What is Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) ?
A class of lung conditions known as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) results in breathing difficulties and airflow obstruction. Because of its progressive nature, the illness worsens with time. Long-term exposure to irritants such as dust, air pollution, and cigarette smoke is the main cause of COPD.
Breathing becomes difficult with the progressive lung condition known as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). It is brought on by prolonged exposure to allergens such as dust, pollution from the air, and cigarette smoke.
The bronchi, or airways that transport air to and from the lungs, are primarily impacted by COPD. It gets harder to exhale because of the inflammation and narrowing of these airways.
Table of Contents
COPD symptoms
Shortness of breath : This is the most typical symptom, particularly when exercising.
Wheezing : Wheezing is a respiratory sound that is frequently caused by constricted airways.
Chronic cough : A chronic cough is one that lasts for a long time and sometimes produces phlegm.
Chest tightness : Tightness or pressure in the chest: A sensation of tightness in the chest.
Fatigue: A state of weakness and exhaustion brought on by the body having to work harder to breathe.
Recurrent respiratory infections: Colds, the flu, and bronchitis are more common in people with COPD.
Causes of COPD
Ninety percent of COPD cases are caused by smoking, making it the most prevalent cause.
Air pollution: COPD may be exacerbated by exposure to ozone, particulate matter, and other pollutants.
Occupational dusts: Workers in dusty industries, such as mining, agriculture, and construction, are susceptible.
Genetics: An increased risk may result from a family history of COPD.
alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency : Emphysema, a kind of COPD, can be brought on by a genetic disorder called alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency.
Types of COPD
Chronic bronchitis: This involves inflammation and irritation of the airways, leading to excessive mucus production.
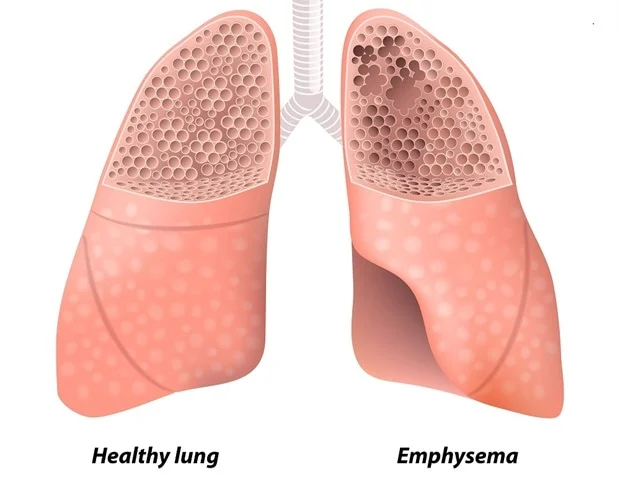
Emphysema: This involves damage to the air sacs in the lungs, making them less elastic and reducing their ability to exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide.
Diagnosis of COPD
Medical history and physical exam: The doctor will ask about symptoms and risk factors.
Spirometry: This test measures how much air you can breathe in and out, and how quickly you can exhale.
Chest X-ray and CT scan: These imaging tests can reveal changes in the lungs consistent with COPD.

COP treatment
Quitting smoking : Giving up smoking is the most crucial action you can do to stop future lung harm.
Medication : Antibiotics, corticosteroids, bronchodilators, and inhalers can all be used to treat symptoms.
Pulmonary rehabilitation :Programs for pulmonary rehabilitation can enhance endurance, strength, and breathing.
Oxygen therapy :In the event that blood oxygen levels are low, oxygen therapy may be required.
Surgery: To remove damaged lung tissue, surgery may be necessary in certain situations.
Living with COPD
Observe what your doctor has prescribed: Adhere to recommended drug regimen, schedule routine examinations, and adopt healthy behaviors.
Keep up a healthy way of living: Consume a healthy diet, do regular exercise, abstain from smoking, and limit your exposure to irritants.
Join a group for support: Having relationships with other COPD patients can help you manage the difficulties associated with the illness.
Speak with a healthcare provider if you have any worries about your breathing or COPD. Early detection and intervention can help control the illness and enhance quality of life.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQ)
Define Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease ?
A class of lung conditions known as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) results in breathing difficulties and airflow obstruction. Because of its progressive nature, the illness worsens with time. Long-term exposure to irritants such as dust, air pollution, and cigarette smoke is the main cause of COPD.
List the treatment of Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease?
The treatment of Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease are,
Quitting smoking : Giving up smoking is the most crucial action you can do to stop future lung harm.
Medication : Antibiotics, corticosteroids, bronchodilators, and inhalers can all be used to treat symptoms.
Pulmonary rehabilitation :Programs for pulmonary rehabilitation can enhance endurance, strength, and breathing.
What are the types of Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease ?
The types of Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease,
Chronic bronchitis
Emphysema
Related Articles