1. Introduction to Biological Classification
Biological classification is a scientific process through which all living organisms are systematically grouped based on their shared features and natural relationships. This system helps us manage and understand the enormous diversity of life on Earth by organizing species into meaningful groups. Because millions of different species exist, from microscopic bacteria to large animals and plants, classification is essential for making the study of biology organized and manageable. It allows scientists to communicate clearly about organisms, recognize patterns in nature, and discover relationships among different species.
Biological Classification is deeply connected with the fields of taxonomy and systematics, which deal with naming and grouping organisms and understanding their evolutionary histories. In recent times, the Biological classification system has evolved to include three major domains of life that encompass all known organisms based on fundamental differences in their genetic material and cell structure.
Summary of Biological Classification
- Biological classification organizes the vast diversity of life into groups based on shared characteristics and evolutionary relationships.
- It uses a hierarchical system, from broad kingdoms to specific species, to systematically name and categorize organisms.
- This system helps scientists communicate, study biodiversity, and understand how all living beings are connected through evolution.
Table of Contents
2. Three Domains of Life
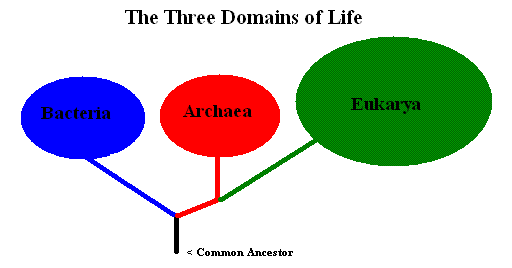
The concept of the three domains of life is a modern and widely accepted way to categorize all living organisms at the broadest level. This system was introduced by scientist Carl Woese after studying the genetic sequences of various microorganisms and discovering that life can be divided into three major groups that are distinct in many ways. These domains are named Archaea, Bacteria, and Eukarya. They differ based on their cellular organization, genetic makeup, and other biological features. Understanding these domains helps us appreciate the vast diversity of life and the evolutionary relationships between different forms of organisms.
2.1 Domain Archaea
The domain Archaea consists of a group of microorganisms that are similar in shape and size to bacteria but are very different at the molecular level. Archaea have unique genetic sequences and biochemical pathways that separate them from bacteria and other life forms. They often live in extreme environments such as hot springs, salt lakes, acidic environments, or even deep underwater vents where very few other organisms can survive. These organisms are known for their ability to endure conditions of extreme temperature, salinity, and acidity. Archaea play important roles in ecosystems, such as producing methane gas in marshes and the digestive tracts of animals. Their study provides insights into early life on Earth and the adaptability of living organisms.
2.2 Domain Bacteria
Domain Bacteria contains what we typically refer to as bacteria, which are found nearly everywhere on Earth. They are unicellular organisms with simple cell structures called prokaryotes, meaning their cells do not have a nucleus or membrane-bound organelles. Bacteria perform many vital ecological functions including decomposing organic matter, recycling nutrients, and helping plants fix nitrogen from the atmosphere. Some bacteria live harmlessly or beneficially in the human body, aiding digestion and protecting against harmful microbes. However, certain bacteria can cause diseases in humans, animals, and plants. Due to their abundance and diverse roles, bacteria are fundamental to life and ecosystems worldwide.
2.3 Domain Eukarya
Domain Eukarya includes all organisms whose cells have a well-defined nucleus enclosed by a membrane, along with other specialized structures called organelles. This domain encompasses a vast range of organisms including animals, plants, fungi, and protists. Eukaryotic organisms can be unicellular or multicellular and show a high level of complexity in structure and function. For example, human beings, trees, mushrooms, and many single-celled algae all belong to this domain. The presence of a nucleus allows eukaryotes to tightly regulate their genetic material and perform complex cellular activities. The evolution of eukaryotes represents a major step in the development of life and biodiversity on Earth.
3. Taxonomy and Systematics
Taxonomy and systematics are scientific disciplines that focus on the identification, naming, classification, and understanding of evolutionary relationships among organisms. They form the foundation of how biologists organize and study the diversity of life. While these fields are closely related, they have distinct goals and methods.
3.1 What is Taxonomy?
Taxonomy is the branch of biology concerned primarily with identifying and naming organisms and grouping them based on shared characteristics. It provides a universal language for biologists across the world to talk about species clearly and consistently, avoiding confusion caused by local or common names. Taxonomy involves the detailed description of species, assigning scientific names, and arranging them into categories or groups according to their similarities and differences. It plays a crucial role in biodiversity studies, conservation efforts, and many applied biological sciences.
3.2 What is Systematics?
Systematics is a broader field that includes taxonomy but focuses mainly on studying the evolutionary relationships between organisms. It attempts to reconstruct the history of life by analyzing characteristics inherited from common ancestors. Systematics uses various types of information including physical traits, genetic sequences, behavior, and ecological data to build evolutionary trees called phylogenies. These trees help visualize how species have diverged from shared ancestors over millions of years. By understanding these relationships, systematics gives insights into the origin of species and the processes driving evolution.
4. Concept of Species
The species is the fundamental unit in biological classification. Understanding what defines a species is essential for organizing life forms and studying biodiversity effectively.
4.1 Definition of Species
The most widely accepted definition of a species is the biological species concept, which states that a species is a group of organisms that can interbreed in nature and produce fertile offspring. Members of a species share a common gene pool and are reproductively isolated from other groups. This concept helps scientists clearly define and distinguish species. However, alternative definitions exist, such as morphological species which classify organisms based on physical appearance, ecological species which consider the role of organisms in their environment, and phylogenetic species which rely on genetic lineage and evolutionary history.
4.2 Importance of Species Concept
The concept of species helps biologists categorize organisms into meaningful groups, which is crucial for conservation, ecological management, and evolutionary biology. By understanding species boundaries, scientists can track biodiversity changes, identify endangered species, and understand how new species arise through the process of speciation. Speciation is the evolutionary process where populations evolve to become distinct species over time, often due to geographical or reproductive isolation.
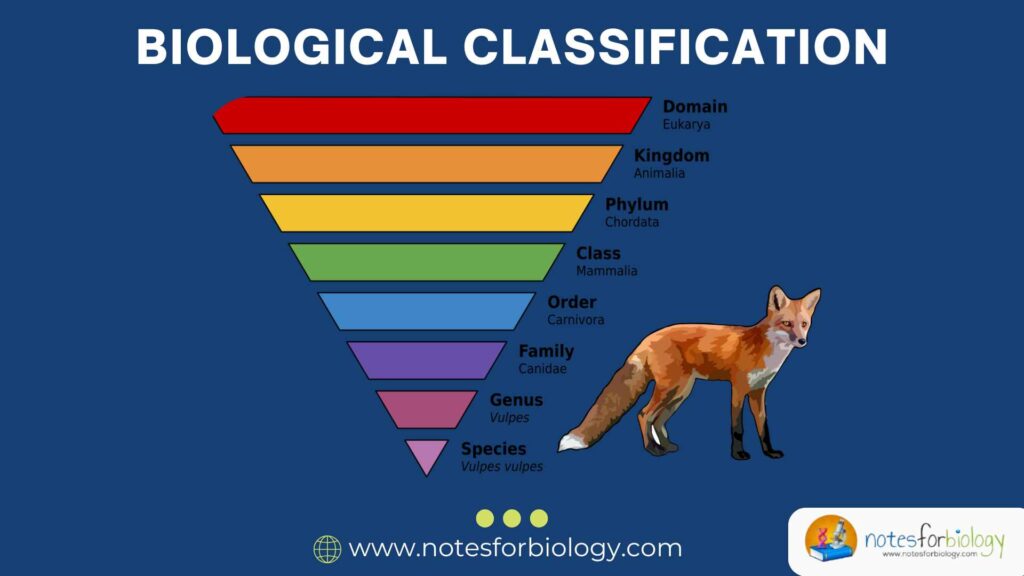
5. Taxonomical Hierarchy
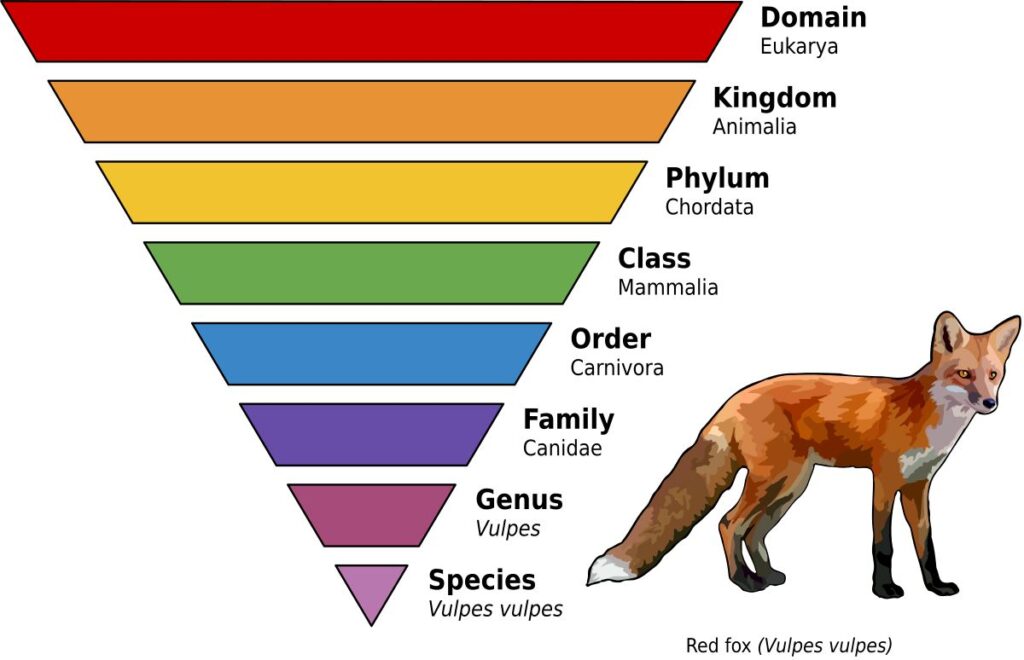
Biological classification arranges organisms into a hierarchical system with multiple ranks that group organisms from very broad categories down to very specific ones. This system is important for organizing the vast number of species into manageable groups.
5.1 Levels of Taxonomic Hierarchy
The hierarchy includes several ranks that represent increasing levels of similarity among organisms. The broadest category is the kingdom, which groups organisms based on very general features such as cell type and mode of nutrition. Below kingdom is the phylum (or division in plants), which groups organisms that share major structural similarities. Classes divide phyla further into more closely related groups. Orders contain families of organisms that are even more alike. Families are made up of related genera, which are groups of closely related species. Finally, species is the most specific rank, identifying individual organisms that can interbreed and share the most characteristics.
5.2 Significance of Hierarchy
The taxonomic hierarchy is significant because it provides an organized framework that reflects the degree of relatedness among organisms. Organisms grouped in the same species share many traits and genetic material, while those in the same genus but different species are slightly less similar. As we move up the hierarchy, organisms share fewer characteristics but are still related at some level. This system helps scientists communicate biological information accurately and helps predict unknown traits of organisms based on their classification.
6. Scientific Naming: Binomial Nomenclature
To avoid confusion caused by different common names in different languages and regions, the binomial nomenclature system was developed. It gives every species a unique, universally accepted scientific name.
6.1 Structure of Scientific Names
In binomial nomenclature, each species is given a name consisting of two parts written in Latin. The first part is the genus name, which identifies the group of closely related species to which the organism belongs. The second part is the species epithet, which identifies the exact species within the genus. Together, these two names uniquely identify a species. For example, Homo sapiens is the scientific name for humans, where Homo is the genus and sapiens is the species.
6.2 Rules for Naming
Scientific names are always written in italics when typed or underlined when handwritten to set them apart from the rest of the text. The genus name is always capitalized, while the species name is written in lowercase letters. This naming system was introduced by Carolus Linnaeus and is used worldwide to ensure that every species has a unique and recognizable name, avoiding confusion and misidentification.
7. Taxonomic Aids
Taxonomic aids are tools and resources that help scientists identify, classify, and study organisms more effectively and accurately.
7.1 Dichotomous Keys
Dichotomous keys are special guides used to identify organisms by choosing between pairs of contrasting traits. They work like a flowchart where each choice leads to another pair of options, gradually narrowing down the possibilities until the organism is identified. These keys are widely used in field biology because they simplify the identification process for scientists and students.
7.2 Herbarium
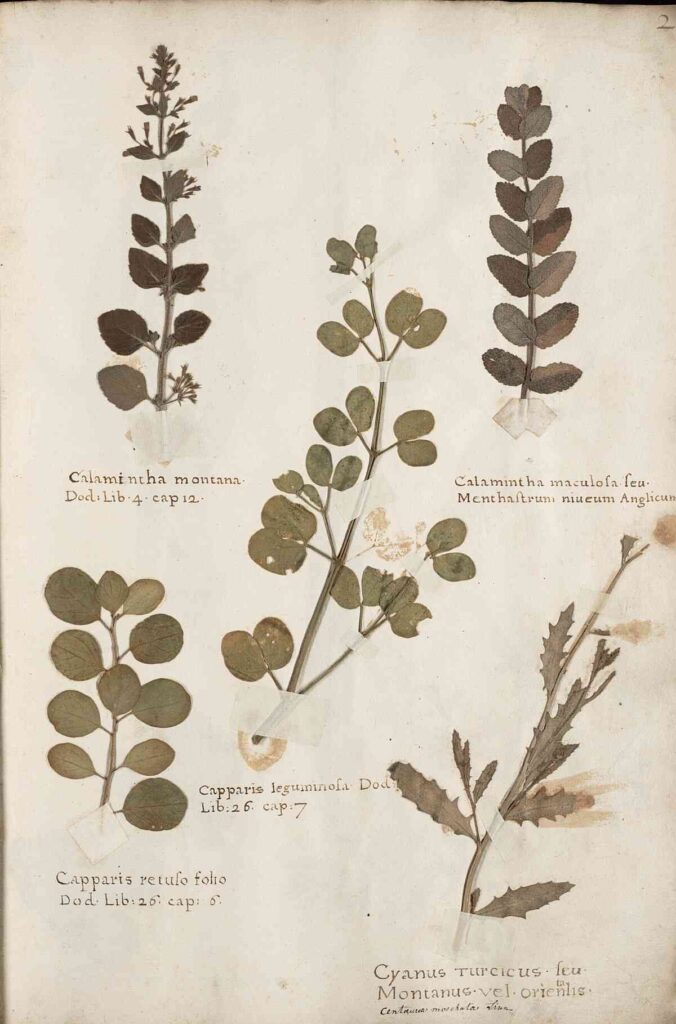

A herbarium is a carefully curated collection of dried and pressed plant specimens mounted on sheets of paper. Each specimen includes detailed information about the plant, such as its scientific name, location, date of collection, and habitat. Herbaria serve as important reference libraries for botanists and researchers, helping in plant identification, comparison, and study of plant diversity over time.
7.3 Museums and Botanical Gardens
Museums preserve animal specimens, fossils, skeletons, and other biological samples that are important for research and education. Botanical gardens and zoological parks maintain live collections of plants and animals in environments that mimic their natural habitats. These institutions play a critical role in conserving biodiversity, supporting research, and raising public awareness about the importance of protecting species and ecosystems.
8. Importance of Taxonomy and Classification
The classification of living organisms is vital beyond just naming species. It helps scientists understand the vast diversity of life on Earth and the evolutionary connections among different organisms. Classification enables communication among scientists globally by providing a standard system to refer to species. It supports various fields such as medicine, agriculture, and conservation biology by predicting characteristics and behavior of organisms based on their classification. It also guides conservation efforts by identifying species that are endangered or threatened and highlighting the relationships between species and their ecosystems.
9. Conclusion
The system of biological classification, which includes the division of life into three domains, the principles of taxonomy and systematics, the concept of species, and the taxonomic hierarchy, provides a comprehensive framework to understand and study the diversity of life. This framework organizes organisms in a way that reflects their natural relationships and evolutionary history, allowing scientists to trace the origins and connections between species. Understanding classification is essential for managing biodiversity, conserving endangered species, and advancing biological research. As science progresses and new technologies such as DNA sequencing become more accessible, our understanding and classification of life continue to improve, helping us protect and appreciate the living world around us.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is biological classification and why is it important?
Biological classification is the system of grouping living organisms based on shared features and evolutionary relationships. It is important because it helps scientists organize the immense diversity of life, making it easier to study, identify, and conserve species.
What are the three domains of life?
The three domains of life are Archaea, Bacteria, and Eukarya. These domains categorize all living organisms based on differences in their cell structure and genetics, forming the broadest classification groups.
What is a species in biological classification?
A species in biological classification is a group of organisms that can interbreed and produce fertile offspring under natural conditions. It is the basic unit of classification representing a distinct group with common characteristics.
Related Articles