What is Bunsen Burner?
Bunsen Burner is a reliable and controlled source of heat, it is a common instrument in labs. After the German chemist Robert Bunsen, who improved its design in the 1800s, it bears his name.
Table of Contents
Principle of operation
The principle of combustion drives the operation of the Bunsen burner. It creates a combustible mixture by combining a fuel gas—typically natural gas or propane—with air. This mixture ignites to produce the flame. The temperature and intensity of the flame are determined by the amount of air combined with the gas.
Parts of Bunsen Burner
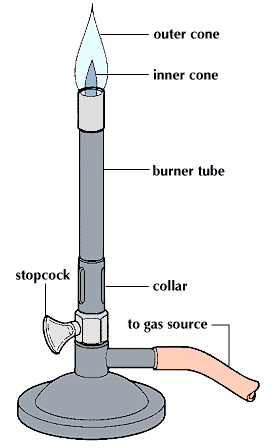
Base: Offers the burner support and stability.
Barrel :A vertical tube that allows gas to pass through and combine with air is called a barrel.
Collar (or Air Inlet) :A moveable ring at the foot of the barrel called the collar, also known as the air inlet, regulates how much air enters the burner.
Gas Inlet :A tube that joins the burner to the gas supply is called the gas inlet.
Gas Control Valve: A lever or knob that controls how much gas enters the burner.
Types
Types of It differ slightly, but the fundamental design is the same:
Standard Burner

The most popular kind of Bunsen burner, with a single barrel and collar, is the standard model. Often employed in laboratories for sterilizing and heating, it gets its name from its inventor, Robert Bunsen. It is a vital instrument for many applications in chemistry, biology, and other scientific fields because of its straightforward construction and effective functioning.
Tirrill Burner

A more advanced model featuring an independent air adjustment screw and a needle valve for accurate gas control. An adjustable, controlled flame is produced by a Tirrill burner, a type of laboratory burner used for heating and other chemical processes. It bears the name Frederick Tirrill in honor of the American scientist who invented it.
Meker Burner
A high-temperature burner that produces a bigger, hotter flame by having several air inlets and a broader barrel. A Meker burner is a specific kind used in laboratory settings for high-temperature heating. It is well-known for having a strong, concentrated flame that can reach temperatures of up to 1200°C (2192°F), which makes it perfect for uses requiring a lot of heat.
How does it works?
Gas (often propane or natural gas) is injected into the burner in a stream.
The burner receives air through movable inlets.
A strong flame is created at the top of the burner when the gas and air mixture is ignited.
Uses
Because they can produce a regulated and controllable flame, Bunsen burners are indispensable instruments in many scientific and laboratory contexts. They are often used for the following purposes:
Heating
Heating solutions: Liquids in test tubes, beakers, and flasks are frequently heated using them. For a variety of investigations, such as producing solutions, conducting chemical reactions, and dissolving solids, this is helpful.
Sterilization: Glassware, metal utensils, and inoculating loops can all be sterilized in a lab setting using the extreme heat of a Bunsen burner flame.
Evaporation: Solvents from solutions can be removed using B. burner, which concentrate the remaining ingredients by carefully managing the heat.
Melting: You may use the heat from a Bunsen burner to melt some materials, such as agar and wax.
Burning and Responses
Testing for flammability: By exposing materials to the flame, Bunsen burners can be used to test for flammability.
Conducting chemical reactions: Bunsen burners offer a convenient and regulated way to supply heat, which is necessary for many chemical reactions.
Gas creation: Reacting certain compounds with the heat of a Bunsen burner can produce gases such as oxygen and hydrogen.
Additional Uses
Glassworking: Glass tubes can be softened with Bunsen burners in order to be bent, shaped, or joined.
Incineration: To eliminate biological matter, small samples can be burned over a Bunsen burner flame.
Arts and Crafts: Glassblowing and other creative uses for Bunsen burners are possible.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
List the uses of B. Burner?
The uses are:
for heating
for burning
for glassworking
Define Meker Burner in short ?
A high-temperature burner that produces a bigger, hotter flame by having several air inlets and a broader barrel. A Meker burner is a specific kind used in laboratory settings for high-temperature heating. It is well-known for having a strong, concentrated flame that can reach temperatures of up to 1200°C (2192°F), which makes it perfect for uses requiring a lot of heat.
What is Tirrill Burner ?
For precise gas control, a more sophisticated model has a needle valve and an independent air adjustment screw. An adjustable, controlled flame is produced by a Tirrill burner, a type of laboratory burner used for heating and other chemical processes. It bears the name Frederick Tirrill in honor of the American scientist who invented it.
Related Articles