What is Mucormycosis?
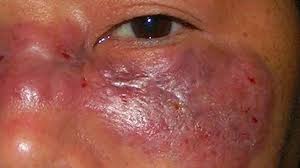
Mucormycosis, also known as zygomycosis, is a rare but serious fungal infection caused by a group of molds called mucormycetes. These fungi are ubiquitous in the environment and can be found in soil, decaying organic matter, and even in the air. While typically harmless to healthy individuals, mucormycosis can pose a significant threat to those with compromised immune systems or underlying health conditions.
Table of Contents
Causative Agents
The causative agents of Mucormycosis are,
- Rhizopus species: The most common causative agent, particularly R. arrhizus and R. oryzae.
- Mucor species: Another frequent culprit, including M. circinelloides and M. racemosus.
- Lichtheimia species: Formerly known as Absidia species, like L. corymbifera and L. ramosa.
- Other less common species: Rhizomucor, Apophysomyces, and Cunninghamella.
Pathogenesis
Mucormycetes are opportunistic pathogens, meaning they take advantage of weakened host defenses to cause infection. The infection typically begins in the nasal sinuses, lungs, or skin, but can spread to other organs, including the brain, eyes, and gastrointestinal tract.
Several factors contribute to the development of mucormycosis:
- Immunosuppression: Conditions like diabetes, organ transplantation, and cancer chemotherapy can significantly increase the risk.
- Underlying health conditions: Iron overload, malnutrition, and prolonged steroid use also elevate susceptibility.
- Exposure to contaminated materials: This can occur through inhalation of spores, wounds exposed to contaminated soil, or direct contact with infected materials.
Symptoms
The symptoms of mucormycosis vary depending on the location of the infection. However, some common signs include:
Sinus and Facial Symptoms
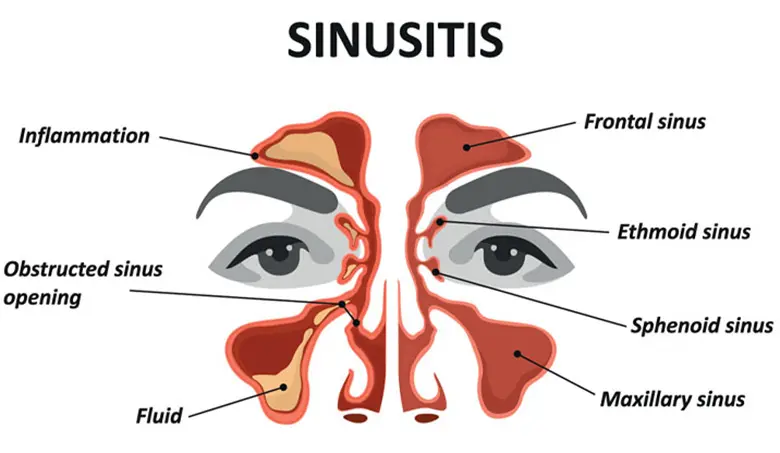
- Nasal congestion
- Facial pain and swelling
- Blackening or discolouration of the nasal septum
- Loss of sense of smell
Pulmonary Symptoms
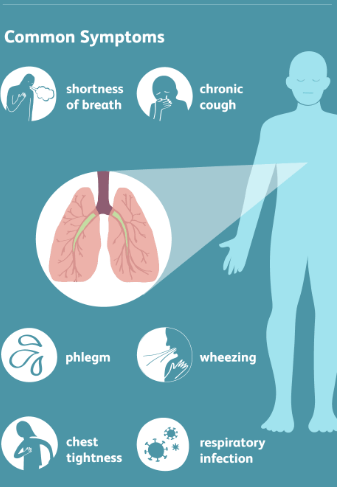
- Cough
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain
- Fever
Skin Symptoms
- Painful sores or ulcers
- Blackened tissue
Ocular Symptoms
- Eye pain
- Swelling around the eye
- Vision loss
Brain Symptoms
- Headaches
- Fever
- Seizures
- Confusion
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of mucormycosis is crucial due to the rapid progression and severity of the infection. It involves a combination of methods:
- Clinical examination: Observing the patient’s symptoms and medical history.
- Imaging studies: X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs can help identify the location and extent of the infection.
- Microscopic examination: Obtaining tissue samples (biopsy) and examining them under a microscope to identify the characteristic fungal hyphae.
- Culture: Growing the fungus in a laboratory to confirm the specific species.
Treatment
Treating mucormycosis requires a multidisciplinary approach involving antifungal drugs, surgery, and supportive care.
- Antifungal medication: Amphotericin B is the primary antifungal agent used, often administered intravenously. Other options include posaconazole and isavuconazole.
- Surgery: Debridement, which is the removal of infected tissue, is essential to control the spread of the infection.
- Supportive Care: Managing blood sugar levels, addressing underlying health conditions, and providing oxygen therapy are crucial for patient recovery.
This is a brief overview of mucormycosis. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
Conclusion
Mucormycosis is a serious infection that can be fatal without prompt diagnosis and treatment. Early recognition and aggressive intervention are essential to improve patient outcomes. Individuals with compromised immune systems or underlying health conditions should be particularly vigilant for any potential symptoms.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQ)
List the skin symptoms of Mucormycosis?
The skin symptoms of Mucormycosis ,
1. Painful sores or ulcers
2. Blackened tissue
List the Sinus and Facial Symptoms ?
The Sinus and Facial Symptoms are,
1. Nasal congestion
2. Facial pain and swelling
3. Blackening or discolouration of the nasal septum
4. Loss of sense of smell
What are the causative agents of Mucormycosis?
The causative agents of Mucormycosis,
Immunosuppression
Underlying health conditions
Exposure to contaminated materials
Related Articles