Introduction
The female reproductive system is a beautifully complex and essential part of the body, playing a critical role in menstruation, fertility, pregnancy, and hormone regulation. However, like any organ system, it can be affected by a wide range of diseases and disorders. These conditions can affect the vagina, cervix, uterus, fallopian tubes, ovaries, or breasts, and they may impact a woman’s reproductive health, hormonal balance, mental well-being, and quality of life.
Understanding these disorders is important not only for prevention and early detection but also for ensuring timely treatment and maintaining overall health. This guide presents a comprehensive overview of common and significant diseases and disorders of the female reproductive system, their causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention.
Table of Contents
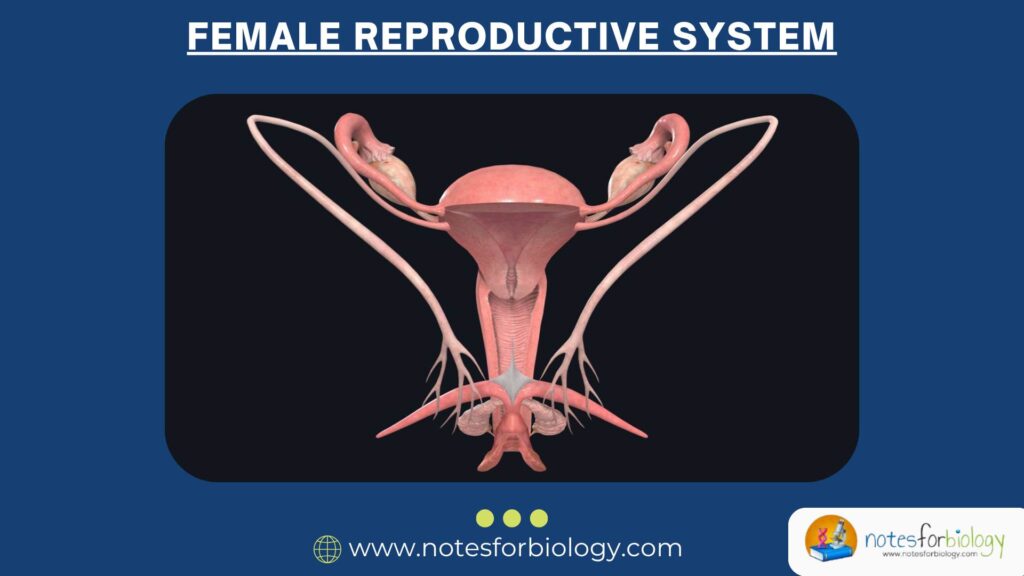
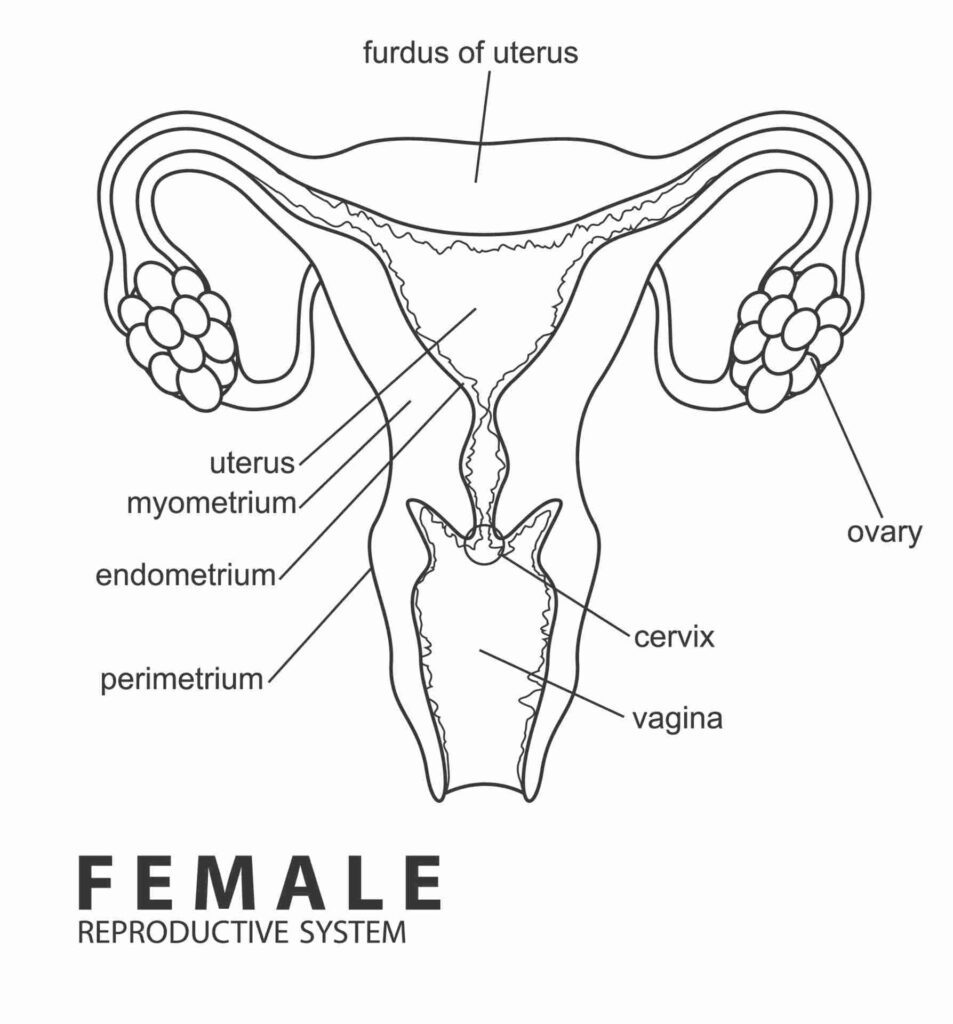
Anatomy of the Female Reproductive System
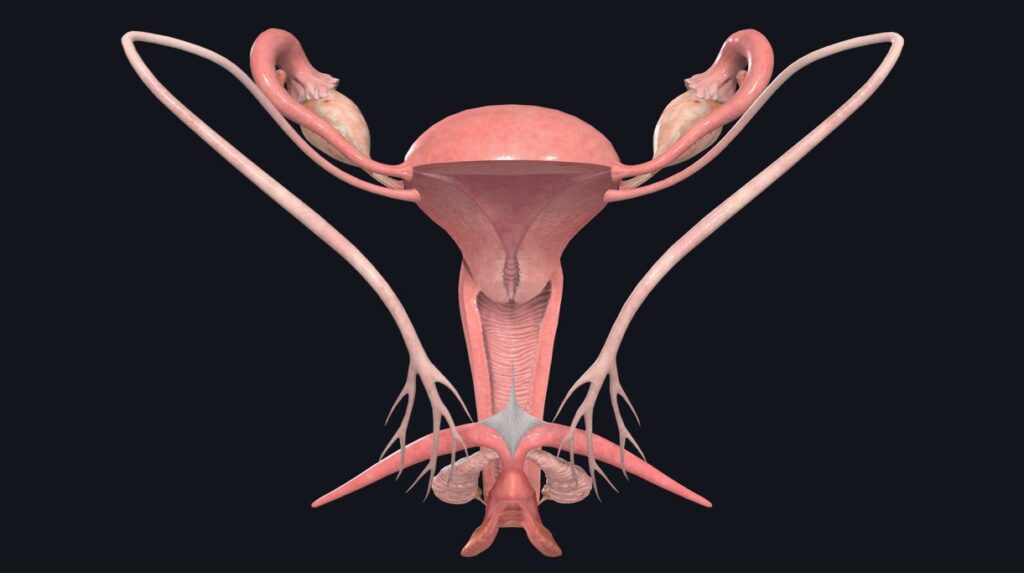
External Organs
- Vulva – includes the labia majora, labia minora, clitoris, and vestibule
- Vaginal opening
Internal Organs
- Vagina
- Cervix
- Uterus
- Fallopian Tubes
- Ovaries
Each organ has a specific role in reproduction, hormone production, and protection against infections.
Categories of Female Reproductive Disorders
1. Infections
2. Structural Abnormalities
3. Hormonal Imbalances
4. Neoplastic Diseases (Benign or Malignant Tumors)
5. Menstrual Disorders
6. Pregnancy-Related Disorders
7. Sexual and Pelvic Pain Disorders
1. Infections of the Female Reproductive System
1.1 Bacterial Vaginosis (BV)
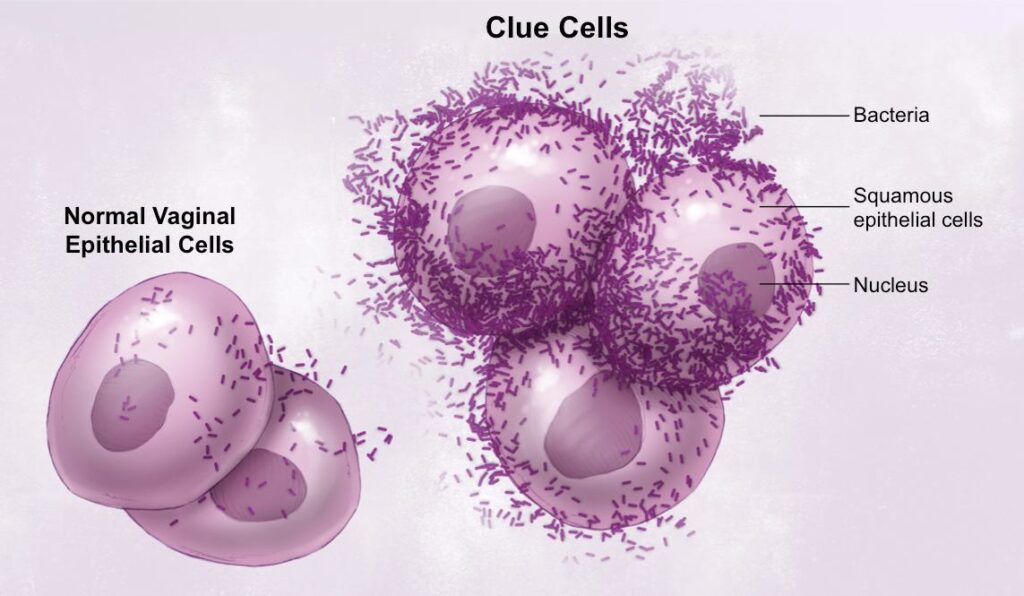
Cause
Overgrowth of normal vaginal bacteria, especially Gardnerella vaginalis.
Symptoms
- Thin, grayish-white vaginal discharge
- Fishy odor, especially after sex
- Mild itching or burning
Treatment
Antibiotics like metronidazole or clindamycin
Prevention
- Avoid douching
- Safe sex practices
1.2 Candidiasis (Yeast Infection)
Cause
Overgrowth of Candida albicans, a type of yeast.
Symptoms
- Thick, white vaginal discharge
- Intense itching
- Redness and swelling
Treatment
Antifungal creams or oral medications
1.3 Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)
Cause
Bacterial infection, usually from STIs like Chlamydia or Gonorrhea.
Symptoms
- Lower abdominal pain
- Fever
- Painful intercourse
- Irregular bleeding
Complications
- Infertility
- Ectopic pregnancy
Treatment
Broad-spectrum antibiotics
2. Menstrual and Hormonal Disorders
2.1 Dysmenorrhea (Painful Periods)
Cause
Excessive prostaglandins causing uterine contractions.
Symptoms
- Cramping
- Back pain
- Nausea
Treatment
- NSAIDs
- Hormonal contraceptives
2.2 Amenorrhea (Absence of Menstruation)
Types
- Primary – No menstruation by age 15
- Secondary – Stopping of menstruation for more than 3 months in someone who previously had periods
Causes
- Hormonal imbalances (PCOS, thyroid issues)
- Extreme stress or weight loss
- Pregnancy
Treatment
Based on underlying cause
2.3 Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
Definition
A hormonal disorder causing enlarged ovaries with small cysts.
Symptoms
- Irregular periods
- Acne
- Excess hair (hirsutism)
- Obesity
- Infertility
Diagnosis
- Hormone tests
- Ultrasound
Treatment
- Lifestyle changes
- Birth control pills
- Metformin
3. Structural and Functional Disorders of Female Reproductive System
3.1 Endometriosis
Definition
Presence of endometrial tissue outside the uterus.
Symptoms
- Pelvic pain
- Painful periods
- Infertility
- Painful intercourse
Treatment
- Pain relievers
- Hormone therapy
- Surgery (laparoscopy)
3.2 Uterine Fibroids
Definition
Benign tumors of the uterus (leiomyomas)
Symptoms
- Heavy periods
- Pelvic pressure
- Frequent urination
- Infertility
Treatment
- Medications (GnRH agonists)
- Surgery (myomectomy, hysterectomy)
3.3 Ovarian Cysts
Types
- Functional (most common and harmless)
- Pathological (dermoid, endometriomas)
Symptoms
- Pelvic pain
- Bloating
- Irregular periods
Treatment
- Often resolve on their own
- Surgery if persistent or painful
3.4 Uterine Prolapse
Definition
Descent of the uterus into the vaginal canal due to weak pelvic muscles.
Symptoms
- Vaginal bulge
- Pelvic heaviness
- Urinary issues
Treatment
- Kegel exercises
- Pessary
- Surgical repair
4. Cancers of the Female Reproductive System
4.1 Cervical Cancer
Cause
Infection with high-risk HPV (Human Papillomavirus) strains.
Symptoms
- Vaginal bleeding after intercourse
- Watery or bloody discharge
- Pelvic pain
Prevention
- HPV vaccination
- Regular Pap smears
Treatment
- Surgery
- Radiation
- Chemotherapy
4.2 Ovarian Cancer
Symptoms
- Abdominal bloating
- Early satiety
- Pelvic pain
Diagnosis
- CA-125 blood test
- Imaging (Ultrasound, CT)
- Biopsy
Treatment
- Surgery
- Chemotherapy
4.3 Endometrial (Uterine) Cancer
Risk Factors
- Obesity
- Diabetes
- Estrogen therapy
Symptoms
- Postmenopausal bleeding
- Abnormal discharge
Treatment
- Hysterectomy
- Radiation
- Hormone therapy
4.4 Vaginal and Vulvar Cancers
Less common but serious
- Often HPV-related
- Symptoms include lumps, itching, pain
5. Pregnancy and Fertility-Related Disorders of Female Reproductive System
5.1 Ectopic Pregnancy
Definition
A pregnancy implanted outside the uterus, usually in the fallopian tube.
Symptoms
- Severe abdominal pain
- Vaginal bleeding
- Dizziness
Treatment
- Surgical removal
- Methotrexate (for early-stage cases)
5.2 Miscarriage
Definition
Loss of pregnancy before 20 weeks
Causes
- Chromosomal abnormalities
- Hormonal problems
- Infections
Symptoms
- Cramping
- Bleeding
- Passing tissue
5.3 Infertility
Definition
Failure to conceive after 12 months of unprotected sex
Causes
- PCOS
- Endometriosis
- Tubal blockages
- Low egg reserve
Treatment
- Ovulation-inducing drugs
- Surgery
- Assisted reproductive technologies (IVF, IUI)
6. Sexual and Pelvic Pain Disorders of Female Reproductive System
6.1 Dyspareunia (Painful Intercourse)
Causes
- Vaginal dryness
- Infections
- Psychological factors
- Endometriosis
Treatment
- Lubricants
- Hormonal creams
- Therapy
6.2 Vaginismus
Definition
Involuntary spasm of vaginal muscles causing pain during penetration.
Treatment
- Pelvic floor therapy
- Counseling
6.3 Vulvodynia
Chronic pain or discomfort around the vulva with no clear cause.
Treatment
- Pain management
- Topical medications
- Nerve blocks
7. Breast Disorders Related to Reproduction
7.1 Mastitis
Definition
Inflammation of breast tissue, often during breastfeeding.
Symptoms
- Swelling
- Redness
- Fever
Treatment
- Antibiotics
- Warm compress
7.2 Fibrocystic Breast Disease
Benign breast lumps that vary with menstrual cycle.
Symptoms
- Lumpiness
- Tenderness
- Swelling
Diagnosis of Female Reproductive Disorders
Common Diagnostic Tools
1. Pelvic Exam
Visual and manual examination of reproductive organs.
2. Pap Smear
For cervical cancer screening.
3. Transvaginal Ultrasound
For examining uterus, ovaries, and fallopian tubes.
4. Blood Tests
For hormone levels, tumor markers, and infections.
5. Laparoscopy
Minimally invasive surgery to look inside the pelvis.
Treatment Approaches
1. Medications
- Hormonal therapies
- Antibiotics
- Pain relievers
2. Surgical Interventions
- Laparoscopy
- Hysterectomy
- Oophorectomy
3. Lifestyle Modifications
- Weight management
- Balanced diet
- Regular exercise
4. Alternative Therapies
- Acupuncture
- Yoga
- Herbal medicine (under supervision)
Prevention and Health Maintenance
1. Regular Gynecological Checkups
- Annual pelvic exams
- Pap tests and HPV screening
2. Safe Sexual Practices
- Use of condoms
- Limiting number of sexual partners
3. Vaccination
HPV vaccine before sexual debut
4. Healthy Lifestyle
- Maintain healthy weight
- Manage stress
- Quit smoking
Conclusion
The female reproductive system is not only central to reproduction but also to a woman’s general health and well-being. Disorders affecting this system can range from mild infections to life-threatening cancers, from hormonal issues to structural problems, and from emotional stress to physical pain.
Fortunately, early detection, awareness, and proper treatment can manage or cure most of these conditions. Educating women and girls about the importance of gynecological health, regular screenings, safe practices, and open conversations is key to breaking the stigma and building healthier futures.
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
What are the most common reproductive disorders in women?
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), endometriosis, fibroids, and bacterial infections like BV are among the most common.
How often should women get Pap smears?
Every 3 years starting at age 21, or as advised by a healthcare provider.
Can reproductive disorders cause infertility?
Yes. Conditions like endometriosis, PCOS, and PID can affect fertility.
Related Articles