What is Three point test cross?
A three point test cross is a method used in genetics to examine the arrangement of three linked genes on a chromosome and to measure the distances between them. It helps researchers understand how these genes are positioned relative to one another (gene order), calculate the distance between them (map distance), and study how often recombination events, or crossovers, occur during meiosis. This approach is commonly used in studies involving organisms like fruit flies or other genetic models.
Let’s break down the process into simple terms:
Table of Contents
1. Gene Order
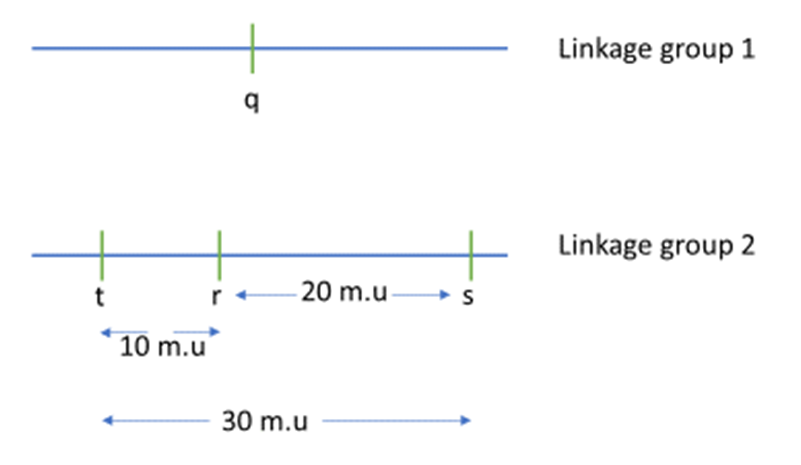
Gene order refers to the specific sequence of three linked genes on a chromosome. In a three-point test cross, you want to find out the relative positions of these genes. Since they are linked, they tend to be inherited together, but recombination can separate them. By studying patterns of recombination, we can determine which gene is in the middle and which ones are on the sides.
The relationship between gene order and a three point test cross is fundamental to understanding how genes are organized on a chromosome and how they are inherited. A three point test cross is a powerful tool used to determine the order of three linked genes and to calculate the distances between them.
How to Find Gene Order
A test cross is performed between a heterozygous individual (carrying two different versions of each gene) and a homozygous recessive individual (having the recessive versions of all three genes).
The resulting offspring show different combinations of the genes due to crossovers. By observing which combinations are common (non-recombinant) and which are rare (recombinant), we can deduce the gene order.
The rarest combinations occur from double crossovers, which reveal the gene in the middle of the sequence.
2. Map Distance
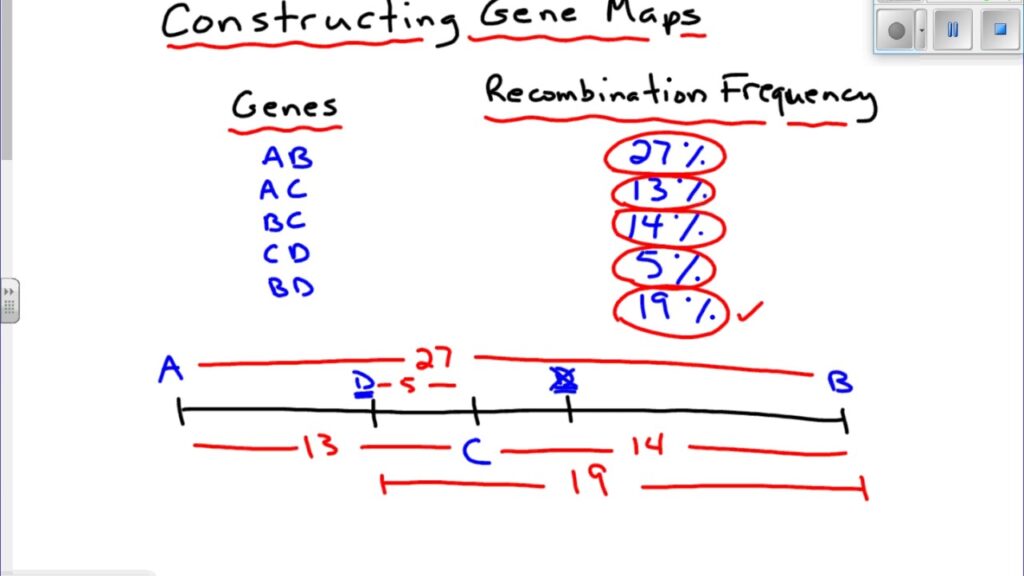
In a three point test cross, the map distances between three linked genes are related to the frequency of recombination events between them. The goal of the test cross is to determine the gene order and map distances between each pair of genes. Map distance measures how far apart genes are on a chromosome. This distance is expressed in centimorgans (cM), where 1 cM represents a 1% chance of recombination between two genes during meiosis.
How to Calculate Map Distance:
The frequency of recombination events between two genes helps estimate their distance. The more often recombination occurs, the farther apart the genes are.
Recombination frequency is calculated by dividing the number of recombinant offspring by the total number of offspring, then multiplying by 100 to get a percentage.
For example, if 10% of the offspring show recombination between two genes, the map distance between them is 10 centimorgans (10 cM).
3. Inference
In genetics, interference and a three point test cross are closely related because a three-point test cross provides the data needed to calculate and understand interference. Interference refers to the phenomenon where the occurrence of a crossover event between two genes on a chromosome affects the likelihood of another crossover happening nearby. A three point test cross helps measure interference by looking at recombination events between three linked genes. In the context of a three-point test cross, inference means drawing conclusions from the data. This includes determining:
The gene order based on the occurrence of double crossover events.
The distances between the genes using the recombination frequencies.
4. Coefficient of Coincidence and Interference
When studying recombination, it’s important to consider how often double crossovers occur compared to what is expected. This leads to the concepts of coefficient of coincidence and interference.
Coefficient of Coincidence:
The coefficient of coincidence (C) compares the observed number of double crossovers to the expected number.
Formula: C=Observed Double CrossoversExpected Double CrossoversC = \frac{\text{Observed Double Crossovers}}{\text{Expected Double Crossovers}}C=Expected Double CrossoversObserved Double Crossovers Expected double crossovers are calculated by multiplying the individual recombination frequencies between the gene pairs. If fewer double crossovers occur than expected, it suggests that crossover events are not happening independently.
Interference
Interference (I) measures how much one crossover event reduces the likelihood of another nearby crossover.
Formula: I=1−CI = 1 – CI=1−C If interference is high, it means one crossover event makes it less likely for another to occur in close proximity. If there’s no interference, crossovers happen independently, as expected.
For example, if the coefficient of coincidence is 0.5, it means that only half of the expected double crossovers occurred, resulting in 50% interference.
Level of Inference
The level of significance in a three point test cross indicates the confidence with which we can reject the hypothesis that observed recombination frequencies occur by chance, helping validate the gene order and map distances determined from the cross. The level of inference refers to what conclusions can be drawn from the test cross. From a three-point test cross, you can determine:
The gene order: which gene is in the middle and which ones are on either side.
The map distances between each gene.
The interference: the extent to which crossover events affect each other.
Summary
A three point test cross is a technique used to study three linked genes to find out their arrangement on a chromosome and how far apart they are. By analyzing the offspring from a cross, the gene order can be determined from recombination patterns, and the map distances can be calculated using recombination frequencies. The coefficient of coincidence and interference help explain how crossover events influence one another. A three point cross method provides valuable insights into gene structure and behavior, which is important for understanding inheritance and genetic variation.
Frerquently Asked Questions(FAQ)
What is a three point test cross?
A three point test cross is a genetic method used to determine the order of three linked genes on a chromosome and measure the distances between them by analyzing the recombination frequencies from offspring produced by crossing a heterozygous individual with a homozygous recessive individual.
What is the relationship between three point test cross and map distance?
In a three point test cross, the map distances between three linked genes are related to the frequency of recombination events between them. The goal of the test cross is to determine the gene order and map distances between each pair of genes. Map distance measures how far apart genes are on a chromosome.
Related Articles