An enhanced medium called blood agar (BA) is used to cultivate bacteria or other microorganisms that are difficult to grow. Because they require a different, more enriched nutritional environment than other bacteria, these bacteria are known as “fastidious.” Many pathogens, especially those that are more challenging to culture, like Neisseria species, Streptococcus pneumoniae, and Haemophilus influenzae, can be grown on it. Identifying and classifying hemolytic bacteria—particularly those belonging to the Streptococcus species is also necessary. Additionally, it functions as a differential medium by permitting the identification of hemolysis—the breakdown of red blood cells—caused by cytolytic toxins released by certain strains of Bacillus, Streptococcus, Enterococcus, Staphylococcus, and Aerococcus bacteria.
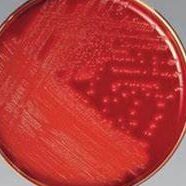
Table of Contents
Composition of Blood Agar
Agar is composed as follows:
- 0.5% Peptone
- 0.3% beef extract/yeast extract
- 1.5% agar
- 0.5% NaCl
- Distilled water
- 5% Sheep Blood
- pH should be from 7.2 to 7.6 (7.4)
Principles of Blood Agar
- It is a nutritionally enhanced medium that can be used as a general medium in the absence of blood or supplemented with blood to assist the development of picky organisms.
- By adding extra growth elements that these picky organisms need, the blood injected into the base gives the medium more nourishment.
- Additionally, the blood helps to visualize the hemolytic effects of various bacteria. The type of animal blood utilized, however, affects the hemolytic effects.
- Sheep blood works best against Group A streptococci; nevertheless, it is unable to promote the growth of Haemophilus hemolyticus. It’s because there aren’t enough pyridine nucleotides in sheep blood.
- Peptone and tryptose supply the carbon, nitrogen, amino acids, vitamins, and minerals that the bacteria need in addition to the blood used in the medium. Because tryptose and peptone are soluble in water, the organism can absorb nutrients more easily.
Preparation of Blood Agar
Prepare the base medium
- Dissolve the appropriate amount of nutrient base (tryptic soy agar or brain heart infusion agar) in distilled water.
- Add sodium chloride if not already included in the nutrient base.
- Autoclave the medium at 121°C for 15 minutes to sterilize.
Cool and add blood
- Pour the medium into sterile petri dishes.
- Store the plates in a refrigerator if not used immediately.
- Allow the agar to solidify at room temperature.
Pour plates
- Cool the sterilized nutrient base to 45-50°C to prevent coagulation of the blood.
- Aseptically add 5% defibrinated blood to the cooled medium.
- Mix gently but thoroughly to avoid creating bubbles or frothing.
Uses of Blood Agar
- It is mostly used to cultivate and isolate picky organisms such as Neisseria and Streptococcus.
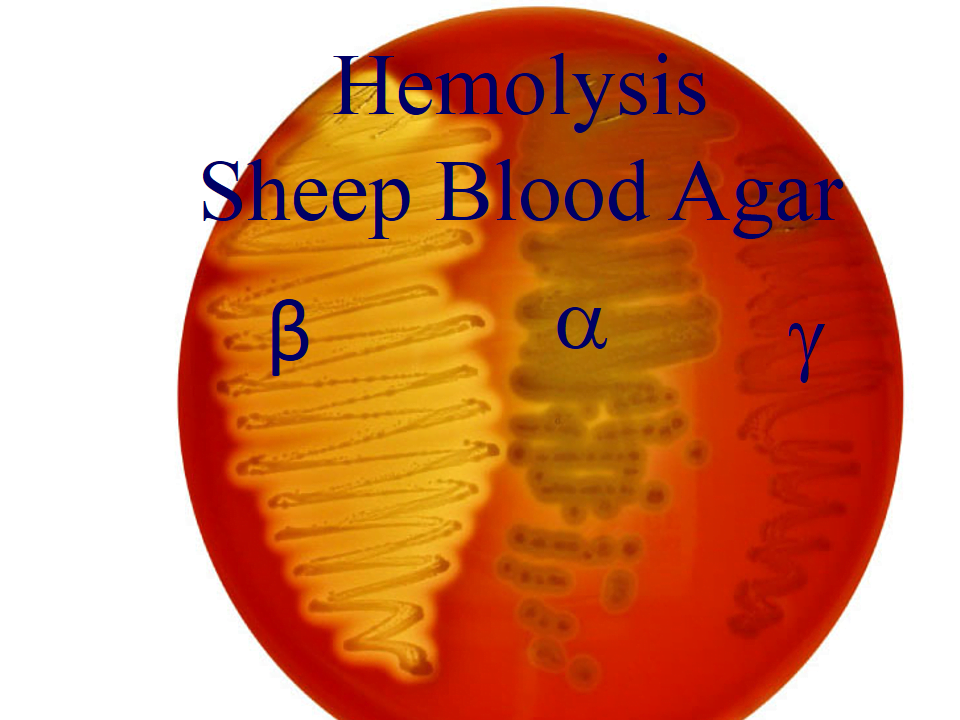
- It can be applied to distinguish between the several types of hemolysis (α-, β-, or γ-hemolytic) that bacteria produce on agar.
- By incorporating phenolphthalein phosphate into the medium, phosphate-producing Staphylococci can be identified using this.
- Salmonella Typhi antigens are frequently prepared on it.
- One common technique for analyzing food samples is the base.
Hemolysis of Blood Agar
Alpha hemolysis
When hemoglobin is converted to methemoglobin by bacteria using hydrogen peroxide or other hemolysins, it results in a brownish or greenish tint.
Beta Hemolysis
Bacteria create a clear zone surrounding colonies by producing hemolysins, such as streptolysin, which lyse red blood cells and break down hemoglobin.
Gamma Hemolysis
Bacteria do not produce hemolysins, which are substances that can cause the lysis, or breaking open, of red blood cells. As a result, there is no lysis of red blood cells and thus no need to change the medium.
Frequently Asked Question
What is blood agar?
Blood agar is an enriched and differential microbiological growth medium containing nutrient-rich base agar and 5% defibrinated blood (usually from sheep, horse, or rabbit). It supports the growth of a wide variety of bacteria and differentiates them based on their hemolytic properties.
What is the purpose of adding blood to the agar?
Adding blood to the agar enriches the medium, providing essential nutrients and growth factors required by fastidious organisms. It also allows for the detection of hemolytic activity, helping in the differentiation and identification of bacteria based on their ability to lyse red blood cells.
Can blood agar be used to grow anaerobic bacteria?
Yes, blood agar can be used to grow anaerobic bacteria, but special conditions are required. The plates must be incubated in an anaerobic environment, such as an anaerobic jar or chamber, to support the growth of anaerobes.
Related Articles

