Human Brain
Human Brain is the primary control center of the human body. It is in charge of all of our mental and emotional processes as well as our bodily functions and senses.
Table of Contents
Ever wonder what’s happening inside your head? It’s a busy place, a symphony of different parts all working together to make you, well, YOU! Let’s take a peek inside, shall we?
The Big Boss: The Cerebrum
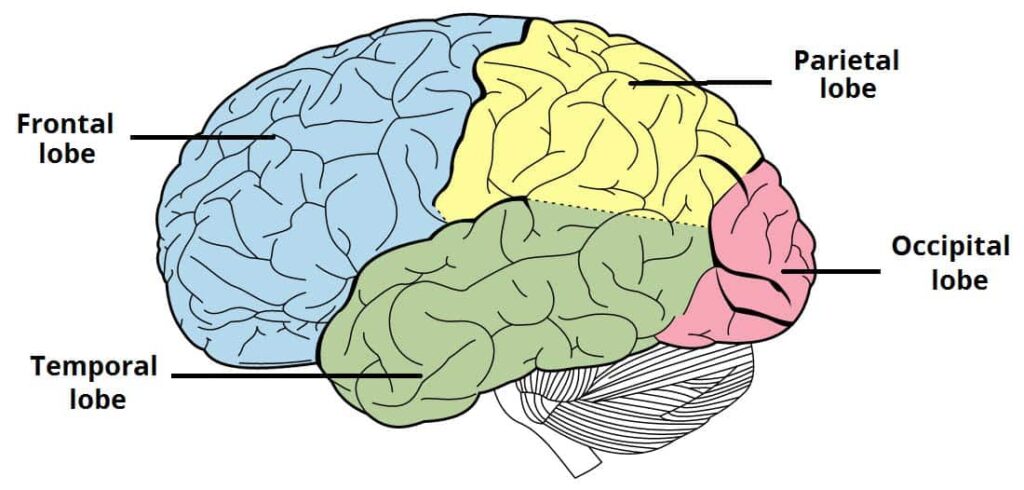
Think of the cerebrum as your brain’s headquarters, the largest part, divided into two halves (hemispheres) like a giant, wrinkly walnut. Each hemisphere controls the opposite side of your body.
Left Side: This is the logical side, the one that crunches numbers, writes essays, and plans your next big adventure.
Right Side: The creative side, the one that paints pictures, dances to music, and understands emotions.
The Memory Keepers: Hippocampus and Amygdala
Your hippocampus is the librarian of your brain, storing memories and helping you navigate your world. The amygdala, a little almond-shaped structure, is your emotional bodyguard, processing fear, anger, and even joy. Think of it as the alarm system that keeps you safe!
The Motor Master: Cerebellum
Want to ride a bike or play the piano? Your cerebellum is the master of coordination, movement, and balance, making sure your body does what your brain tells it to.
The Command Center: Brainstem
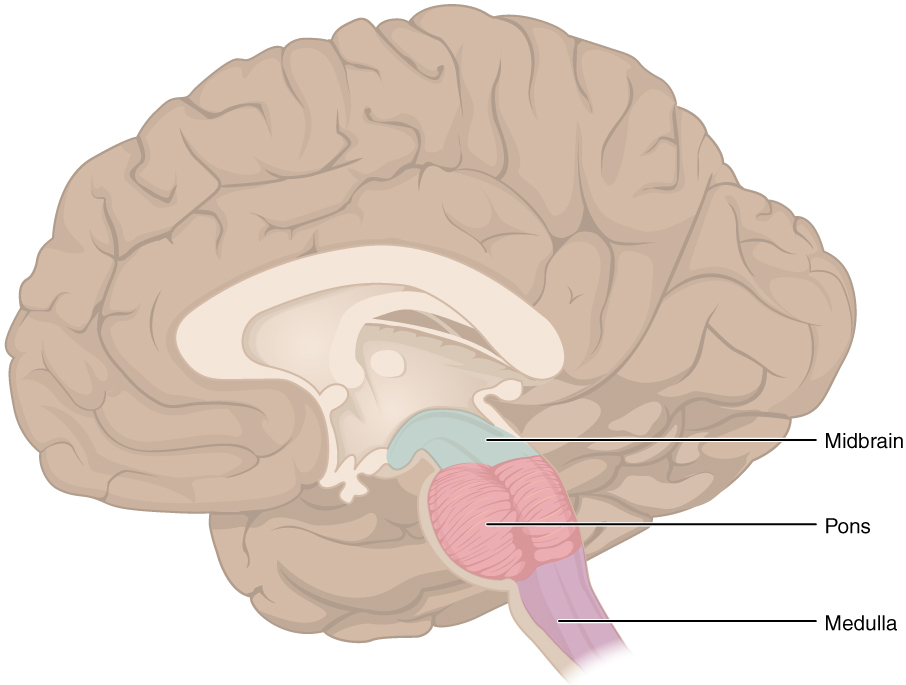
Hidden deep within the brain, the brainstem is the unsung hero, controlling your heartbeat, breathing, and all those vital things you don’t even think about. It’s like the central power station of your body, making sure everything runs smoothly.
The Sensory Squad: Thalamus and Hypothalamus
Think of your thalamus as the central switchboard of your senses, directing information from your eyes, ears, nose, and skin to the appropriate places in the cerebrum. The hypothalamus, a tiny but powerful area, regulates your body temperature, hunger, thirst, and sleep patterns.
Working Together, Not in Isolation
No part of your brain operates in isolation. They all work together, a complex orchestra of signals and information, to create your thoughts, feelings, and actions. Every time you learn something new, experience a new emotion, or even just take a breath, you’re witnessing the remarkable symphony of your brain.
Functions
Sensory processing: Information from our senses is gathered and interpreted by the brain.
Motor control: Our muscles get impulses from motor control, which enables movement.
Cognition: Thinking, learning, memory, language, and problem-solving are all included in cognitive processes.
Emotions: The brain interprets and controls feelings such as joy, grief, rage, and fear.
Sleep and wakefulness: Our biological rhythms, including sleep-wake cycles, are regulated by sleep and wakefulness.
Important Points
Over the course of our lives, the brain changes and adapts continuously. We call this neuroplasticity.
To operate correctly, the brain needs a steady flow of glucose and oxygen.
Brain protection is essential. This include preventing head traumas, leading a healthy lifestyle, and getting help if you have any neurological issues.
So next time you think about your brain, remember it’s not just a lump of grey matter – it’s a masterpiece of evolution, a complex network of parts working tirelessly to make you who you are.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQ)
Define Human Brain ?
Human Brain is the primary control center of the human body. It is in charge of all of our mental and emotional processes as well as our bodily functions and senses.
Listout the functions of the Human Brain ?
The functions of the human brain ,
Sensory processing
Motor control
Cognition
Emotions
Sleep and wakefulness
What is the role of cerebellum in the human?
Your cerebellum is the master of coordination, movement, and balance, making sure your body does what your brain tells it to.
Related Articles