What is Streptococcus mutans?
The bacteria streptococcus mutans is a significant cause of tooth decay. A variety of microbiological methods, such as morphological analysis, growth characteristics, and biochemical testing, are needed to identify this bacteria.
One kind of bacteria that is frequently discovered in human mouths is streptococcus mutans. It is recognised as the main cause of dental caries, or tooth decay as it is more widely known. This bacterium can live in the mouth with the closely related species Streptococcus sobrinus: Oral disease is caused by both, and it is frequently not clinically required to spend the money on laboratory tests to distinguish between them. Consequently, they are sometimes referred to as a group, the mutans streptococci, for clinical purposes.
Table of Contents
Biochemical Test of Streptococcus mutans
Expanding Through Selective Media
Tellurite is present in Mitis Salivarius (MS) Agar, which inhibits the development of most streptococci with the exception of S. mutans and S. salivarius. Because of the tellurite reduction, S. mutans forms small, translucent, slightly pitted colonies with a greenish-brown colour.
Blood Agar: S. mutans causes a greenish tint surrounding the colonies by exhibiting alpha-hemolysis on blood agar.
Tests for Sugar Fermentation
Mannitol Fermentation: When mannitol is fermented by S. mutans, acid is produced that lowers pH and turns phenol red from red to yellow.
Fermentation of Sucrose: S. mutans is also capable of fermenting sucrose, yielding both acid and dextran, a sticky polysaccharide that aids in the development of plaque.
Catalase Test
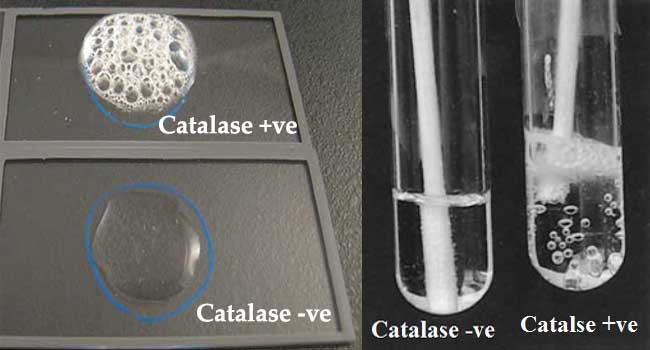
Because S. mutans is catalase negative, it is devoid of the catalase enzyme. Aerobic bacteria have the ability to break down hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen through the enzyme catalase. S. mutans can be distinguished from catalase-positive staphylococci with this test.
Esculin Hydrolysis in Bile

Other streptococci, such as S. faecalis, are positive for bile esculin hydrolysis, whereas S. mutans is negative. In this test, esculin is broken down in the presence of bile, forming a dark brown precipitate as a result.
Sensitivity to Bacitracin
Whereas other streptococci, such as S. pyogenes, are resistant to bacitracin, S. mutans is susceptible to it. For this test, an agar plate that has been inoculated with the bacteria is covered with a bacitracin disc. The disc’s surrounding zone of inhibition is present .
The sensitivity of optochin
Optochin does not affect S. mutans, however S. pneumoniae is vulnerable to it. An optochin disc is used in this test, and a zone of inhibition on the agar plate signifies susceptibility.
Molecular Methods
S. mutans can be precisely identified using more modern methods like DNA sequencing and polymerase chain reaction (PCR). These techniques provide a very precise diagnosis by focusing on particular DNA sequences that are exclusive to S. mutans.
It’s crucial to stress that these assessments aren’t always carried out one-on-one. A multitude of tests are frequently run in tandem to obtain a thorough and trustworthy identification of S. mutans.
Importance of Biochemical Test of Streptococcus mutans
The following are critical outcomes of these tests:
Precise identification: They aid in distinguishing S. mutans from other species of streptococci, facilitating precise diagnosis and management.
Comprehending virulence factors: The examinations offer valuable understanding of the metabolic processes, like acid generation and biofilm development, that underpin S. mutans’ capacity to induce dental caries.
Creating targeted therapies: Creating particular medications and treatments to fight dental caries requires an understanding of the biochemical characteristics of S. mutans.
Through an understanding of S. mutans’s biochemical properties, scientists and medical professionals can more effectively comprehend and manage the harm this common oral bacterium poses.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQ)
What is Streptococcus mutans?
The bacteria streptococcus mutans is a significant cause of tooth decay. A variety of microbiological methods, such as morphological analysis, growth characteristics, and biochemical testing, are needed to identify this bacteria.
What are the importance of Biochemical test of Streptococcus mutans?
The importance of Biochemical test of Streptococcus mutans are
They aid in distinguishing S. mutans from other species of streptococci, facilitating precise diagnosis and management.
The examinations offer valuable understanding of the metabolic processes, like acid generation and biofilm development, that underpin S. mutans’ capacity to induce dental caries.
Creating particular medications and treatments to fight dental caries requires an understanding of the biochemical characteristics of S. mutans.
What is Catalase Test ?
S. mutans is catalase negative, it is devoid of the catalase enzyme. Aerobic bacteria have the ability to break down hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen through the enzyme catalase. S. mutans can be distinguished from catalase-positive staphylococci with this test.
Related Articles