The world around us is teeming with microscopic life, from the bacteria in our gut to the fungi in the soil. These microbes play crucial roles in our environment, our health, and even in industrial processes. To understand these invisible forces, scientists utilize various tools, including microbiological assays, a powerful arsenal of techniques that allow us to study and quantify the activity of microorganisms.
Table of Contents
What is a Microbiological Assay?
A microbiological assay is essentially a biological experiment that uses microorganisms to measure the presence, concentration, or activity of a specific substance. It works by exploiting the sensitivity of microbes to changes in their environment, particularly the presence of specific compounds.
The Power of Microbes
Microbes, especially bacteria, are incredibly versatile and responsive to their surroundings. They can be used to detect a wide range of substances, from antibiotics and vitamins to toxins and pollutants. This ability makes microbiological assays incredibly valuable in various fields, including:
Pharmaceutical Industry: Assessing the potency and purity of antibiotics, antifungal agents, and other pharmaceuticals.
Food Industry: Detecting foodborne pathogens, monitoring the effectiveness of food preservation methods, and ensuring the safety and quality of food products.
Environmental Monitoring: Analyzing water and soil samples for the presence of pollutants, monitoring the effectiveness of bioremediation efforts, and assessing the impact of environmental changes.
Research and Development: Studying the mechanisms of microbial growth, investigating the effects of different compounds on microbes, and developing new antimicrobial agents.
Common Types of Microbiological Assays
There are numerous types of microbiological assays, each with its own unique application. Some of the most common ones include:
Antibiotic Sensitivity Testing
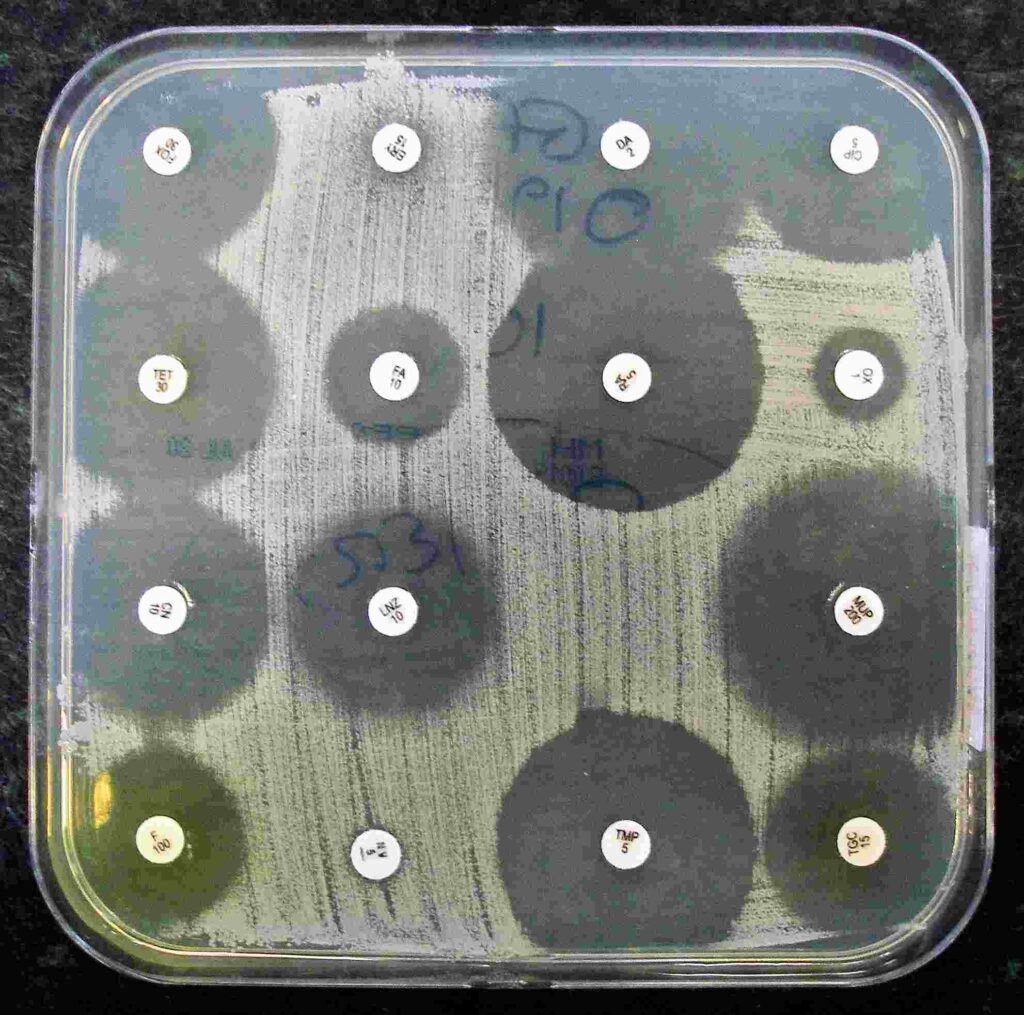
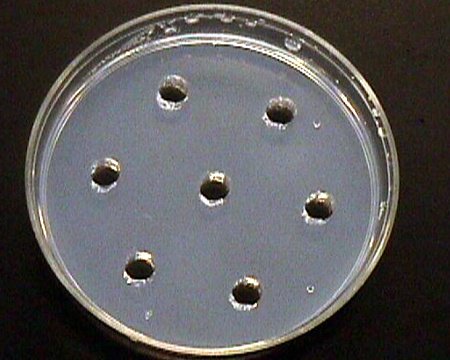
This assay determines the susceptibility of bacteria to various antibiotics. It is essential for guiding antibiotic treatment in clinical settings.
Turbidity Measurement
This method measures the cloudiness of a microbial culture to quantify the growth of microbes. It is widely used for assessing the effectiveness of antimicrobial agents and disinfectants.
Microbial Enumeration
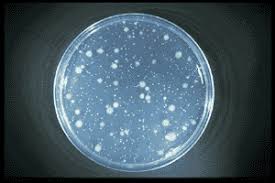
This assay determines the number of viable microbes present in a sample. It is crucial for monitoring the quality of water, food, and other products.
Bioassays
These assays exploit the growth response of microbes to a specific substance, allowing for the quantification of vitamins, hormones, and other biomolecules.
Microbial Toxicity Testing
This assay uses microbes to assess the toxic effects of chemicals and pollutants.
Methods of Microbiological Assay
Microbiological assays utilize various methods to assess microbial growth and activity. Some of the most common approaches include:
Agar Diffusion Method: This method involves spreading a microbial culture on an agar plate and then placing a paper disk containing a test substance on the agar surface. The size of the zone of inhibition around the disk indicates the antimicrobial activity of the substance.
Broth Dilution Method: This method involves growing microbes in a liquid broth containing different concentrations of a test substance. The concentration at which microbial growth is inhibited is determined as the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC).
Microplate Reader: This instrument uses light absorbance to measure the growth of microbes in a microplate. It is a high-throughput method, allowing for the simultaneous analysis of multiple samples.
Real-time PCR: This technique quantifies the number of microbial DNA copies in a sample, providing a sensitive and specific measure of microbial abundance.
Key Considerations
When designing and performing microbiological assays, it is crucial to consider the following factors:
Specificity: The assay should only measure the activity of the target microbe or substance.
Sensitivity: The assay should be able to detect even low concentrations of the target substance.
Reproducibility: The results of the assay should be consistent across different experiments and laboratories.
Accuracy: The results of the assay should be accurate and reflect the true concentration or activity of the target substance.
Safety: The assay should be performed in a safe manner, minimizing the risk of exposure to hazardous materials.
The Future of Microbiological Assays
The field of microbiological assays is constantly evolving, with new technologies and methodologies emerging to improve the sensitivity, accuracy, and throughput of these techniques. Advancements in automated systems, molecular methods, and high-throughput screening are revolutionizing the way we study and utilize microbes. This continued innovation promises to unlock even more secrets of the microbial world, leading to significant breakthroughs in healthcare, environmental science, and various other fields.
In Conclusion
Microbiological assays are powerful tools that allow us to understand the intricate world of microbes. By exploiting the sensitivity and versatility of these microscopic organisms, we can detect, quantify, and study a wide range of substances, providing invaluable insights into our health, environment, and the world around us. As our understanding of microbes continues to evolve, so too will the sophistication and applications of microbiological assays, further shaping the future of research and technology.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQ)
What is Microbiological assays?
Microbiological assays are powerful tools that allow us to understand the intricate world of microbes. By exploiting the sensitivity and versatility of these microscopic organisms, we can detect, quantify, and study a wide range of substances, providing invaluable insights into our health, environment, and the world around us.
What are the methods of microbiological assays?
The methods of it are,
1. Agar Diffusion Method
2. Broth Dilution Method
3. Microplate Reader
4. Real-time PCR
What are its key considerations?
Its key considerations are,
1. Specificity
2. Sensitivity
3. Reproducibility
4. Accuracy
5. Safety
Related Articles