regulate plant illnesses.
Bio fertilization
They promote the growth of plants.
Biotechnological Applications
Their yield important chemicals such as enzymes and antibiotics.
Research and Medicine
They are necessary for both medical and scientific research.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQ)
Define Actinobacteria in short?
A phylum of Gram-positive bacteria notable for its varied metabolic capacities, unique branching filamentous shape, and high G+C concentration in their DNA .
List their Significance and Applications?
The significance and applications are
1.Biodegradation
2.Bioremediation
3.Biocontrol
4.Research and Medicine
Mention their general characteristics ?
The general characteristics are mentioned below ;
1.rod-shaped, branching filamentous, or gram-positive.
2.reproduction by the creation and breaking of spores.
3.Aerial and substrate mycelium resembling fungi grow in vitro.
4.pigmentation seen in the majority of animals.
Related Articles

