What is Bone Marrow?
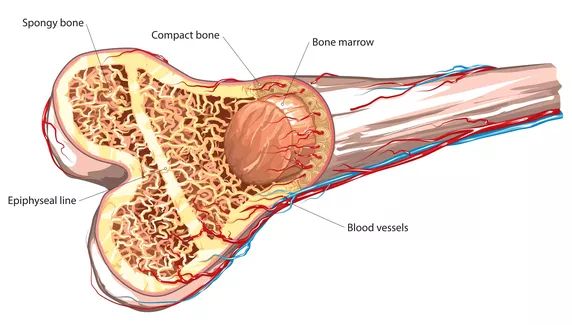
Stem cells make up bone marrow. Red bone marrow, which produces blood cells and platelets for your blood, is made from these stem cells. The primary components of yellow bone marrow are fat and stem cells, which help your body make cartilage and bone.
Most bones have hollow regions that contain the soft, spongy substance is called.It is an essential part of the human body that produces new immunological and blood cells. Let’s examine the types, structures, and functions of its as we delve into its complexity.
Table of Contents
Types
Red Bone Marrow
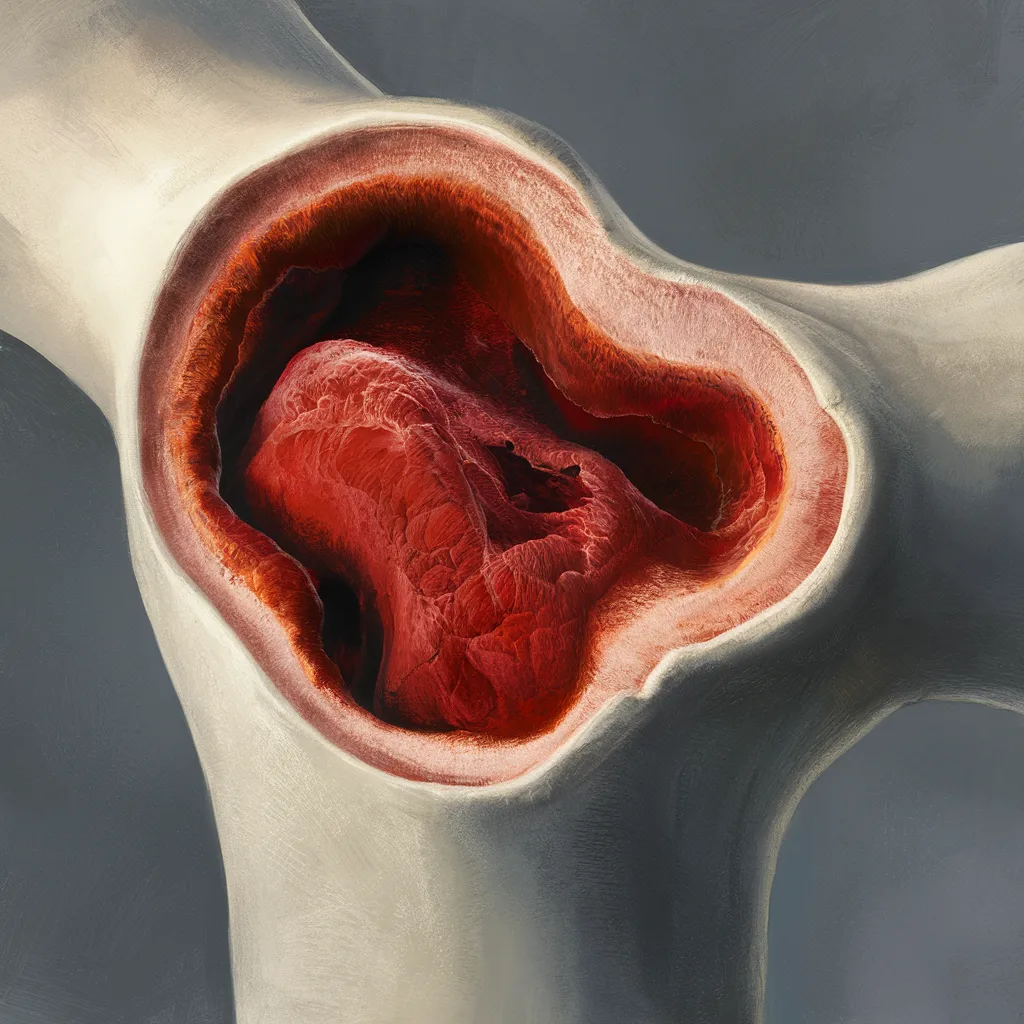
The hematopoietic stem cells found in this kind are active; they give rise to all blood cells, including platelets, white blood cells (WBCs), and red blood cells (RBCs). The extremities of long bones, the ribs, the skull, the pelvis, and the sternum are among the flat bones that contain red marrow.
Yellow Bone Marrow
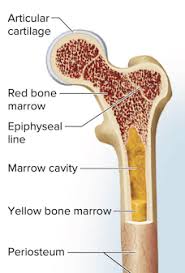
Yellow bone marrow increasingly replaces red bone marrow as we age. It is mostly made up of fat cells and does not produce any blood cells. If the body requires additional time to produce red blood cells, yellow marrow can turn back into red marrow.
Structure
Stroma
The stroma, a fibrous network that supports the hematopoietic cells and blood vessels, makes up the framework of the bone marrow.
Blood Vessels
The bone marrow is abundantly supplied with blood vessels that carry waste materials out of the cells and deliver nutrients and oxygen.
hematopoietic cells
The cells that create blood, or hematopoietic cells, are in charge of creating all blood cell types. Among them are:
pluripotent stem cells
The most basic cells found in bone marrow are called pluripotent stem cells, which have the ability to differentiate into any kind of blood cell.
Progenitor cells
Progenitor cells are more specialised blood cells that pledge allegiance to a certain blood cell lineage, such as white blood cells or red blood cells.
Mature Blood Cells
These blood cells are completely formed and prepared to carry out their designated roles in the body.
Role of the Bone Marrow:
Hematopoiesis
The production of all blood types is the main purpose of bone marrow. Hematopoiesis is the process that is necessary for:
Oxygen Transport
The body uses red blood cells, which are made in the bone marrow, to transport oxygen.
Immune Defence
The body is shielded against infections and illnesses by white blood cells, which are also made in bone marrow.
Blood Clotting
The bone marrow produces platelets, which aid in blood clotting to stop excessive bleeding.
Bone Repair and Remodelling
By providing the cells and growth factors necessary for bone regeneration, bone marrow aids in the repair and remodelling of the bone.
Immunological Regulation
Immune cells produced in bone marrow, such as lymphocytes, are essential for the immunological response.
Clinical Importance
Blood Disorders: Blood cell production is impacted by bone marrow disorders such as lymphoma and leukaemia, which can cause a variety of symptoms.
Bone Marrow Transplantation: This procedure replaces the damaged marrow with healthy cells in patients suffering from cancer or serious blood problems.
In Conclusion
Our immune system and blood cells are developed in the intricate and essential bone marrow. To recognise its significance in preserving general health, one must comprehend its composition and operations.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQ)
What is Bone marrow?
Most bones have hollow regions that contain the soft, spongy substance known as bone marrow. It is an essential part of the human body that produces new immunological and blood cells.
What is the clinical Importance of Bone marrow?
Its clinical importance are
1.Blood Disorders: Blood cell production is impacted by bone marrow disorders such as lymphoma and leukaemia, which can cause a variety of symptoms.
2.Bone Marrow Transplantation: This procedure replaces the damaged marrow with healthy cells in patients suffering from cancer or serious blood problems.
What is Progenitor cells ?
Progenitor cells are more specialised blood cells that pledge allegiance to a certain blood cell lineage, such as white blood cells or red blood cells.
Related Articles