1. Introduction to Classification of Plant Kingdom
The plant kingdom is one of the most important groups of living organisms on Earth, providing oxygen, food, shelter, medicine, and many other essentials for life. Because plants are so diverse ranging from tiny algae living in water to huge flowering trees scientists use a system called the classification of plant kingdom to organize and study them. This system groups plants according to similarities in their structure, reproduction, and evolutionary history. It helps us understand how plants have evolved over millions of years, adapted to various environments, and how they relate to each other.
The classification of plant kingdom divides plants into five major groups Algae, Bryophytes, Pteridophytes, Gymnosperms, and Angiosperms. Each group represents a stage in plant evolution showing increasingly complex structures and ways to survive. Studying this classification allows us to appreciate the diversity of plant life and the ways plants have changed over time.
Summary of Classification of Plant Kingdom
- The classification of plant kingdom organizes plants into five major groups Algae, Bryophytes, Pteridophytes, Gymnosperms, and Angiosperms based on their structure, reproduction, and evolution.
- Each group shows unique features and adaptations, from simple aquatic algae to complex flowering plants that produce seeds enclosed in fruits.
- Understanding this classification helps us appreciate plant diversity, evolutionary history, and the important roles plants play in ecosystems and human life.
Table of Contents
2. Algae in the Classification of Plant Kingdom

2.1 Salient Features of Algae in Plant Kingdom Classification
Algae are the simplest and most primitive group in the classification of plant kingdom. They are mostly aquatic organisms found in freshwater and marine environments but some can live on moist soil or tree bark. They perform photosynthesis using chlorophyll pigments which means they make their own food from sunlight just like other plants. However algae do not have true roots, stems, or leaves. Instead they have a body called a thallus which is a simple plant body without differentiation.
Algae can exist as single cells, groups of cells forming colonies, or large multicellular forms such as seaweeds. They reproduce in many ways including fragmentation, producing spores, or sexual reproduction by gametes. Their simple body structure and reproductive methods make them important in understanding the earliest stages of plant evolution within the classification of plant kingdom.
2.2 Classification and Examples of Algae
Algae are classified into three main groups based on the type of pigments they contain:
Chlorophyceae (Green Algae): These algae are green due to chlorophyll a and b. They are often found in freshwater and sometimes on moist soil. Examples include Chlamydomonas, a unicellular algae, and Ulothrix, which forms filaments.
Phaeophyceae (Brown Algae): These algae appear brown because of the pigment fucoxanthin. They mostly grow in cold marine environments and are usually large and complex, like seaweeds. Examples include Fucus and Laminaria.
Rhodophyceae (Red Algae): These algae have a red pigment called phycoerythrin, allowing them to live in deeper ocean water. They often contribute to coral reefs and are used commercially. Examples are Polysiphonia and Gelidium.
Algae play an important role in ecosystems as primary producers and form the base of many aquatic food chains.
3. Bryophytes in the Classification of Plant Kingdom

3.1 Salient Features of Bryophytes in Plant Kingdom Classification
Bryophytes are small, soft, green plants found mainly in moist and shady environments such as forest floors, rocks, and tree trunks. They are the first true land plants in the classification of plant kingdom but they are non-vascular meaning they lack specialized tissues xylem and phloem to transport water and nutrients. Instead, they absorb water directly through their surface.
Bryophytes have structures that resemble roots, stems, and leaves but these are simpler and called rhizoids, caulids, and phyllids respectively. Their dominant life form is the gametophyte which carries out photosynthesis and produces gametes sex cells. Because bryophytes require water for the sperm to swim to the egg, they are limited to damp environments. Bryophytes are crucial in soil formation as they help break down rocks and retain moisture preparing the land for other plants.
3.2 Classification and Examples of Bryophytes
Bryophytes are grouped into three classes:
- Liverworts: These are the simplest bryophytes with flat, leaf-like bodies that often lie close to the ground. Examples include Riccia and Marchantia.
- Mosses: These grow upright with small leaf-like structures around a stem-like axis. They are more complex than liverworts. Examples are Funaria and Polytrichum.
- Hornworts: These have a unique elongated sporophyte that looks like a horn. Anthoceros is a typical example.
4. Pteridophytes in the Classification of Plant Kingdom
4.1 Salient Features of Pteridophytes in Plant Kingdom Classification
Pteridophytes represent the first vascular plants in the classification of plant kingdom. They have specialized tissues xylem and phloem that transport water and nutrients efficiently allowing these plants to grow taller and larger. They have true roots, stems, and leaves which make them more similar to modern plants compared to algae and bryophytes.
These plants reproduce by producing spores rather than seeds and the dominant life stage is the sporophyte which produces spores. The gametophyte stage is small and short-lived. Pteridophytes often grow in moist habitats and play important roles in soil conservation and forest ecosystems.
4.2 Classification and Examples of Pteridophytes
Pteridophytes include several groups such as:
- Lycopodiopsida (Club Mosses): These are small, evergreen plants. Lycopodium is a common example.
- Equisetopsida (Horsetails): Known for their jointed stems and silica deposits. Equisetum is the best-known horsetail.
- Psilotopsida (Whisk Ferns): Simple plants lacking roots and leaves. Example: Psilotum.
- Pteropsida (Ferns): The most common group with large, divided leaves called fronds. Examples include Pteris and Dryopteris.
5. Gymnosperms in the Classification of Plant Kingdom
5.1 Salient Features of Gymnosperms in Plant Kingdom Classification
Gymnosperms are seed-producing plants whose seeds are not enclosed within fruits but lie naked on the surface of cone scales. This adaptation marks a key evolutionary advancement allowing them to reproduce without water unlike earlier plants that needed water for fertilization.
Most gymnosperms are evergreen trees or shrubs with needle-like or scale-like leaves which reduce water loss and help them survive in cold or dry environments. Their pollen is dispersed by wind eliminating the need for water for fertilization.
5.2 Classification and Examples of Gymnosperms
Gymnosperms are classified into:
- Cycadophyta: Palm-like plants found in tropical regions such as Cycas.
- Coniferophyta: Cone-bearing trees like Pinus (pine) and Cedrus (cedar).
- Gnetophyta: Advanced gymnosperms like Gnetum which show some features similar to angiosperms.
6. Angiosperms in the Classification of Plant Kingdom
6.1 Salient Features of Angiosperms in Plant Kingdom Classification
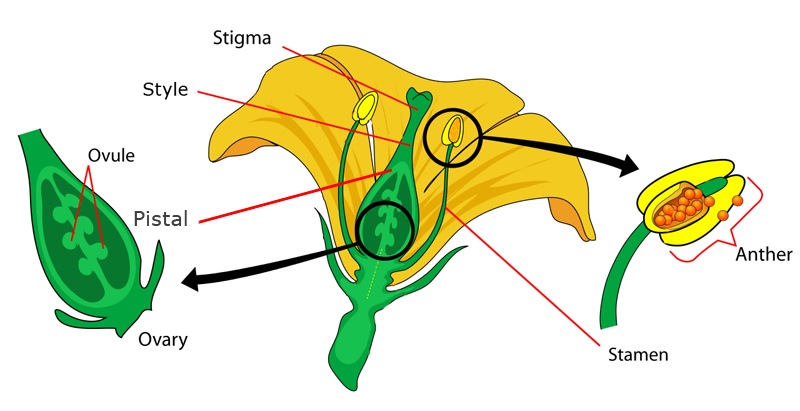
Angiosperms are the largest and most advanced group in the classification of plant kingdom. They are flowering plants that produce seeds enclosed within fruits which develop from flowers after fertilization. This protects the seeds and aids in their dispersal.
Angiosperms are found in nearly all habitats and show an incredible range of diversity. They also have a unique reproductive process called double fertilization where one sperm fertilizes the egg to form an embryo while another fertilizes the central cell to form endosperm which nourishes the developing embryo.
6.2 Classification of Angiosperms Up to Class
Angiosperms are divided into two major classes:
Monocotyledonae (Monocots):
These plants have seeds with one cotyledon seed leaf. Their leaves have parallel veins and the vascular bundles in the stem are scattered. The root system is fibrous. Examples include Wheat, Maize, and Banana.
Dicotyledonae (Dicots):
These have two cotyledons in their seeds. Their leaves display a network of veins and vascular bundles are arranged in a ring in the stem. They usually have a taproot system. Examples are Pea, Mango, and Sunflower.
7. Conclusion
The classification of plant kingdom is a fundamental concept that helps us understand the diversity and evolutionary development of plants. From simple algae living in water to complex flowering plants that dominate the land, each group in the classification shows important adaptations and features that allowed plants to survive and thrive in their environments.
Algae represent the simplest forms of plant life providing a foundation for photosynthesis in aquatic habitats. Bryophytes take the first steps onto land but still depend on water for reproduction. Pteridophytes show the evolution of vascular tissues allowing plants to grow larger and colonize more habitats. Gymnosperms advance the reproductive system with seeds that can survive dry conditions without fruit covering. Finally angiosperms introduce flowers and fruits becoming the most diverse and ecologically significant group on Earth.
Understanding the classification of plant kingdom is essential for botanists, ecologists, students, and farmers because it informs how plants grow, reproduce, and interact with their environment. This knowledge is also crucial for agriculture, forestry, conservation, and medicine. By learning about the different plant groups and their characteristics, we can better appreciate the complex web of life on Earth and work towards protecting plant biodiversity for future generations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the main groups in the classification of the plant kingdom?
The plant kingdom is mainly divided into five groups: Algae, Bryophytes, Pteridophytes, Gymnosperms, and Angiosperms. Each group has unique features and ways of living. These groups represent different stages in plant evolution, from simple aquatic plants to complex flowering plants.
How do algae differ from other plants?
Algae are simple plants mostly found in water. They do not have true roots, stems, or leaves, and they make food through photosynthesis using sunlight. Unlike other plants, algae can be unicellular or multicellular and often live in aquatic environments.
Why are bryophytes important in plant evolution?
Bryophytes were the first plants to live on land. They don’t have vascular tissues and need water for reproduction, showing an early step in land plant evolution. Their ability to survive on land laid the foundation for the development of more advanced plants.
Related Articles