What is Staphylococcus aureus ?

Many people frequently have Staphylococcus aureus, also known as “Staph aureus,” on their skin and in their noses. For the most part, it’s benign and even helpful, acting as a check on other dangerous germs. It can, however, also result in a variety of infections, ranging from small skin irritations to serious illnesses.
One species of bacteria found in the Staphylococcus family is Staphylococcus aureus. It is thought to be one of the most significant pathogens that affect people and, in terms of disease-causing potential, the most deadly member of the Staphylococcus genus. A major human pathogen with a variety of clinical presentations, Staphylococcus aureus presents a substantial challenge in healthcare environments due to its propensity to acquire drug resistance.
Table of Contents
Biochemical Test of Staphylococcus aureus
Often found on the skin and in the nose, Staphylococcus aureus is a common bacteria that can cause a variety of diseases. Accurately diagnosing it is essential for successful treatment. Tests using biochemistry are crucial in identifying it. Here are a few tests that are often used:
Catalase Test
Concept: Identifies the existence of the catalase enzyme, which converts hydrogen peroxide into oxygen and water.
Procedure: A bacterial colony is given a drop of hydrogen peroxide.
Outcome: Positive reaction: The production of oxygen bubbles suggests the presence of catalase. Negative response: The lack of bubbles suggests that catalase is not present.
Relevance: S. aureus exhibits catalase positivity. It can be distinguished from other catalase-negative bacteria, such as Streptococcus, using this test.
Coagulase Test
Principle: Identifies the presence of the enzyme coagulase, which is responsible for plasma coagulation.
Procedure: Rabbit plasma is combined with a sample of the bacterium.
Outcome: Positive reaction: The presence of coagulase is shown by the formation of a clot at 37°C within 4 hours. Reaction negative: No clot formed.
Significance: Generally speaking, staphylococcal species are coagulase-negative, however S. aureus is coagulase-positive.
Mannitol Salt Agar(MSA)
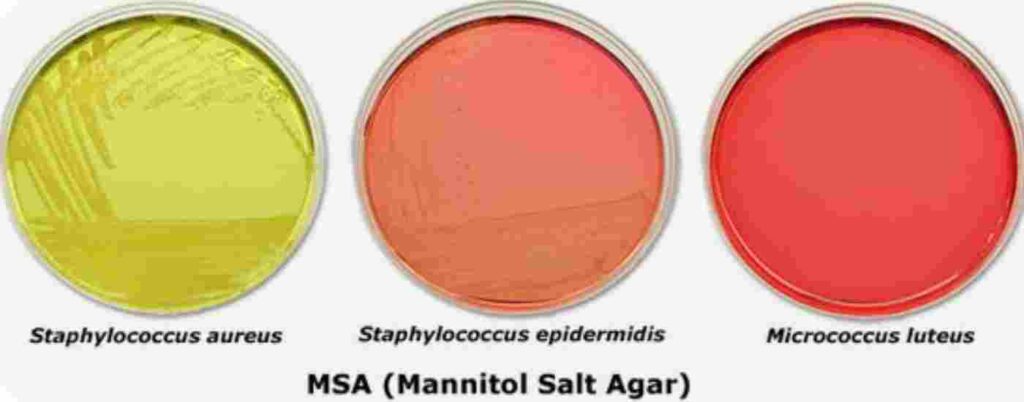
Principle: S. aureus is distinguished from other staphylococcal species by its capacity to ferment mannitol and withstand elevated salinity levels.
Method: On MSA, a selective and differential medium with 7.5% NaCl and mannitol, bacteria are injected.
Result Positive reaction: Mannitol fermentation and acid generation surrounding the colonies cause a yellow halo. Adverse reaction: The absence of colour change signifies the absence of mannitol fermentation.
Significance: S. aureus creates acid by fermenting mannitol, which causes yellow colonies.
The DNase Test
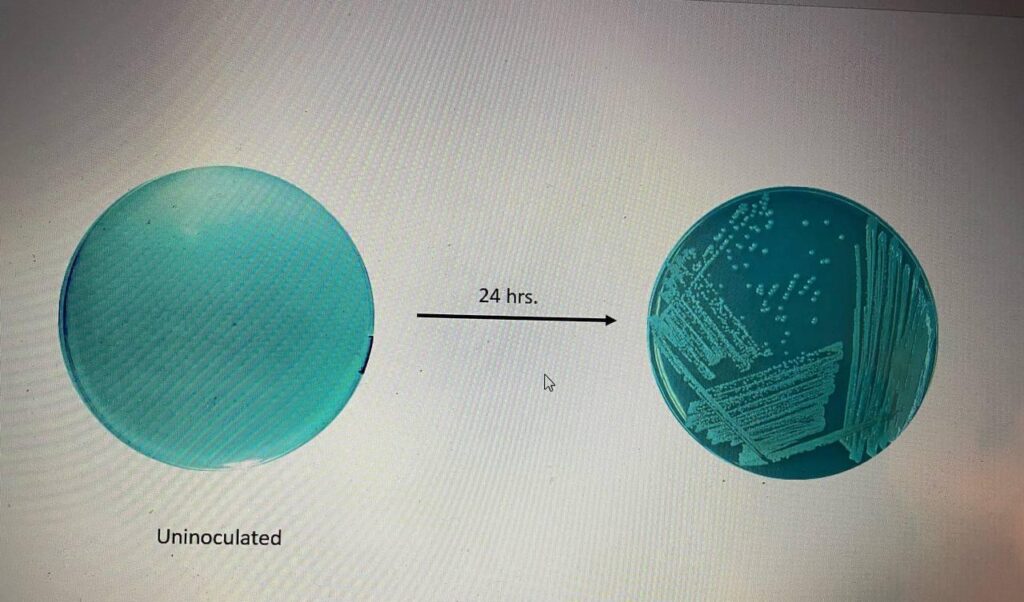

The basic idea is to identify the synthesis of the enzyme DNase, which breaks down DNA.
Method: A DNA-containing media is used to inoculate bacteria.
Result Positive response: The colonies’ clear halo is a result of DNA deterioration. Reaction negatively: Hardly a halo.
Significance: DNase-positive S. aureus is frequently found.
Additional Tests
Hemolysis
On blood agar plates, S. aureus can generate beta-hemolysis, which is a total lysis of red blood cells.
Pigmentation
Yellow pigments are frequently produced by S. aureus.
Novobiocin Sensitivity
Novobiocin, an antibiotic, typically causes S. aureus to become resistant.
Note
To obtain a thorough identification of S. aureus, biochemical assays are typically run in tandem.
It’s crucial to keep in mind that qualified experts should always identify germs in a lab setting using the proper tools and procedures.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQ)
What is the concept of Catalase Test ?
The concept of Catalase Test is Identifies the existence of the catalase enzyme, which converts hydrogen peroxide into oxygen and water.
What is Staphylococcus aureus ?
Many people frequently have Staphylococcus aureus, also known as “Staph aureus,” on their skin and in their noses. For the most part, it’s benign and even helpful, acting as a check on other dangerous germs. It can, however, also result in a variety of infections, ranging from small skin irritations to serious illnesses.
What is the result of The DNase Test ?
The result of The DNase Test is Positive response, The colonies’ clear halo is a result of DNA deterioration. Reaction negatively : Hardly a halo.
Related Articles