Vermicomposting is a process that uses various species of worms, primarily earthworms, to decompose organic waste material into a rich, nutrient-dense humus known as vermicompost or worm castings. This method of composting is highly efficient and produces a high-quality organic fertilizer.
Table of Contents
Vermicomposting
Vermicomposting is the process of using earthworms to decompose organic waste material into a nutrient-rich, humus-like product known as vermicompost or worm castings. This method of composting leverages the natural digestive process of worms to break down organic matter efficiently and sustainably.
Vermicomposting is the process of using earthworms to convert organic waste into nutrient-rich compost. This method harnesses the natural digestive processes of worms to decompose food scraps, garden waste, and other organic materials, producing a valuable soil amendment known as vermicompost or worm castings. This composting technique is environmentally friendly and enhances soil health by providing essential nutrients and beneficial microorganisms.

Key Components
Worm species:
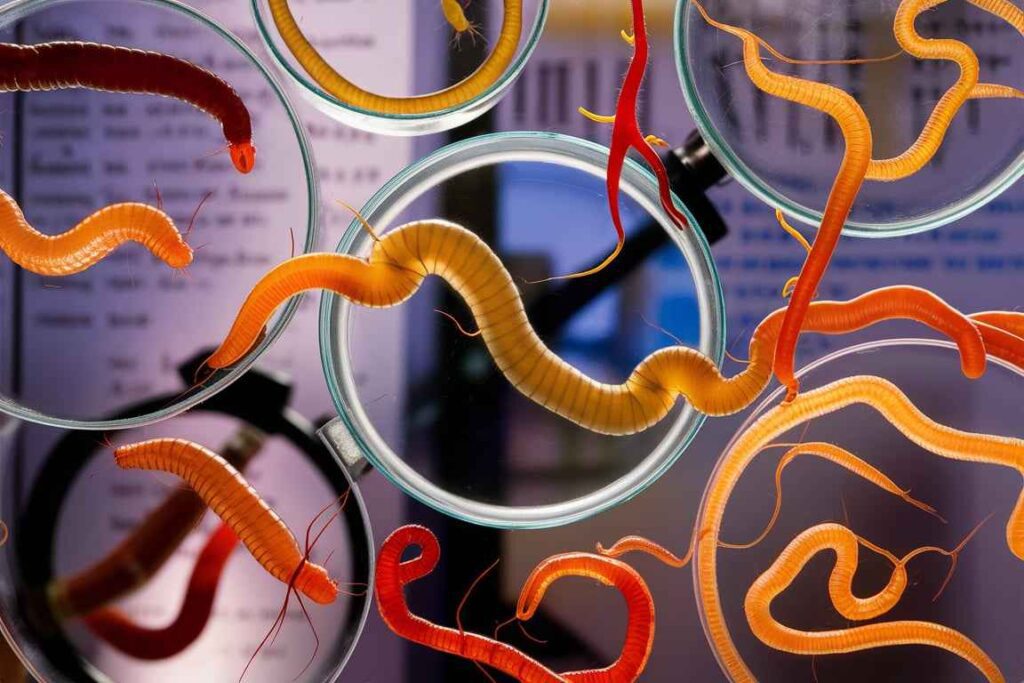

- Eisenia fetida (Red Wigglers): The most often employed vermicomposting organism due to its adaptability to a variety of environmental circumstances and efficiency in processing organic waste.
- Lumbricus rubellus: Another species utilized, albeit less commonly than E. fetida.
Organic Waste:

- Food scraps include fruits, veggies, coffee grounds, and eggshells.
- Garden waste includes grass clippings, leaves, and plant trimmings.
- Other organic material includes paper, cardboard, and biodegradable garbage.
Bedding Materials:
- Types include shredded newspaper, cardboard, coconut coir, and straw.
- Purpose: Provides a habitat for worms and aids in the early decomposition of organic waste.
Process Preparation:
- Choosing a Bin: You can use either a commercial vermicomposting bin or a homemade container. It should be shallow, well-ventilated, and contain drainage holes.
- Adding Bedding: Fill the bin with moist bedding material to provide a cozy environment for the worms.
- Worms: Add the worms to the bedding. Each square foot of surface area requires around one pound of worms.
Feeding:
- Organic trash: Add organic trash in small amounts, making sure it is thoroughly mixed with the bedding.
- Feed the worms periodically, adding new garbage as the previous batch decomposes.
Maintenance:
- Moisture: Keep the bedding damp but not soggy. The ideal moisture content is roughly 70-80%.
- Aeration: Turn the bedding on occasion to keep it aerated and prevent anaerobic conditions.
- Temperature: The optimal temperature range is 55-77°F (13-25°C). Excessive heat should be avoided.
Harvest Vermicompost:
- Signs of Completion: Vermicompost is ready when it is black, crumbly, and smells earthy.
Methods:
- Side-by-Side Method: Transfer finished compost to one side of the bin while adding fresh bedding and food to the other. Worms will move, providing for simple harvest.
- Light Method: First expose the compost to light, which drives the worms deeper, and then remove the top layer of compost.
Benefits
Environmental:
- Waste reduction involves diverting organic waste from landfills.
- Reduced Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Anaerobic decomposition in landfills produces less methane.
Soil improvement:
- Vermicompost contains vital elements like as nitrogen, phosphate, and potassium.
- Improved Soil Structure: Increases soil aeration, drainage, and water retention.
- Helpful Microorganisms: Introduces helpful microbes to improve soil health and plant growth.
Plant Growth:
- Improved Yields: Vermicompost encourages strong plant development and increases yields.
- Disease Resistance: Enhances plant resistance to diseases and pests.
Challenges
- Odor Management: Poorly kept containers can emit unpleasant odors. Avoid adding excessive food or non-compostable things.
- Pest Control: Keep the bin covered and watch for fruit flies and ants.
- Temperature Sensitivity: Worms are sensitive to severe temperatures and may need extra care in hot or cold locations.
Frequently Asked Question
What is Vermicomposting?
Vermicomposting is the process of using earthworms to decompose organic waste material into a nutrient-rich, humus-like product known as vermicompost or worm castings. This method of composting leverages the natural digestive process of worms to break down organic matter efficiently and sustainably.
What are the Benefits of Vermicomposting?
The Benefits of Vermicomposting are:
1. Environmental
2. Soil improvement
3. Plant Growth
Related Article
Isolation and Identification of normal microbial flora of skin and throat