The salivary glands are small but very important organs in our mouth that help us chew, taste, and even digest food. These glands produce a liquid called saliva the watery fluid we feel in our mouths, especially when we think of or see delicious food. Saliva may not seem like a big deal, but without it, even basic things like speaking or swallowing would become difficult.
Table of Contents
What Are Salivary Glands?
Salivary glands are groups of special tissues in the mouth that produce saliva. These glands are always working even when we’re not eating. They keep the mouth moist and help wash away leftover food particles and bacteria.
Saliva is made mostly of water, but it also contains enzymes, mucus, and antibodies. All of these ingredients are very useful for keeping our mouths healthy and helping us digest food.
Why Is Saliva Important?

Saliva plays many roles in our day-to-day life. Here are a few key reasons why it’s important:
- Helps in Digestion: Saliva contains an enzyme called amylase that starts breaking down food (especially starches) right in your mouth before it even reaches your stomach.
- Makes Chewing and Swallowing Easier: Saliva moistens the food, turning it into a soft ball called a bolus, which is easy to swallow.
- Keeps the Mouth Clean: It washes away food bits and bacteria, helping to prevent bad breath and tooth decay.
- Protects Teeth: Saliva contains minerals that help repair tooth enamel and neutralize acids produced by bacteria.
- Helps with Speaking: A dry mouth can make it hard to talk clearly. Saliva keeps everything moving smoothly.
What is Saliva Made Of?
Saliva is a complex fluid made of:
- Water (about 98%)
- Enzymes (like amylase and lipase)
- Mucus (makes food slippery and easy to swallow)
- Electrolytes (like sodium and potassium)
- Antibodies (help fight infections)
- Proteins (for healing and digestion)
Each part of saliva has a special job to do in keeping your mouth healthy and helping with digestion.
Salivary Glands Histology
Salivary glands are specialized exocrine glands responsible for producing saliva, which plays a crucial role in digestion, oral lubrication, and maintaining oral health. Histologically, these glands exhibit a complex architecture composed of secretory units and a ductal system.
Histological Structure of Salivary Glands
1. Connective Tissue Capsule and Lobular Organization
Each salivary gland is encapsulated by connective tissue that divides the gland into lobes and further into lobules. Within these lobules are the functional units known as acini, which are clusters of secretory epithelial cells.
2. Types of Acini
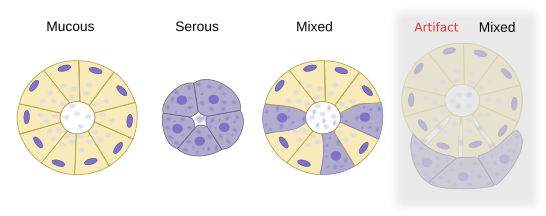
There are three types of acini based on the nature of their secretions:
- Serous Acini: These consist of pyramidal-shaped cells with round, centrally located nuclei and basophilic cytoplasm due to abundant rough endoplasmic reticulum. They produce a watery, enzyme-rich secretion containing proteins like amylase.
- Mucous Acini: Composed of cells with flattened nuclei pushed towards the basal end and pale, foamy cytoplasm due to mucin content. They secrete a viscous, mucin-rich fluid that lubricates the oral cavity.
- Mixed Acini: These contain both serous and mucous cells. In conventional histological preparations, serous cells often form crescent-shaped caps called serous demilunes around mucous acini.
Surrounding the acini are myoepithelial cells, which have contractile properties that aid in expelling secretions into the ductal system.
3. Ductal System
The ductal network transports saliva from the acini to the oral cavity and undergoes modifications along the way:
- Intercalated Ducts: These are the smallest ducts lined by simple cuboidal epithelium. They receive secretions directly from the acini and begin the process of modifying the saliva’s composition.
- Striated Ducts: Lined by simple columnar epithelium with basal striations due to elongated mitochondria, these ducts actively reabsorb sodium and secrete potassium and bicarbonate, further modifying the saliva.
- Excretory (Interlobular) Ducts: These larger ducts, lined by stratified cuboidal or columnar epithelium, transport the final saliva product to the oral cavity.
Types of Salivary Glands
Salivary glands are essential components of our digestive system, responsible for producing saliva that aids in digestion, maintains oral hygiene, and facilitates speech. These glands are categorized into two main types: major salivary glands and minor salivary glands.
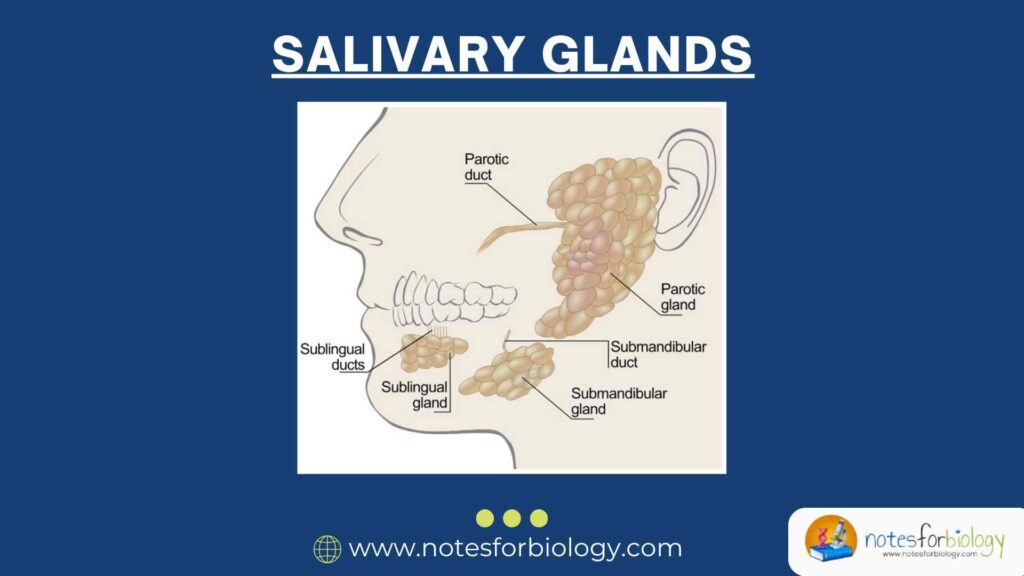
Major Salivary Glands
There are three pairs of major salivary glands, each with distinct locations and functions:
1. Parotid Glands
- Location: Situated just in front of and below each ear.
- Function: These are the largest salivary glands and produce a watery, enzyme-rich saliva that initiates the digestion of starches.
- Duct: Saliva from the parotid glands is delivered to the mouth through Stensen’s duct, which opens near the upper second molar.
- Clinical Note: The facial nerve passes through the parotid gland, making surgical procedures in this area delicate to avoid nerve damage.
2. Submandibular Glands
- Location: Found beneath the lower jaw, towards the back of the mouth.
- Function: These glands produce a mixed saliva containing both serous (watery) and mucous components, contributing approximately 70% of the total saliva in the mouth.
- Duct: Saliva is secreted into the mouth via Wharton’s duct, which opens at the base of the tongue.
- Clinical Note: Due to the composition of their saliva, submandibular glands are more prone to developing salivary stones (sialolithiasis).
3. Sublingual Glands
- Location: Located beneath the tongue, under the floor of the mouth.
- Function: These are the smallest of the major salivary glands and primarily produce mucous saliva, which helps lubricate the mouth.
- Ducts: Saliva is secreted through multiple small ducts known as the ducts of Rivinus, with some joining to form Bartholin’s duct.
- Clinical Note: Though rare, these glands can develop cysts or tumors, necessitating medical evaluation if abnormalities are detected.
Minor Salivary Glands
- Location: Scattered throughout the oral cavity, including the lips, cheeks, palate, and tongue.
- Function: These numerous small glands continuously secrete mucous saliva to keep the mouth moist and aid in the initial stages of digestion.
- Clinical Note: While less commonly affected by diseases, minor salivary glands can develop benign or malignant tumors, often requiring biopsy for diagnosis.
How Do Salivary Glands Work?
Salivary glands are connected to the mouth by small tubes called ducts. These ducts carry the saliva from the glands to your mouth.
When you eat or even think about food, your brain sends signals to the salivary glands to start producing saliva. This process is automatic and happens without us needing to think about it.
Sometimes, just the smell of tasty food can make your mouth water that’s your salivary glands in action!
Common Problems with Salivary Glands
Salivary glands are vital for producing saliva, which keeps our mouth moist, aids in digestion, and helps protect against infections. However, various issues can affect these glands, leading to discomfort and health problems. Let’s explore some common salivary gland disorders in simple terms:
1. Dry Mouth (Xerostomia)
Dry mouth occurs when the salivary glands don’t produce enough saliva. This can result from dehydration, certain medications, cancer treatments, nerve damage, or autoimmune diseases like Sjögren’s syndrome. Symptoms include a sticky feeling in the mouth, difficulty swallowing, altered taste, and increased risk of dental decay.
2. Salivary Stones (Sialolithiasis)
Salivary stones are small, calcified structures that can block the ducts of the salivary glands, especially the submandibular glands. This blockage can cause pain and swelling, particularly during meals when saliva production increases. In some cases, the blockage may lead to infection.
3. Salivary Gland Infections (Sialadenitis)
Sialadenitis is an infection of the salivary glands, often resulting from a blockage like a stone. It can cause painful swelling, redness, fever, and pus discharge in the mouth. The condition is more common in older adults and infants.
4. Salivary Gland Tumors
Tumors can develop in the salivary glands, most commonly in the parotid glands. These tumors can be benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous). Symptoms include a lump or swelling in the cheek, jaw, or mouth area, sometimes accompanied by pain or facial numbness.
5. Sjögren’s Syndrome
Sjögren’s syndrome is an autoimmune disorder where the body’s immune system attacks its own salivary and tear glands. This leads to dry mouth and dry eyes, along with joint pain and swelling of the salivary gland
6. Salivary Duct Strictures
A salivary duct stricture is a narrowing of the duct that carries saliva from the gland to the mouth. This can cause pain and swelling, especially during meals. The condition may result from chronic inflammation or injury.
7. Parotitis
Parotitis is the inflammation of the parotid glands, the largest salivary gland located near the ears. It can be caused by viral infections like mumps, bacterial infections, or autoimmune conditions. Symptoms include swelling, pain, and sometimes fever.
8. Cysts
Cysts are fluid-filled sacs that can form in the salivary gland. They may cause painless swelling and can interfere with eating or speaking if they grow large. Treatment may involve drainage or surgical removal
9. Sialadenosis
Sialadenosis is a non-inflammatory, non-cancerous swelling of the salivary gland, often associated with systemic conditions like diabetes or malnutrition. It typically causes painless enlargement of the glands.
10. Mumps
Mumps is a viral infection that primarily affects the parotid glands, leading to swelling and pain. It was more common before the introduction of the MMR vaccine. Symptoms include fever, headache, and swollen salivary gland.
If you experience persistent dry mouth, swelling, pain, or lumps in your mouth or jaw area, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Taking care of Salivary Gland
Taking care of your salivary gland is essential for maintaining a healthy mouth and aiding digestion. Here are some simple, human-friendly tips to keep your salivary gland in good shape:
1. Stay Hydrated
Drinking plenty of water throughout the day helps keep your salivary gland active and prevents dry mouth. Aim for at least 8 glasses daily, and carry a water bottle to sip regularly.
2. Stimulate Saliva Production
Chewing sugar-free gum or sucking on sugarless candies can encourage saliva flow. Opt for flavors like lemon or mint, which are particularly effective.
3. Maintain Good Oral Hygiene
Brush your teeth twice a day and floss daily to keep your mouth clean. Regular dental check-ups can help detect any issues with your salivary gland early on.
4. Avoid Dehydrating Substances
Limit intake of caffeine and alcohol, as they can dry out your mouth. Also, avoid tobacco products, which can harm your salivary gland and overall oral health.
5. Use a Humidifier
Using a humidifier, especially at night, can add moisture to the air and help prevent dry mouth, keeping your salivary gland comfortable.
6. Eat Moist Foods
Incorporate foods with high water content into your diet, such as cucumbers, melons, and soups. These can help keep your mouth moist and support saliva production.
7. Massage Your Glands
Gently massaging your salivary gland can promote saliva flow and relieve any minor blockages. Use clean hands and apply light pressure in a circular motion.
8. Be Mindful of Medications
Some medications can cause dry mouth as a side effect. If you notice this, consult your healthcare provider for alternatives or solutions.
By following these straightforward steps, you can keep your salivary gland functioning properly, ensuring a comfortable and healthy mouth. If you experience persistent dry mouth or other issues, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice.
Conclusion
In conclusion, salivary gland are essential for maintaining oral and overall health. They produce saliva, which facilitates digestion, keeps the mouth moist, and protects against infections. The three major pairs of salivary gland parotid, submandibular, and sublingual each contribute to saliva production, ensuring that our mouths function properly. By staying hydrated, practicing good oral hygiene, and being mindful of factors that can affect saliva production, we can support the health of our salivary glands. Recognizing and addressing any issues early on is important to prevent complications and maintain overall well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How many pairs of Salivary Glands are founds in human?
The human body contains three pairs of major salivary glands: the parotid glands (located near the ears), the submandibular glands (under the jaw), and the sublingual glands (beneath the tongue). Additionally, there are hundreds of tiny minor salivary glands (600–1,000) distributed throughout the mouth and throat lining.
What causes swollen salivary glands?
Swollen salivary glands can be caused by several common conditions:
1. Infections – Viral (like mumps) or bacterial infections can inflame the glands.
2. Blocked Salivary Ducts – Stones or thick saliva can block ducts, causing swelling and pain.
3. Dehydration – Low fluid intake reduces saliva flow, leading to gland swelling.
4. Autoimmune Diseases – Conditions like Sjögren’s syndrome attack saliva-producing cells.
5. Tumors – Rarely, benign or cancerous growths can enlarge the glands.
Where are salivary glands found?
Humans have three pairs of major salivary glands: the parotid glands (near ears), submandibular glands (under jaw), and sublingual glands (under tongue), plus hundreds of minor glands throughout the mouth. Together they produce saliva for digestion and oral health, with major glands making most saliva (90%) and minor glands keeping the mouth moist between meals.
Related Articles