What is Theta Plasmid Replication ?
Bacteria contain a particular kind of circular DNA molecule called theta plasmid. Because of the distinctive intermediate structure that forms throughout the process, its replication is named after the Greek letter theta (θ).
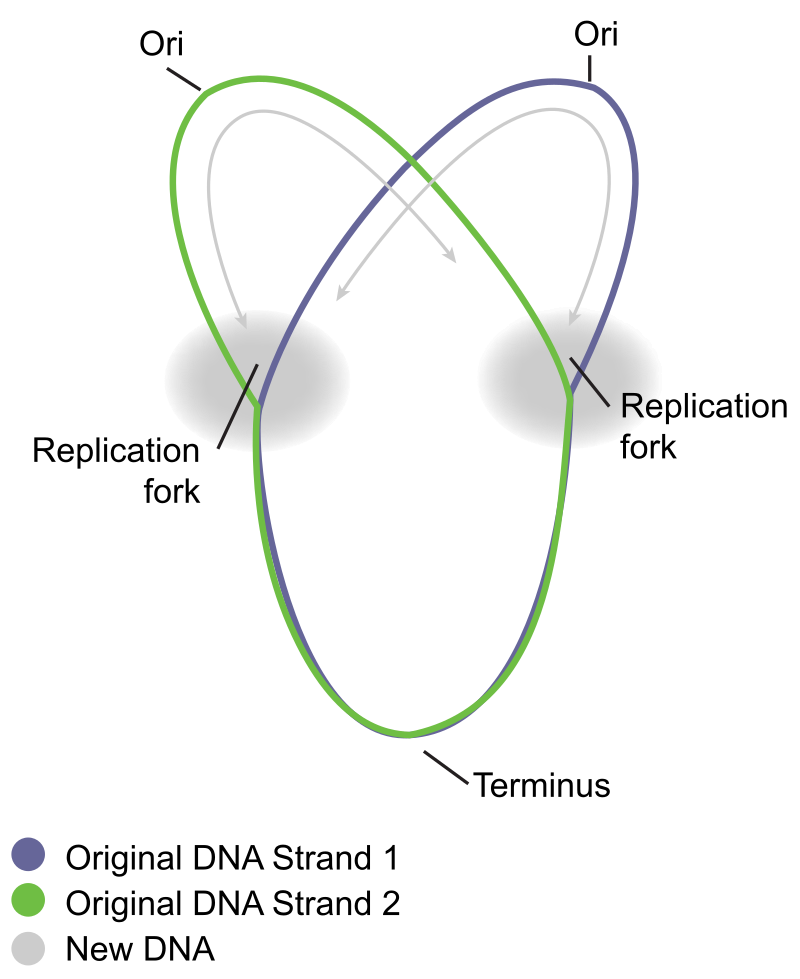
Theta plasmid replication is a DNA replication technique present in certain circular plasmids, so called because the replicating DNA mimics the shape “theta” (θ). It is a bidirectional replication process, which means it begins at a single replication origin and moves simultaneously in both directions.
Table of Contents
Initiation
Origin of replication (ori) : The replication process starts at a particular plasmid sequence known as the origin of replication.
Initiator proteins :Proteins known as initiator proteins attach to the ori sequence, unravel the DNA double helix, and start a little replication bubble.
Unwinding and Synthesis of Primer
Helicase: This enzyme separates the two strands of DNA by further unwinding it.
Single-stranded binding proteins (SSBs): These proteins keep the split strands from re-annealing by stabilizing them.
Primase: This enzyme creates a brief RNA primer on every unwinding strand, giving DNA polymerase a place to begin.
Elongation
DNA polymerase III: Using the parental strand as a template, this enzyme adds nucleotides to the primer’s 3′ end. Leading strand: As the replication fork moves, one strand is continuously produced in the5′ to 3′ direction. Lagging strand: In the same 5′ to 3′ direction, the other strand is synthesized discontinuously in brief segments known as Okazaki fragments.
DNA polymerase I: This enzyme substitutes DNA nucleotides for the RNA primers.
DNA ligase: This enzyme forms a continuous lagging strand by connecting the Okazaki fragments.
Termination
Termination sequences: When the replication forks meet at a certain termination sequence on the plasmid, the replication process comes to an end.
Topoisomerase: This enzyme separates the freshly duplicated plasmids by resolving the entangled DNA molecules.
Key Features of Theta Replication
Bidirectional: Two replication forks are produced when replication spreads from the origin in both directions.
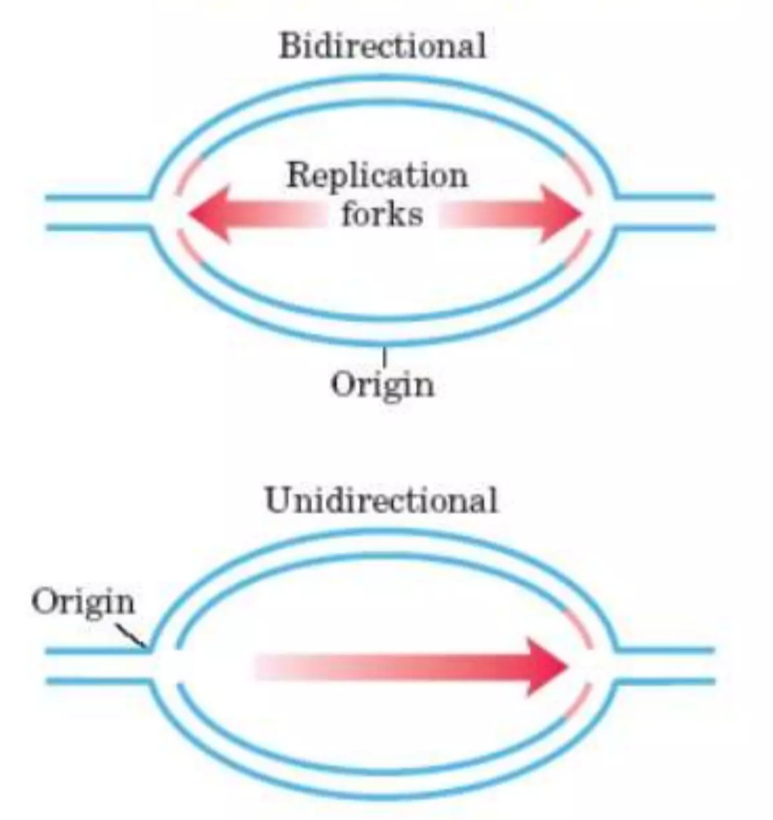
Semiconservative: One parental strand and one freshly synthesized strand make up each new plasmid molecule.
Two types of synthesis occur: discontinuous synthesis occurs for the lagging strand and continuous synthesis for the leading strand.
Creation of a theta structure: During replication, the unwound DNA creates a structure resembling a theta, thus the name.
Importance
In bacterial populations, plasmid inheritance and propagation depend on theta plasmid replication. Genes that confer advantageous characteristics to bacteria, such resistance to antibiotics or the capacity to absorb particular nutrients, are frequently carried by plasmids. During cell division, theta replication makes sure that these genes are accurately replicated and transferred to daughter cells.
Crucial to the survival and adaptability of bacteria
Horizontal gene transfer: Genes for antibiotic resistance, toxin production, or the capacity to break down particular substances are frequently carried by Theta plasmids. Through conjugation, this genetic information can be passed to new bacteria, enabling quick adaptation to shifting conditions and selective pressures.
Metabolic adaptability: A number of theta plasmids encode enzymes that enable bacteria to make use of novel carbon sources, expanding their options for food and habitats.
Bioremediation: Theta plasmids are useful instruments for cleaning up contaminated settings since they can carry genes for digesting contaminants.
Essential to comprehending the genetics and evolution of bacteria
Model system for researching DNA replication: Because theta plasmids are straightforward and thoroughly described, they are perfect for researching the mechanisms underlying bacterial DNA replication.
Evolutionary insights: The evolution of theta plasmids provides information on gene acquisition and loss as well as population adaptation of bacteria to changing environments.
Possibility of using biotechnology
The expression and cloning of genes: Theta plasmids can be employed as carriers to transfer and express desired genes in bacteria.
Environmental cleanup and bioremediation: Certain theta plasmids have genes that can be used to degrade contaminants and clean up contaminated areas.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQ)
What is Theta Plasmid ?
Bacteria contain a particular kind of circular DNA molecule called theta plasmid. Because of the distinctive intermediate structure that forms throughout the process, its replication is named after the Greek letter theta (θ).
What is Theta Plasmid Replication ?
Theta plasmid replication is a DNA replication technique present in certain circular plasmids, so called because the replicating DNA mimics the shape “theta” (θ). It is a bidirectional replication process, which means it begins at a single replication origin and moves simultaneously in both directions.
What is the importance of Theta Plasmid ?
The importance of Theta Plasmid ,
Crucial to the survival and adaptability of bacteria
Essential to comprehending the genetics and evolution of bacteria
Related Articles