Cholesterol is much more than just a dietary concern, it is a fundamental molecule in human physiology. It contributes to cell membrane integrity, serves as a precursor for vital compounds, and plays a key role in cellular communication. Despite its essential functions, elevated cholesterol levels particularly LDL cholesterol are associated with increased risk of cardiovascular disease, making it a molecule with dual significance in health and disease.
In this article, we provide a comprehensive overview of it’s molecular nature, its biosynthesis and regulatory pathways, physiological roles, and clinical importance. We examine how it interacts with various systems in the human body, what happens when it becomes imbalanced, and how emerging therapies are shaping its management.
Table of Contents
What is Cholesterol?
It is a complex lipid belonging to the sterol family, notable for its rigid molecular structure and amphipathic characteristics. It is carried in the blood by lipoproteins such as LDL, HDL, VLDL, and chylomicrons each performing distinct functions in lipid metabolism and vascular health.
Understanding it’s classification is essential to interpreting blood lipid test results and implementing lifestyle or therapeutic interventions. In this section, we clarify what it is and describe how its different forms impact human physiology.
Definition and Classification
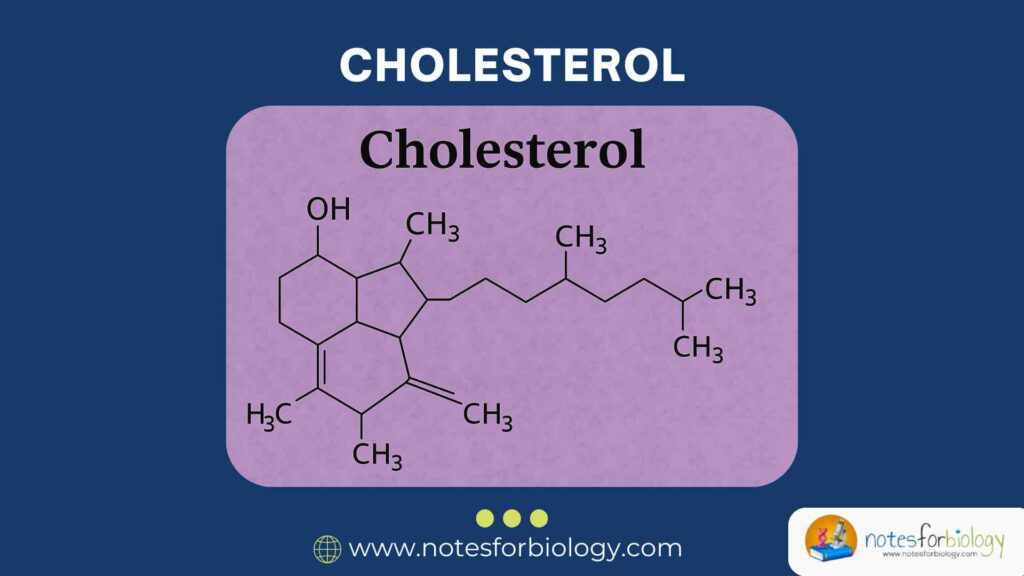
It is a sterol molecule characterized by its rigid four‑ring structure and a hydrophilic hydroxyl group. It is essential for maintaining membrane fluidity and synthesizing hormones, bile acids, and vitamin D. In the bloodstream, lt is classified by the lipoprotein complexes HDL, LDL, VLDL, and total cholesterol each reflecting different metabolic functions and health implications.
It’s role is multifaceted: it stabilizes cell membranes, acts as a biochemical precursor, and is a key marker in disease diagnostics. Categorizing cholesterol levels into LDL, HDL, VLDL, and total cholesterol helps researchers and clinicians assess risk and guide treatment.
Types of Cholesterol: HDL, LDL, VLDL, and Total Cholesterol
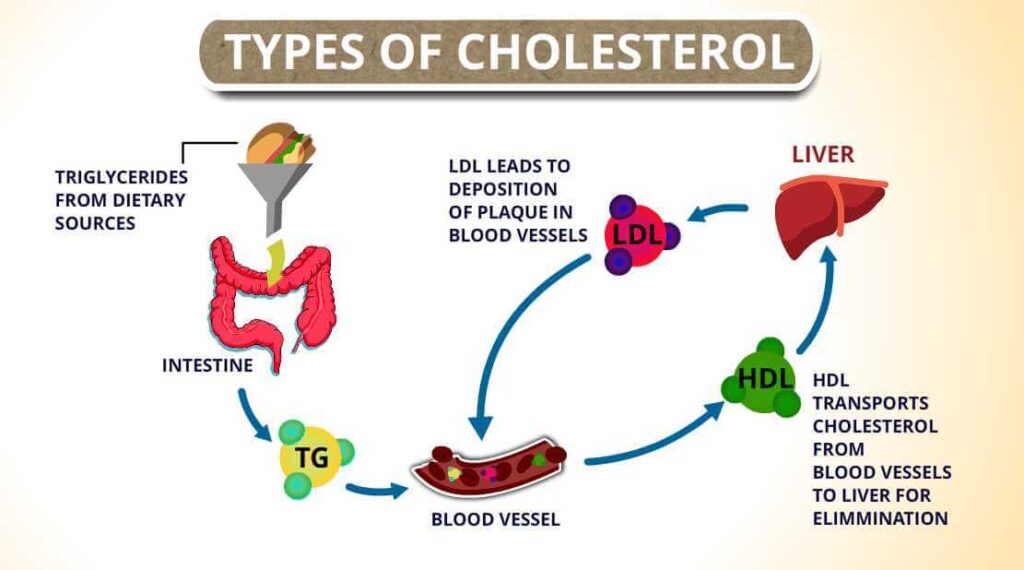
High-density lipoprotein (HDL) is considered “good” cholesterol because it transports excess cholesterol from tissues back to the liver, helping to prevent plaque formation. Low-density lipoprotein (LDL), often termed “bad” cholesterol, delivers cholesterol to peripheral tissues but can deposit it in arterial walls, leading to atherosclerosis. Very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) primarily transports triglycerides from the liver and contributes to LDL formation, while chylomicrons carry dietary lipids from the intestines.
Total cholesterol refers to the combined cholesterol content across all these lipoproteins. Monitoring the balance between HDL, LDL, and VLDL is crucial for assessing cardiovascular risk and guiding preventive or therapeutic strategies.
Molecular Structure
It’s molecular architecture underlies its roles in cells and tissues. It consists of a hydrophobic sterane skeleton and a single hydroxyl group, allowing it to integrate within cell membranes, modulate their properties, and serve as a biosynthetic precursor.
This section explores the functional aspects of its molecular structure, how variations in its configuration affect membrane dynamics, and why its molecule is vital in multiple biochemical processes across the body.
Chemical Structure Overview
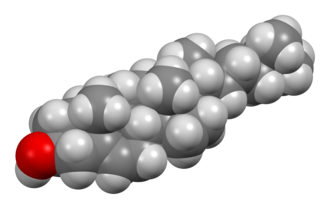
It comprises 27 carbon atoms arranged in a rigid, four-ring steroid nucleus with a hydroxyl group at carbon 3 and a hydrocarbon tail at carbon 17. This structure confers amphipathic properties, enabling the molecule to interact with both aqueous and lipid environments. The combination of a polar head and hydrophobic body is key to its positioning and function within cell membranes.
It’s structural rigidity and ring system help it to reduce membrane fluidity at high temperatures while preventing tight phospholipid packing at lower temperatures. This dual action ensures membrane stability and proper functioning of embedded proteins.
Functional Groups and Their Roles
The hydroxyl group on carbon-3 is the only polar region of the cholesterol molecule and forms hydrogen bonds with phospholipid headgroups in cell membranes, influencing membrane orientation and fluidity. The hydrophobic rings and tail insert into the lipid bilayer, facilitating cell signaling and structural integrity.
These structural elements also enable it to act as a precursor for steroid hormones, bile acids, and vitamin D, precisely controlled by enzymatic pathways that target its hydroxyl and hydrocarbon regions for chemical transformations.
Physical and Chemical Properties
It is a waxy, non-polar solid at room temperature, with low water solubility but good solubility in organic solvents like ethanol or chloroform. Its melting point (approx. 148 °C) and solubility properties make it suitable for extraction and analysis in biochemical assays.
These physical attributes underpin its behavior in membranes, how it packs with phospholipids, and how it metabolites are transported and transformed within the body.
3D Configuration and Structural Diagrams
In a three-dimensional framework, it is almost planar across its four-ring steroid core, while the hydrocarbon tail is more flexible. The molecule forms a “wedge” shape, disrupting neighboring phospholipid chains in membrane bilayers and preventing excessive rigidity.
Structural models illustrate the orientation of the hydroxyl head toward the aqueous environment, with the tail buried within the hydrophobic core—giving insight into how it modulates membrane order and facilitates vital biological processes.
Biosynthesis : An Overview
Its synthesis is a multi-step process occurring primarily in the liver but also in other tissues like the intestine and adrenal cortex. It starts from simple molecules such as acetyl-CoA and proceeds through complex enzymatic cascades governed by stringent regulation.
Understanding this biosynthetic pathway is critical for managing cholesterol-related diseases and developing therapeutic agents such as statins, which target specific enzymatic steps.
Where It is Synthesized in the Body
The liver is the central site for it’s synthesis, accounting for most endogenous production. The small intestine, adrenal glands, and gonads also contribute to synthesis due to their needs for steroid hormones and bile acids.
At the cellular level, its assembly takes place in the cytosol and endoplasmic reticulum, positioning biosynthetic enzymes close together to ensure efficient metabolic flux.
Key Steps in Biosynthesis
Starting Materials: Acetyl‑CoA and HMG‑CoA
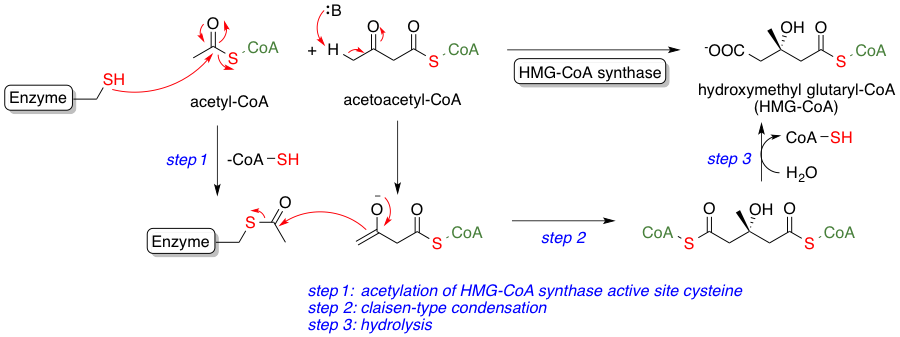
Its synthesis begins when two molecules of acetyl-CoA are condensed to form acetoacetyl-CoA, which then reacts to yield HMG-CoA. This compound is pivotal in initiating the pathway toward cholesterol and other isoprenoids.
Mevalonate Pathway: The Committed Step
HMG-CoA reductase converts HMG-CoA to mevalonate, marking a crucial regulatory checkpoint. This step is tightly regulated and is the main pharmacological target for cholesterol-lowering drugs like statins.
Isoprenoid Formation
Mevalonate undergoes multiple phosphorylation and decarboxylation events to produce isopentenyl pyrophosphate and dimethylallyl pyrophosphate. These five-carbon units are the building blocks for larger isoprenoid compounds.
Squalene Synthesis
Six isoprenoid units (IPPs) combine stepwise to form farnesyl pyrophosphate, and two farnesyl units then merge to produce squalene, catalyzed by squalene synthase. Squalene is the first linear precursor in its biosynthesis.
Squalene Cyclization and Lanosterol Formation
Squalene is first epoxidized and then cyclized to form lanosterol, the first sterol in the pathway. This reaction, mediated by squalene epoxidase and oxidosqualene cyclase, establishes the steroid backbone core.
Conversion of Lanosterol
Lanosterol undergoes multiple enzymatic rearrangements, demethylations, and reductions 14 steps in total to finally yield cholesterol. Each step is meticulously governed by specific enzymes that shape the final sterol configuration.
Enzymes Involved in Its Synthesis
HMG‑CoA Reductase: The Rate‑Limiting Enzyme
HMG-CoA reductase catalyzes the pathway’s rate-limiting transformation and is finely regulated by feedback, phosphorylation, and sterol regulatory element-binding proteins. Its inhibition is central to statin therapy.
Other Key Enzymes and Their Roles
Enzymes like squalene synthase, squalene epoxidase, lanosterol demethylase, and 7-dehydrocholesterol reductase each execute critical transformations. Dysregulation at any step can impact overall production of it and lead to metabolic disorders.
Regulation of Its Synthesis
Its homeostasis results from a balance of synthesis, dietary absorption, and excretion of metabolites. Multi-level regulatory systems ensure it remains within physiological range to support health and prevent disease.
Feedback Inhibition Mechanisms
Elevated levels of cholesterol and intermediates like mevalonate downregulate HMG-CoA reductase and reduce gene transcription via SREBPs. This negative feedback loop prevents excessive cholesterol accumulation.
Role of Dietary Cholesterol
Dietary intake contributes significantly to cholesterol levels. When high, dietary cholesterol reduces endogenous synthesis via feedback mechanisms. However, absorption efficiency varies among individuals due to factors like genetics and digestive health.
Hormonal Regulation (Insulin, Glucagon, Thyroid Hormones)
Hormones modulate its synthesis based on metabolic demand. Insulin promotes its production, while glucagon and thyroxine reduce it. Hormonal balancing is essential for metabolic and endocrine health.
Pharmaceutical Regulation (Statins and Their Mechanism)
Statins mimic HMG-CoA structure, competitively inhibiting the reductase enzyme. This inhibition lowers its synthesis and increases LDL receptor expression, reducing circulatory LDL levels and cardiovascular risk.
Functions in the Body
It is indispensable in multiple biological roles maintaining membrane integrity, producing essential molecules, and mediating metabolic homeostasis.
Structural Role in Cell Membranes
It fine-tunes membrane fluidity, ensuring optimal permeability and the function of transmembrane proteins. It also helps create lipid rafts specialized microdomains that anchor signaling molecules and facilitate communication between cells.
Precursor for Steroid Hormones
It is converted into steroid hormones, including cortisol (stress response), aldosterone (electrolyte and blood pressure regulation), estrogen, progesterone, and testosterone (reproductive health). These hormones are crucial regulators of metabolism, immunity, and reproduction.
Bile Acid Formation
In the liver, it undergoes enzymatic conversion to bile acids, which help in digesting and absorbing dietary fats and fat-soluble vitamins in the intestines. This pathway represents a vital route of its catabolism and elimination.
Vitamin D Synthesis
When UV-B light strikes the skin, 7-dehydrocholesterol derived from cholesterol is converted to vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol). This compound regulates calcium homeostasis, bone mineralization, and modulates immune function.
Transport in the Body
Since it cannot dissolve in water, the body packages it into lipoproteins complexes that allow safe and targeted transport through the bloodstream to various tissues.
Lipoprotein Carriers: HDL, LDL, VLDL, and Chylomicrons
Chylomicrons transport dietary fats from the intestines to tissues and liver. VLDL releases triglycerides and transforms into LDL. LDL transports cholesterol to peripheral cells, while HDL collects excess cholesterol and delivers it back to the liver often termed “reverse transport.”
Receptor-Mediated Endocytosis of LDL
LDL cholesterol enters cells via LDL receptors on the cell surface, followed by endocytosis and lysosomal breakdown, releasing cholesterol. This process regulates intracellular cholesterol levels and feedback to the liver for cholesterol synthesis control.
Disorders Associated with Imbalance
It imbalance contributes to a range of diseases, especially related to cardiovascular health and metabolic function.
Hypercholesterolemia
Elevated LDL cholesterol promotes arterial plaque formation, contributing to stiffening and narrowing of arteries. Chronic hypercholesterolemia increases risk of heart attacks, strokes, and peripheral artery disease.
Atherosclerosis and Cardiovascular Disease
LDL-mediated plaque accumulation and inflammation in arterial walls lead to atherosclerosis the underlying condition aggravating coronary artery disease and vascular complications. Tick plaque rupture can result in thrombosis and acute cardiovascular events.
Genetic Disorders (Familial Hypercholesterolemia)
Mutations in LDL receptor genes lead to familial hypercholesterolemia, causing extremely high LDL levels from birth, often resulting in early cardiovascular disease. Early diagnosis and aggressive LDL reduction are vital for patient outcomes.
Diagnostic Techniques for Assessment
Assessing it accurately helps manage cardiovascular risk and guides treatment decisions based on individual health profiles.
Blood Lipid Panel Tests
A standard fasting lipid profile measures total cholesterol, LDL, HDL, and triglycerides. Derived values, such as LDL-to-HDL ratio, offer insights into cardiovascular risk. These results inform lifestyle and pharmacological interventions.
Genetic Testing for Lipid Disorders
Genetic analysis can identify mutations in LDL receptor or ApoB genes to confirm familial hypercholesterolemia, enabling personalized prevention and targeted lipid-lowering strategies.
Imaging for Atherosclerosis Detection
Non-invasive modalities like carotid artery ultrasound and coronary artery calcium scoring via CT help detect subclinical atherosclerosis and assess cardiovascular risk, guiding clinical decisions beyond typical lipid testing.
Recent Advances in Research
The landscape of its research is rapidly evolving with novel therapies and lifestyle interventions that complement traditional strategies like diet and statin therapy.
Novel Therapies Targeting Metabolism
PCSK9 inhibitors are monoclonal antibodies that prevent PCSK9 from degrading LDL receptors, thereby enhancing LDL clearance. RNA-based therapies are also emerging to modulate cholesterol-related gene expression for individualized treatment.
Plant Sterols and Dietary Interventions
Plant-derived sterols (phytosterols) compete with cholesterol for absorption in the intestines, thus lowering LDL cholesterol levels modestly when consumed regularly. Dietary patterns like the Mediterranean diet also improve cholesterol profiles and cardiovascular outcomes.
Ethical and Clinical Considerations in It’s Management
It’s management strategies range from lifestyle changes to pharmacotherapy, and ethical considerations often emerge regarding patient guidelines and long-term safety.
Statin Therapy Controversies
While statins have strong efficacy in reducing cardiovascular events, they are sometimes controversial concerning their effects in lower-risk populations, their side effects (like muscle pain or diabetes risk), and the need for individualized risk-benefit assessment.
Public Health Guidelines
Leading health organizations issue evidence-based cholesterol guidelines that consider global and population-specific factors. These prescriptions guide medical practice and insurance coverage in the fight against cardiovascular disease.
Conclusion
It is a critical biological molecule, essential for membrane structure, hormone and vitamin production, and lipid digestion but its levels must be carefully regulated. Understanding its structure, pathways of synthesis and regulation, transport mechanisms, and clinical implications helps in managing health and disease.
Ongoing research in precision therapies, genetic modulation, and public health strategies promises better patient outcomes and more personalized approaches to cholesterol management in the years ahead.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Why is cholesterol essential for the human body?
Cholesterol is essential because it maintains cell membrane structure, serves as a precursor for steroid hormones, bile acids, and vitamin D, and supports important biological functions.
How is cholesterol different from other lipids?
Cholesterol is a sterol with a rigid four-ring structure and a polar hydroxyl group, unlike most lipids that are triglycerides or phospholipids; this unique structure allows it to modulate membrane fluidity and act as a biochemical precursor.
Which foods most influence cholesterol synthesis?
Foods high in saturated fats, trans fats, and dietary cholesterol such as fatty meats, full-fat dairy products, and processed foods most strongly influence cholesterol synthesis and blood levels.
Related Contents
Chlorophyll- Definition, Structure, Types, Biosynthesis, Uses