Protoplast fusion is a powerful technique in biotechnology that allows scientists to combine the genetic material of two different cells, creating a hybrid cell with unique characteristics. This method has potential applications in various fields, including agriculture, medicine, and industry.
Table of Contents
What are protoplasts?
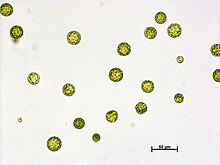
Protoplasts are plant or fungal cells with their cell walls removed. This leaves behind the cell membrane, cytoplasm, and nucleus, making the cell vulnerable and allowing for fusion with other protoplasts.
The Process of Protoplast Fusion
The process of protoplast fusion involves several key steps:
Protoplast Isolation
The first step is to isolate protoplasts from the desired cells. This is achieved by using enzymes like cellulase and pectinase, which break down the cell wall without damaging the cell membrane.
Different methods are used for different types of cells, including enzymatic digestion, mechanical disruption, and osmotic shock.
Protoplast Purification
Once isolated, protoplasts need to be purified to remove any remaining cell wall fragments and other debris. This is done through techniques like centrifugation, filtration, and washing.
Protoplast Fusion
The purified protoplasts are then treated with specific agents that induce fusion. This can be achieved through:
Chemical methods: Using polyethylene glycol (PEG) or sodium nitrate. These agents cause dehydration and promote membrane fusion.
Electrical methods: Applying a brief electrical pulse (electrofusion) creates pores in the cell membrane, allowing the protoplasts to fuse.
Laser-induced fusion: Focusing a laser beam on the cell membrane can also induce fusion.
Selection and Regeneration
Once fused, the hybrid protoplasts are placed in a suitable culture medium for regeneration. This allows them to form new cell walls and develop into whole plants or other organisms.
Specific selection techniques are employed to identify and isolate the desired hybrid cells.
Advantages of Protoplast Fusion
Protoplast fusion offers several advantages over traditional breeding methods:
Wider Genetic Diversity: It enables the fusion of cells from different species and even genera, expanding the potential genetic pool.
Faster Development: Protoplast fusion can be significantly faster than conventional breeding methods, allowing for quicker development of new traits.
Direct Gene Transfer: It allows for the direct introduction of foreign DNA into the protoplasts, enabling specific genetic modifications.
Overcoming Barriers: Protoplast fusion can overcome breeding barriers that exist between different species, enabling the transfer of desired traits between incompatible organisms.
Applications of Protoplast Fusion
Protoplast fusion has various applications in different fields:
Agriculture: Creating new crop varieties with improved traits like disease resistance, pest tolerance, yield, and nutritional content.
Medicine: Developing new drugs, vaccines, and therapeutic proteins.
Industry: Producing enzymes, antibiotics, and other valuable products.
Environmental Science: Developing plants that can tolerate harsh environments and remediate pollution.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite its potential, protoplast fusion faces several challenges:
Efficiency: The process can be time-consuming and inefficient, requiring specific conditions and expertise.
Regeneration: Regenerating whole plants from fused protoplasts can be challenging and requires specialized techniques.
Stability: The hybrid cells may not always be stable, and the desired traits may be lost over time.
Ethical Considerations: Concerns exist about the potential risks associated with creating new organisms and their impact on ecosystems.
Conclusion
It is a powerful tool for biotechnology, offering vast potential for improving crop production, developing new medicines, and addressing environmental challenges. While challenges and limitations remain, ongoing research and advancements continue to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of this technique, paving the way for exciting innovations in various fields.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQ)
What do you mean by Protoplast fusion?
With the use of the potent biotechnology process known as protoplasts fusion, researchers may fuse the genetic material of two distinct cells to produce a hybrid cell with special properties. Potential uses for this technique exist in a number of industries, including manufacturing, agriculture, and medical.
What do you mean by therapeutic proteins ?
All things considered, therapeutic proteins are a major medical advancement that show promise in treating a variety of illnesses. They are still being developed and researched to fully realize their potential and overcome their obstacles.
Related Articles