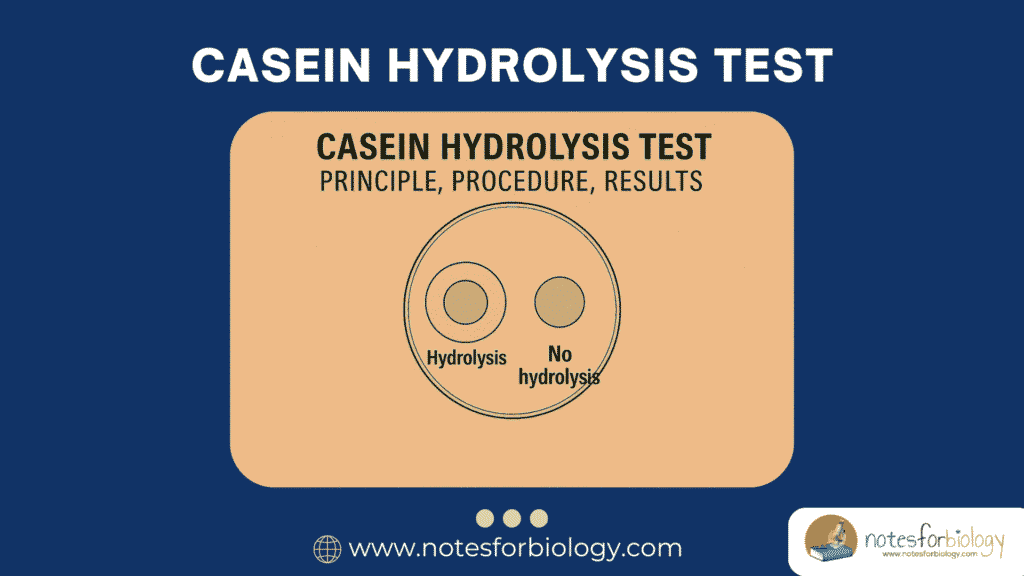
Casein Hydrolysis Test- Principle, Procedure, Results
The Casein Hydrolysis Test is a vital biochemical test performed in microbiology to detect the ability of microorganisms to produce extracellular proteolytic enzymes known as caseinases. These enzymes break down casein, a major milk protein, into smaller, soluble products like amino acids and peptides. The test is widely used for differentiating proteolytic bacteria from non-proteolytic […]
Casein Hydrolysis Test- Principle, Procedure, Results Read More »