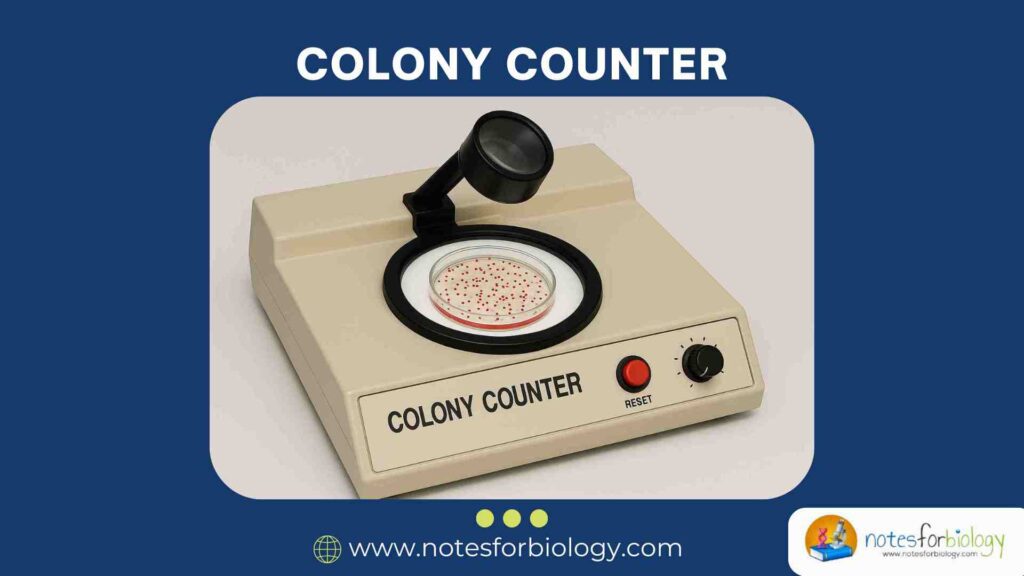
Colony Counter- Types, Principle, Parts, Uses, Examples
Microbial enumeration is a critical process in microbiology, ensuring the accurate measurement of viable microorganisms in a given sample. Whether testing food safety, water purity, pharmaceutical sterility, or conducting basic research, counting microbial colonies is essential for quality control and experimental validation. To simplify and standardize this process, colony counters have been developed. These instruments […]
Colony Counter- Types, Principle, Parts, Uses, Examples Read More »