1. Introduction
All living organisms are made of cells. While animal cells have only a flexible cell membrane, many other living things like plants, fungi, and bacteria have an additional, rigid layer called the cell wall.
The cell wall is like armor—it gives the cell shape, strength, and protection. Even though it serves similar purposes across different organisms, the structure and materials that make up the cell wall differ depending on whether it’s found in a plant, fungus, or bacterium.
In this explanation, we will understand:
- What a cell wall is
- Its basic functions
- The differences and similarities between plant, fungal, and bacterial cell walls
Table of Contents
2. What is a Cell Wall?
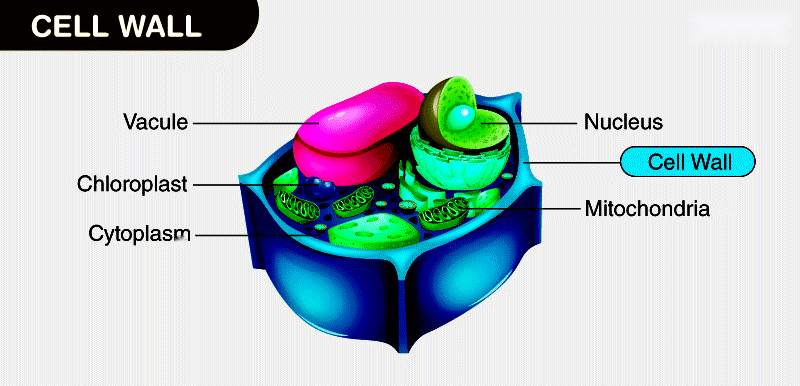
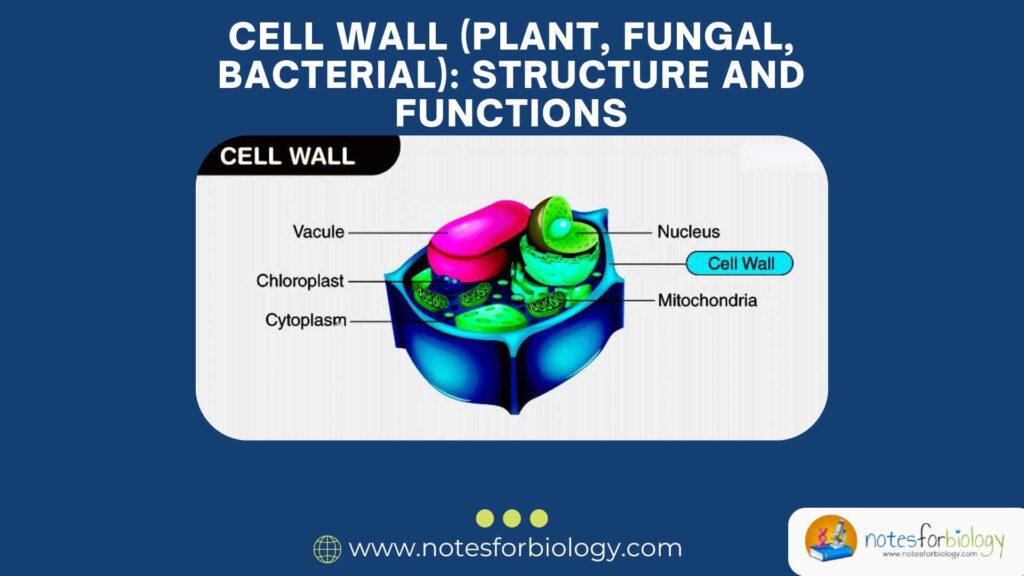
A cell wall is a tough, rigid layer that lies outside the cell membrane. It is found in:
- Plants
- Fungi
- Bacteria
- Some algae and archaea
The cell wall gives strength to the cell and protects it from outside forces. It also helps the cell maintain its shape, especially when water flows in and out.
3. Main Functions of the Cell Wall
Regardless of the type of organism, the cell wall performs several important tasks:
- Provides structure and shape to the cell
- Protects the cell from mechanical damage
- Prevents bursting when water enters the cell (called turgor pressure)
- Acts as a barrier to harmful substances
- Supports the whole organism in the case of plants and fungi
- Regulates the entry and exit of certain materials
4. Plant Cell Wall
A. Structure
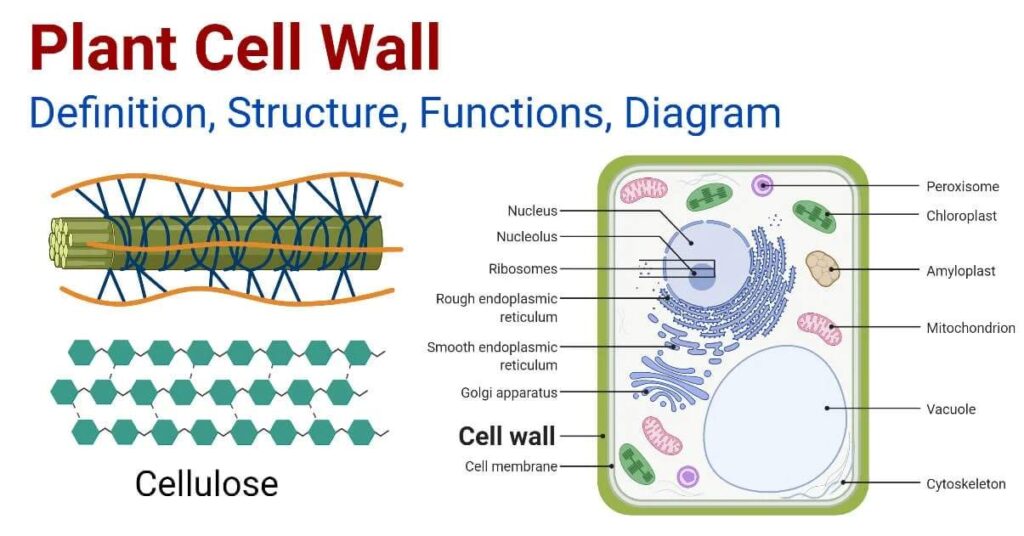
The plant cell wall is made mostly of a carbohydrate called cellulose. Cellulose is a tough, fibrous material that humans cannot digest (it is what gives vegetables their crunch!).
The plant cell wall has three layers:
- Primary cell wall
- Thin and flexible
- Made during cell growth
- Secondary cell wall
- Thicker and stronger
- Found in older, mature cells
- Contains cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin (makes wood hard)
- Middle lamella
- Layer between two adjacent plant cells
- Rich in pectin (sticky substance)
- Helps glue cells together
B. Composition
- Cellulose (main component)
- Hemicellulose
- Pectin
- Lignin (in woody plants)
C. Functions
- Gives mechanical support to the plant
- Maintains shape and prevents the cell from bursting when water enters
- Helps in transport of water and nutrients
- Supports upright growth
- Acts as a barrier to pathogens like bacteria and viruses
5. Fungal Cell Wall
A. Structure
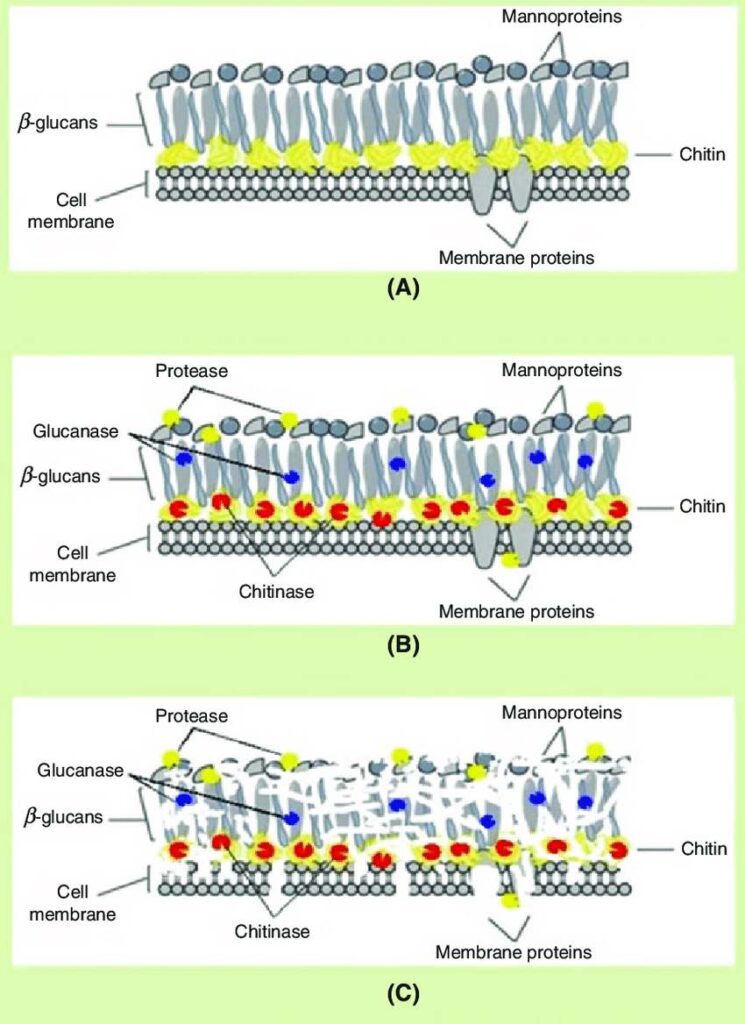
The fungal cell wall is different from that of plants. It is not made of cellulose. Instead, it contains chitin—a strong and flexible substance also found in the exoskeleton of insects.
The fungal cell wall is multi-layered and includes:
- Inner layer: Provides strength
- Outer layer: More flexible and involved in interaction with the environment
B. Composition
- Chitin (main component)
- Glucans (β-glucans)
- Mannoproteins
- Sometimes melanin
C. Functions
- Provides rigidity and shape
- Protects from osmotic pressure (water movement)
- Helps fungi grow through tough materials like wood or skin
- Protects from environmental stresses and chemicals
- Plays a role in fungal pathogenicity (ability to cause disease)
6. Bacterial Cell Wall
A. Structure
Bacterial cell walls are very different from plant and fungal cell walls. They are mainly made of a unique substance called peptidoglycan, also known as murein.
There are two main types of bacteria based on their cell wall structure:
- Gram-positive bacteria
- Thick peptidoglycan layer
- Stains purple in Gram stain test
- Gram-negative bacteria
- Thin peptidoglycan layer
- Surrounded by an outer membrane
- Stains pink or red in Gram stain test
B. Composition
- Peptidoglycan (a mesh of sugars and amino acids)
- Teichoic acids (in Gram-positive)
- Lipopolysaccharides (in Gram-negative)
- Proteins and phospholipids
C. Functions
- Gives the bacteria shape (coccus, bacillus, spirillum, etc.)
- Prevents bursting due to internal pressure
- Protects against toxins and antibiotics
- Helps in host infection (for disease-causing bacteria)
- Allows transport of small molecules
7. Comparison Table of Cell Walls
| Feature | Plant Cell Wall | Fungal Cell Wall | Bacterial Cell Wall |
|---|---|---|---|
| Main Component | Cellulose | Chitin | Peptidoglycan (murein) |
| Other Components | Hemicellulose, pectin | Glucans, mannans | Teichoic acids, LPS |
| Structure | Multilayered, rigid | Flexible, layered | Thick (Gram+) or thin (Gram−) |
| Found In | Plants, algae | Fungi (mushrooms, yeasts) | Most bacteria |
| Permeability | Semi-permeable | Semi-permeable | Permeable to small molecules |
| Extra Layer | Middle lamella | Outer protein layer | Outer membrane (Gram−) |
8. Importance of Cell Walls in Science and Medicine
- Antibiotics like penicillin work by damaging bacterial cell walls, which causes the bacteria to die.
- In agriculture, understanding the plant cell wall helps in improving crop resistance.
- Fungal infections are treated with drugs that target chitin or glucan synthesis.
- Cell wall components are used in biotechnology and biofuel research.
9. Similarities and Differences
Similarities:
- All provide support and protection
- All lie outside the cell membrane
- Help maintain cell shape
- Control entry and exit of materials
Differences:
- Made of different materials (cellulose vs chitin vs peptidoglycan)
- Plant and fungal cell walls are eukaryotic, bacterial walls are prokaryotic
- Some (like Gram-negative bacterial walls) have extra outer layers
10. Conclusion
The cell wall is one of the most essential parts of many living organisms. It acts as a protective shield and gives the cell its shape and strength. Though plant, fungal, and bacterial cell walls serve similar purposes, they are built differently and have different compositions.
Understanding how each type of cell wall works helps scientists:
- Create medicines (like antibiotics and antifungals),
- Develop better crops,
- Study infections,
- And even make biofuels and industrial products.
From the crunchy bite of a vegetable to the survival of microscopic bacteria, the cell wall is a silent but strong player in the game of life.
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
What is a cell wall and what does it do?
A cell wall is a tough, rigid layer found outside the cell membrane in plants, fungi, bacteria, and some algae. It provides structural support, gives the cell shape, protects against physical damage, and prevents the cell from bursting due to excess water intake.
How is a plant cell wall different from a fungal or bacterial cell wall?
Plant cell walls are made mainly of cellulose, fungal cell walls contain chitin, and bacterial cell walls are built from peptidoglycan. These materials are chemically different and give each type of cell wall its unique properties and strength.
What is the role of the cell wall in bacterial cells?
In bacteria, the cell wall maintains the cell’s shape, protects it from bursting due to internal pressure, and acts as a barrier to harmful substances. It also plays a key role in bacterial classification (Gram-positive or Gram-negative) based on its structure.
Related Articles