1. Introduction
In the world of medical research and public health, it is important to understand what causes diseases, how they spread, and how we can prevent them. To do this, researchers use different types of studies. One commonly used study method is the case-control study.
This type of study is especially useful when we want to find out whether a certain behavior, exposure, or condition is linked to a disease. For example, we may want to know if smoking is connected to lung cancer or if drinking unclean water is related to diarrhea.
Let’s break it down in a simple way.
Table of Contents
2. What is a Case-Control Study?
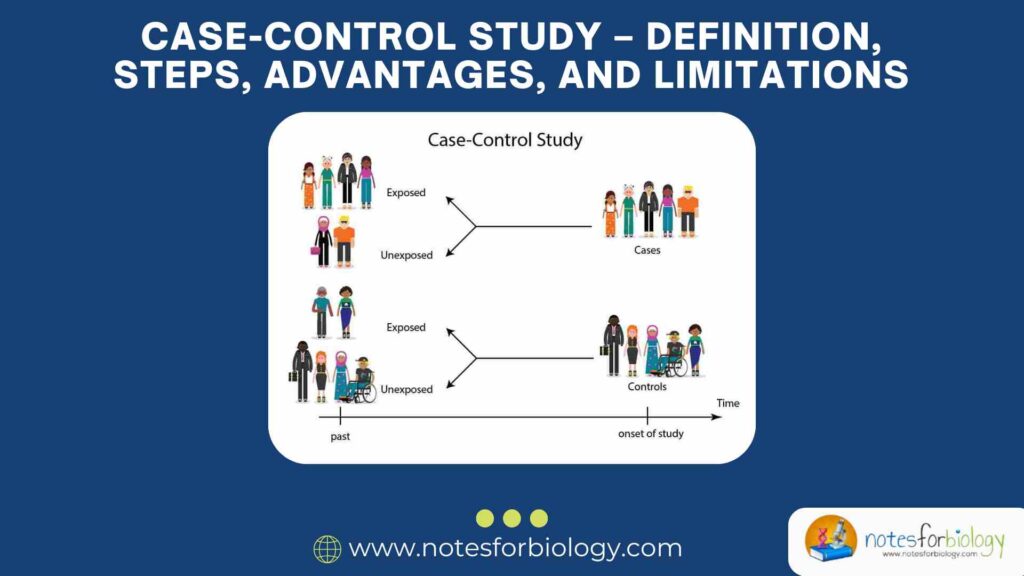
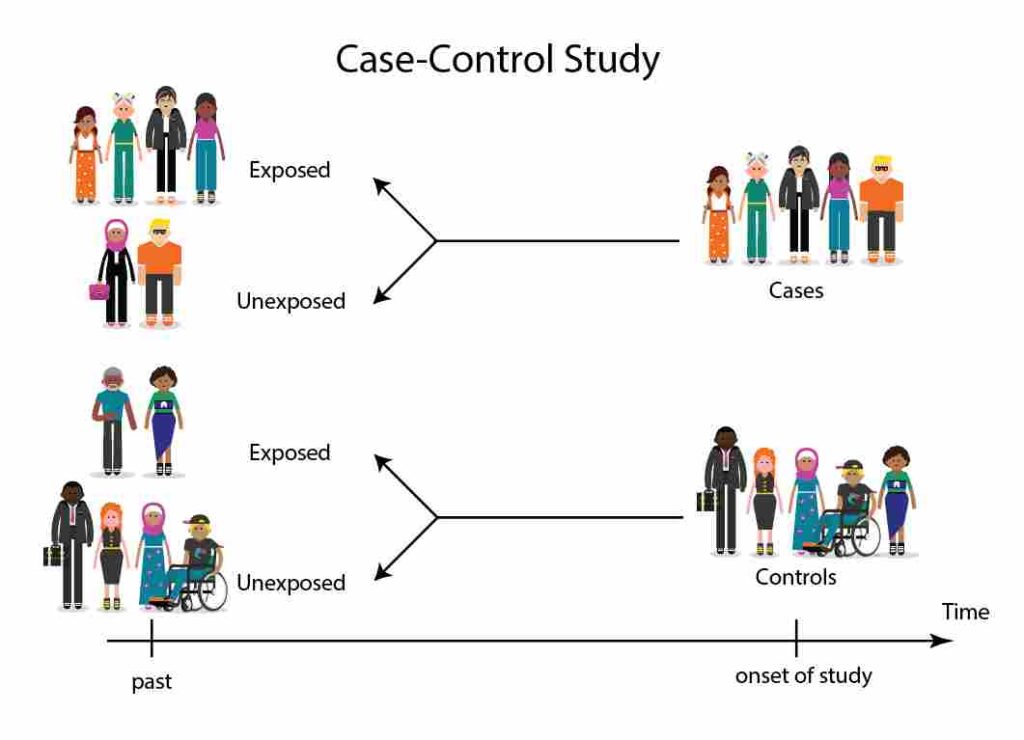
A case-control study is an observational study where researchers compare two groups of people:
- Cases – People who already have the disease or health condition.
- Controls – People who do not have the disease.
The researcher then looks backward to see whether the people in both groups were exposed to a possible risk factor in the past.
Key Point:
A case-control study does not involve giving treatments or controlling exposure. It simply observes what has already happened in both groups.
3. Purpose of a Case-Control Study
The main purpose is to find out if a particular exposure or behavior is associated with a specific disease. It helps researchers understand the possible causes of diseases or conditions.
Example:
To check if smoking is linked to heart disease, researchers select people with heart disease (cases) and people without heart disease (controls), and look into their smoking history.
4. When to Use a Case-Control Study
This study is best used when:
- The disease is rare (e.g., a rare type of cancer).
- You need results quickly.
- The disease takes a long time to develop.
- You have limited resources (money, time, staff).
5. Basic Design of a Case-Control Study
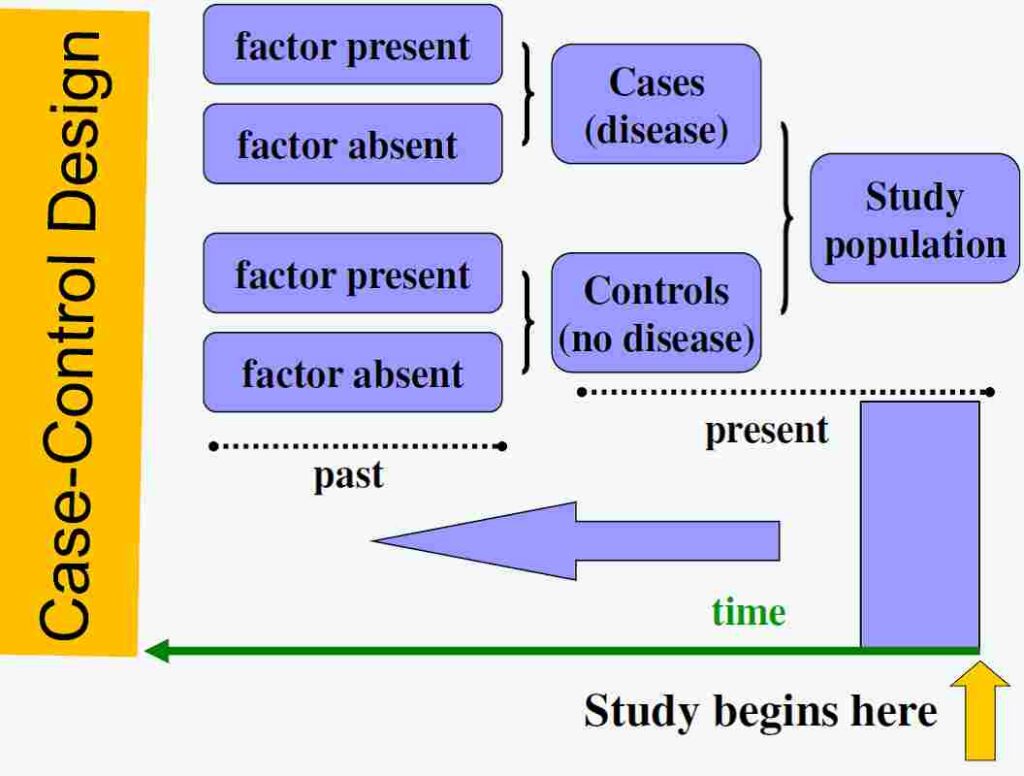
The study follows these basic steps:
- Identify cases (people with the disease).
- Select controls (people without the disease).
- Collect information about past exposures.
- Compare how many in each group were exposed to the risk factor.
- Analyze whether exposure is more common in cases than controls.
This study always looks backward in time to compare exposure history.
6. Key Steps in Conducting a Case-Control Study
Let’s go through the process step by step.
Step 1: Define the Research Question
Before starting, researchers need to ask a clear question.
Example:
“Is long-term exposure to air pollution associated with asthma in children?”
Step 2: Select the Cases
- Choose people who already have the disease.
- Make sure all cases meet the same definition of the disease.
- Cases can be found in hospitals, clinics, or registries.
Step 3: Select the Controls
- Choose people without the disease.
- Controls should be similar to the cases in terms of age, gender, location, etc.
- Controls should come from the same population as the cases.
Important: Controls must be representative of the population that gave rise to the cases.
Step 4: Collect Data on Past Exposure
- Gather information on risk factors or exposures.
- Use interviews, questionnaires, medical records, or laboratory reports.
- Make sure the data collection is the same for both groups.
Step 5: Analyze the Data
- Compare how many cases and controls were exposed to the risk factor.
- Use a measure called the Odds Ratio (OR) to estimate the strength of association between exposure and disease.
Odds Ratio (OR)
If OR > 1: Exposure may increase disease risk.
If OR < 1: Exposure may protect against disease.
If OR = 1: No link between exposure and disease.
7. Example of a Case-Control Study
Research Question: Does smoking increase the risk of lung cancer?
- Cases: 100 people with lung cancer.
- Controls: 100 people without lung cancer.
- Data collection: Interview about smoking habits over the past 20 years.
If 80 out of 100 cases were smokers, and only 30 out of 100 controls were smokers, the odds ratio would be high, suggesting smoking is strongly associated with lung cancer.
8. Advantages of Case-Control Studies
Case-control studies are widely used because they offer many benefits.
A. Efficient for Rare Diseases
You don’t have to wait for the disease to occur; you start with people who already have it.
B. Quick and Less Expensive
These studies are faster and cheaper than other studies like cohort studies.
C. Useful for Studying Long-Term Effects
Good for diseases that take years to develop, like cancer or heart disease.
D. No Need to Follow People Over Time
No long follow-up is needed. The study is based on events that have already happened.
E. Can Study Multiple Risk Factors
You can explore many possible causes or exposures for one disease.
9. Limitations of Case-Control Studies
Even though they are useful, case-control studies have some weaknesses.
A. Recall Bias
People may not remember past exposures accurately, especially if the event happened long ago.
B. Selection Bias
If the cases and controls are not chosen properly, the results may be wrong or misleading.
C. Cannot Prove Cause and Effect
They can show a link but not prove that the exposure caused the disease.
D. Difficult to Choose the Right Controls
If controls are not similar to cases (except for the disease), results can be biased.
E. Prone to Confounding
Other hidden factors may influence both the exposure and the disease.
10. Differences Between Case-Control and Other Studies
| Feature | Case-Control Study | Cohort Study |
|---|---|---|
| Direction of Study | Retrospective (looks back) | Prospective (looks forward) |
| Time Taken | Short | Long |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Best for | Rare diseases | Common diseases or rare exposure |
| Outcome Known at Start? | Yes | No |
| Can Measure Incidence? | No | Yes |
11. How to Improve the Quality of a Case-Control Study
- Use clear definitions for cases and controls.
- Choose controls from the same population as cases.
- Use reliable and objective ways to collect exposure data.
- Blind interviewers to case/control status.
- Use matching to reduce confounding (e.g., match by age or gender).
- Use statistical adjustments when needed.
12. Ethical Considerations
Even though it is observational, case-control studies must:
- Respect participants’ privacy.
- Use informed consent.
- Avoid causing psychological or emotional distress.
- Be approved by an ethics review board.
13. Real-Life Examples of Case-Control Studies
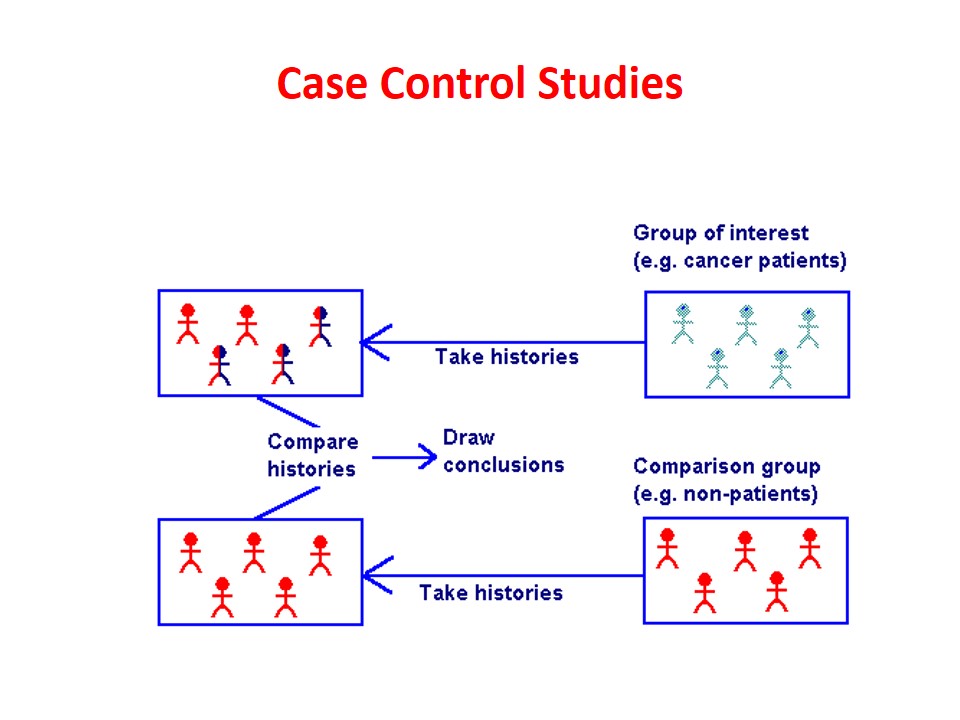
- A study linking human papillomavirus (HPV) to cervical cancer.
- A study showing the relationship between asbestos exposure and lung disease.
- Research linking contaminated water to cholera outbreaks.
These examples show how powerful case-control studies can be in identifying risks and saving lives.
14. Summary Table
| Aspect | Case-Control Study |
|---|---|
| Main Goal | Compare exposure between cases and controls |
| Study Direction | Retrospective (looks into the past) |
| Best Used For | Rare diseases, long-latency diseases |
| Time and Cost | Quick and inexpensive |
| Measure of Association | Odds Ratio (OR) |
| Strengths | Efficient, cost-effective, handles rare diseases |
| Weaknesses | Recall bias, selection bias, no causality, hard to find controls |
15. Conclusion
A case-control study is a simple yet powerful tool in medical and public health research. It helps scientists and doctors explore the possible causes of diseases by comparing those with a condition to those without it. When conducted properly, it can provide valuable insights—especially for rare diseases or conditions that take a long time to develop.
Although this method has some limitations, such as recall bias and the inability to prove causation, it remains a quick, efficient, and affordable option for research. Understanding how case-control studies work helps students, researchers, and health professionals interpret study results and make informed decisions for improving health.
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
What is a case-control study?
A case-control study is an observational research method where two groups are compared: one group with a disease (cases) and another group without the disease (controls). The study looks back in time to find out if there was a difference in exposure to a certain risk factor between the two groups.
When is a case-control study most useful?
It is most useful when studying rare diseases, diseases with a long incubation period, or when the research needs to be done quickly and at low cost. It is ideal when it’s not practical to follow people for a long time.
What are some limitations of case-control studies?
Key limitations include:
Recall bias (people may not remember exposures accurately),
Selection bias (improper choice of controls),
Inability to prove causation, and
Confounding factors (other variables that affect results).
Related Articles