Pancreas: Structure, Hormones, and Functions
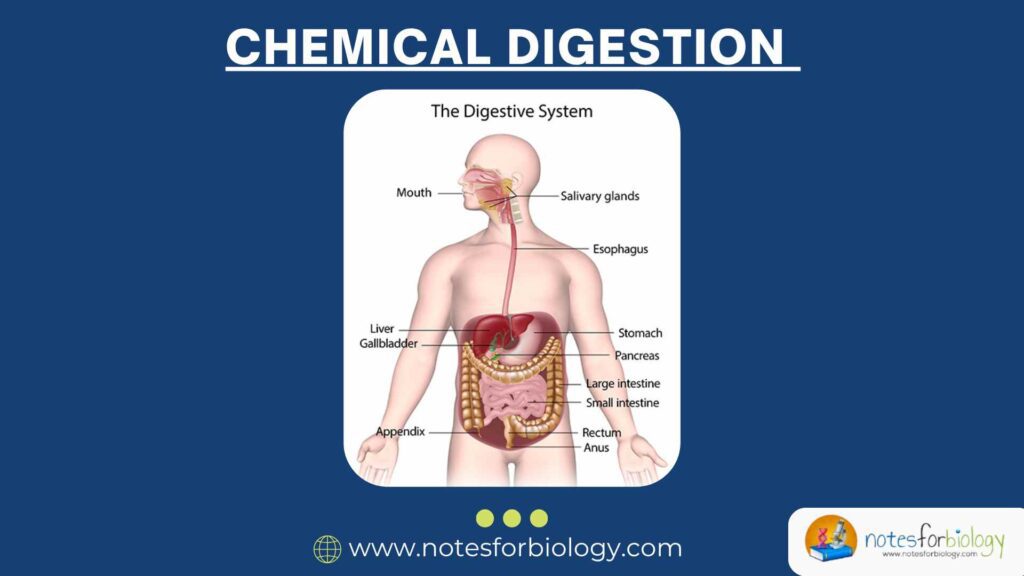
1. Introduction to the Pancreas The pancreas is a vital organ in our body that does two important jobs — it helps us digest food and control our blood sugar. It is part of both the digestive system and the endocrine system. Although small and soft, the pancreas plays a big role in keeping us […]