1. Definition of Chloroplasts
Chloroplasts are double-membrane-bound organelles found in the cells of plants and some protists like algae. They are primarily responsible for conducting photosynthesis the process by which light energy is converted into chemical energy stored in glucose. These organelles contain the green pigment chlorophyll, which plays a crucial role in capturing sunlight. Chloroplasts are considered semi-autonomous organelles because they have their own DNA and ribosomes, allowing them to produce some of their own proteins. Their presence is one of the key differences between plant and animal cells.
Summary of Chloroplasts
- Chloroplast are plant cell organelles responsible for photosynthesis, converting sunlight into chemical energy using chlorophyll.
- Their structure includes double membranes, stroma, and thylakoid stacks (grana) where light and dark reactions occur.
- Chloroplast also help synthesize organic compounds, store starch, and support energy production for plant growth.
Table of Contents
2. Structure
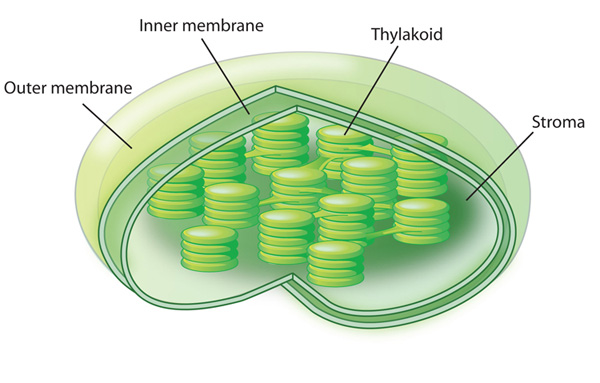
Chloroplast have a complex structure that supports their function in photosynthesis. Their components include:
Outer Membrane: The outermost boundary of the chloroplast, which is smooth and selectively permeable, allowing small molecules and ions to pass through easily.
Inner Membrane: Located just beneath the outer membrane, it is less permeable and contains transport proteins that regulate the movement of substances into and out of the chloroplast’s internal environment.
Stroma: The fluid-filled space enclosed by the inner membrane. It contains enzymes necessary for the Calvin cycle, as well as chloroplast DNA, ribosomes, and starch granules.
Thylakoids: Disk-shaped membrane sacs suspended within the stroma. Thylakoids are arranged in stacks called grana. They contain chlorophyll and are the sites where light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis occur.
Grana (singular: Granum): Stacks of thylakoids that increase surface area for photosynthetic reactions. They are interconnected by lamellae.
Lamellae: Tubular membranes that connect and support the grana, helping to maintain proper spacing and function.
Chlorophyll: The green pigment located within the thylakoid membranes that captures light energy required for photosynthesis.
3. Functions
Chloroplast perform several essential functions within plant and algal cells:
Photosynthesis: The most vital function of chloroplast is converting light energy into chemical energy via photosynthesis. This process occurs in two main stages light-dependent reactions in the thylakoids, and the Calvin cycle (light-independent reactions) in the stroma.
Synthesis of Organic Compounds: Besides glucose, chloroplast also help synthesize amino acids, fatty acids, and lipids that are necessary for plant growth and development.
ATP and NADPH Production: During the light-dependent reactions, chloroplast produce ATP and NADPH, which are energy-rich molecules used to drive the Calvin cycle and other biosynthetic processes.
Starch Storage: Excess glucose produced during photosynthesis is converted into starch and stored temporarily within the stroma.
Photorespiration: In conditions of high oxygen and low carbon dioxide, chloroplasts participate in photorespiration, a metabolic pathway that can limit the efficiency of photosynthesis.
4. Diagram of Chloroplast
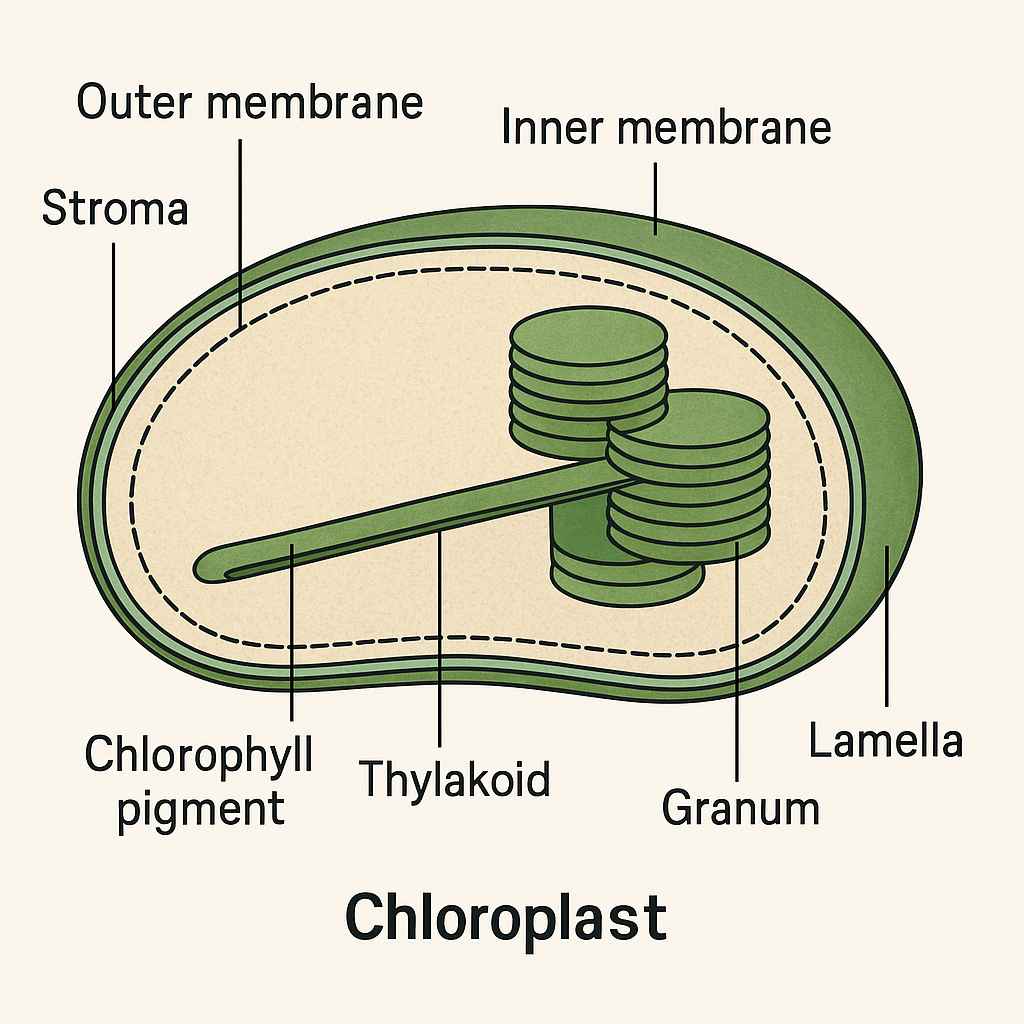
This diagram helps visualize the arrangement of internal structures and their roles in photosynthesis.
5. Conclusion
Chloroplast are one of the most vital organelles in plant biology. Their primary role in converting solar energy into chemical energy sustains the base of the food chain and supplies oxygen necessary for life on Earth. Their double-membrane structure, internal thylakoid membranes, and unique pigment composition make them highly efficient at capturing light and initiating photosynthetic reactions. Beyond photosynthesis, they contribute to the synthesis of critical organic molecules and energy storage. Their semi-autonomous nature, due to the presence of their own DNA and ribosomes, further underscores their complexity and evolutionary importance. Understanding chloroplasts is essential not only for grasping how plants grow and survive but also for appreciating the broader ecosystem functions they support.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is a chloroplast and why is it green?
A chloroplast is a special part inside plant and algae cells that helps them make their own food. It does this through a process called photosynthesis, where sunlight is turned into energy the plant can use. The reason chloroplasts look green is because they contain a pigment called chlorophyll. This pigment absorbs sunlight, especially the blue and red parts of the light, but it reflects the green part. That’s why plants appear green when we look at them.
How are chloroplasts structured and where are photosynthesis reactions located?
Chloroplast are like tiny energy factories inside plant cells. They have two outer membranes that protect and control what goes in and out. Inside, there is a jelly-like fluid called the stroma, which holds important enzymes and the plant’s DNA. Floating inside the stroma are thylakoids small, round disks that stack up like pancakes in a pile called grana. The light reactions of photosynthesis, which need sunlight, happen in the thylakoids. The next part of photosynthesis, called the Calvin cycle, happens in the stroma. This part doesn’t need light and helps turn carbon dioxide into sugar.
Do animal cells have chloroplasts?
No, animal cells do not have chloroplast. Only plant cells and some algae have chloroplast because they make their own food using sunlight. Animals, on the other hand, cannot make their own food. They eat plants or other animals to get energy, so they do not need chloroplast.
Related Articles