What is Biodiversity?

Biodiversity is the range of diverse forms of life that can be found in one place includes fungi, plants, animals, and even microbes like bacteria that make up our natural world. Together, these various species and organisms form ecosystems that support life and preserve equilibrium, much like a complex web.
It speaks of differences between species of plants, animals, and microbes. The quantity of various creatures and their varying frequencies within an ecosystem are considered components of it. It also depicts how creatures are arranged at various levels. Ecological and economic value are attached to it.
Table of Contents
Elements of Biodiversity
The key elements are,
Genetics Diversity
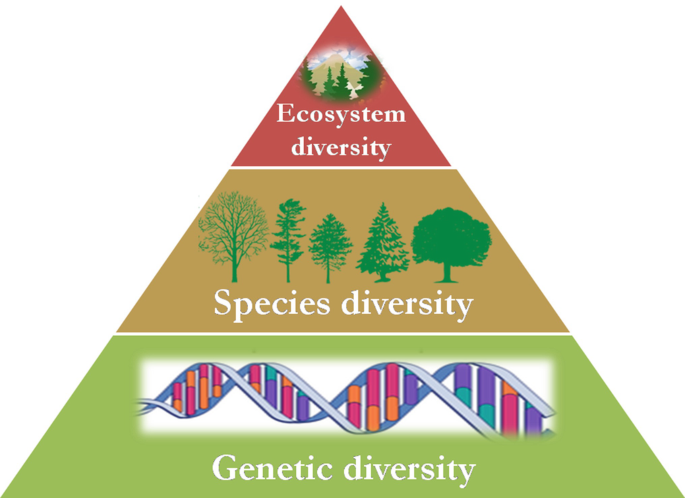
This is a reference to genetic variety within a species.
It is necessary for populations to adjust to shifting environmental conditions and is necessary for long-term survival.
Examples include different dog breeds and variances in the color of a person’s hair and eyes.
Species Diversity
This is a reference to the diversity of species that exist in a given location or on Earth overall.
It comprises the total number of species (species richness) as well as the relative abundance of those species (species evenness).
Examples are the wide variety of animals and plants that can be found in a tropical jungle and the several bird species that live in a particular marsh.
Ecosystems Diversity
This alludes to the diversity of Earth’s ecosystems.
Along with specific physical characteristics like soil type, climate, and geography, every ecosystem has its own distinct collection of creatures and their interactions.
Coral reefs, lakes, rivers, meadows, woodlands, and deserts are a few examples.
Why is Biodiversity important?
Ecosystem Services: It offers vital ecosystem services such as clean water and air, food, pollination, climate regulation, and natural pest control.
Economic Benefits: It forms the basis of numerous industries, such as forestry, agriculture, fisheries, tourism, and pharmaceuticals.
Cultural and Ethical Values: It is extremely significant to many people’s cultural and spiritual beliefs worldwide.
Resilience: Diverse ecosystems are better equipped to tolerate and recover from shocks such as pollution, invasive species, and climate change.
Threats to Biodiversity
Habitat loss and degradation : The main factor causing biological diversity loss is habitat loss and degradation, which is brought on by urbanization, agriculture, and deforestation.
Climate Change: Increasing sea levels, fluctuating temperatures, and extreme weather events damage ecosystems and endanger species.
Pollution: Pollution of the air, water, and soil can destroy habitats and endanger living things.
The decrease and extinction of species can result from overfishing, hunting, and poaching.
Invasive Species :Introduced species have the ability to displace native species and cause havoc on ecosystems.
Protecting Biodiversity

Conservation activities include resource management that is sustainable, the creation of protected areas, and the restoration of degraded environments.
Encouraging actions that satisfy current demands without jeopardizing the capacity of future generations to satisfy their own needs is known as sustainable development.
Spreading knowledge among the general population about the value of biological diversity and the dangers it confronts.
An essential component of the health and wellbeing of the earth is biological diversity. We can guarantee a sustainable and healthy future for everybody by being aware of its significance, the dangers it confronts, and the steps we can take to safeguard it.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQ)
What is Biological diversity?
Biodiversity is the range of diverse forms of life that can be found in one place includes fungi, plants, animals, and even microbes like bacteria that make up our natural world
Why is Biological diversity important?
It is important,
Ecosystem Services: It offers vital ecosystem services such as clean water and air, food, pollination, climate regulation, and natural pest control.
Economic Benefits: It forms the basis of numerous industries, such as forestry, agriculture, fisheries, tourism, and pharmaceuticals.
Cultural and Ethical Values: It is extremely significant to many people’s cultural and spiritual beliefs worldwide.
Resilience: Diverse ecosystems are better equipped to tolerate and recover from shocks such as pollution, invasive species, and climate change.
Related Articles
Spore staining technique: principle, requirements and procedure