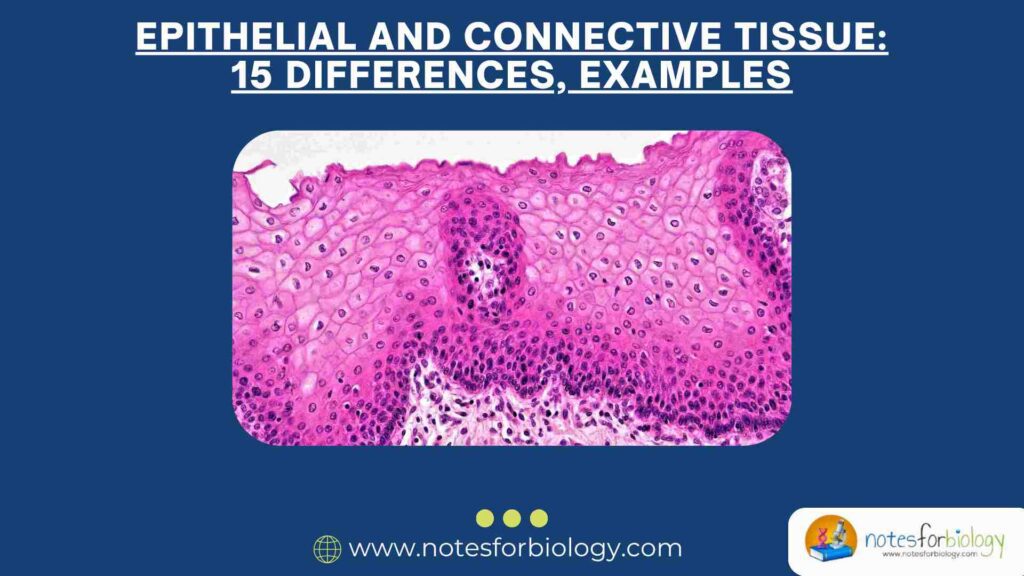
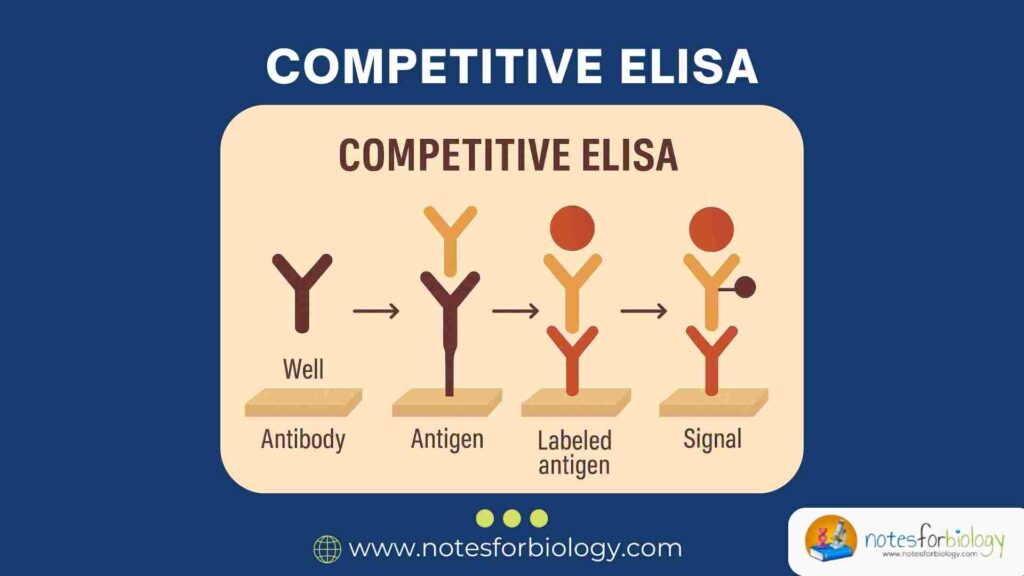
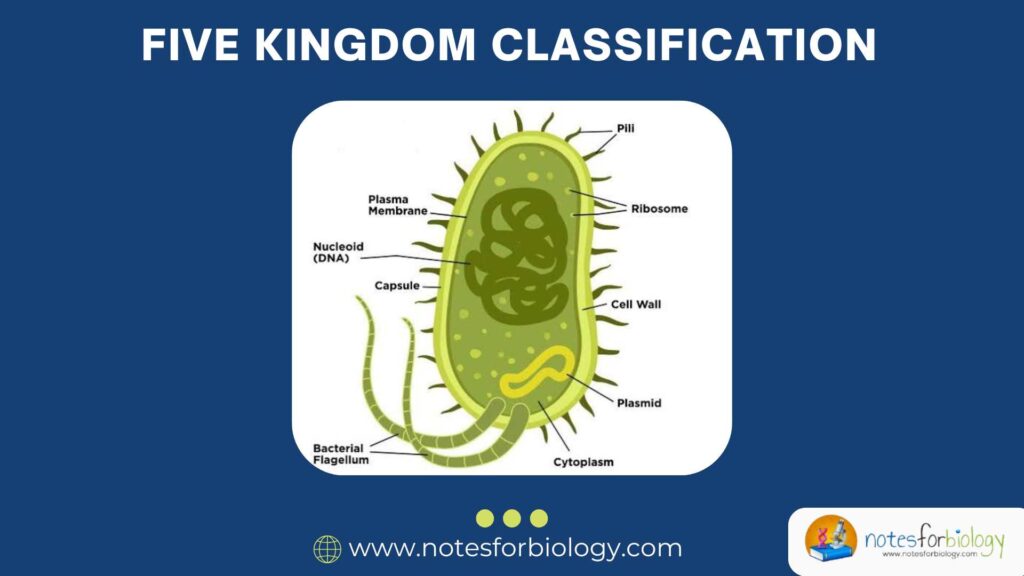
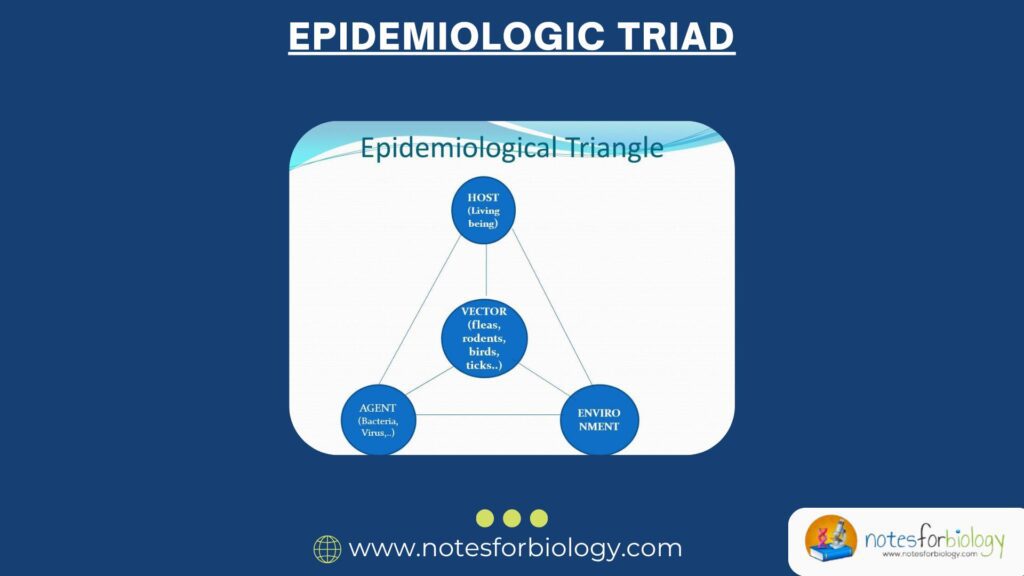
Error – Types, Sources, and Control
Introduction In our everyday lives, as well as in scientific experiments, industries, laboratories, and even in classrooms, we often need to measure things or collect data. But no matter how careful we are or how good our instruments are, we may still face differences between what we measure and what the actual value should be. […]