What is Citrobacter freundii ?
Citrobacter freundii is a facultative anaerobic, gram-negative bacterium that is frequently found in both the environment and the human intestine is called Citrobacter freundii. Despite not being regarded as a pathogen in most cases, it can infect people who are immunocompromised or have underlying medical issues. It is distinguished from other Enterobacteriaceae by a number of biochemical tests.
Table of Contents
One of the 13 known species of facultative anaerobic Gram-negative bacteria in the Enterobacteriaceae family is Citrobacter freundii. These bacteria are shaped like rods, usually ranging in length from 1 to 5 μm. Although many non-motile taxa lack flagella, the majority of C. freundii cells do.
Biochemical test of Citrobacter freundii
Several biochemical tests are utilised to identify Citrobacter freundii. These include the following:
Production of Indoles
Result: Negative
Process: Tryptophan is broken down to create indole. To do this test, inoculate a broth medium with tryptophan, then let it sit for a while. A few drops of Kovac’s reagent are applied following incubation. A crimson ring forms on top of the broth, signifying a successful outcome.
Methyl Red Test

Result: Positive
Method: This test assesses the bacteria’s capacity to ferment glucose to create mixed acids. The broth is supplemented with a few drops of methyl red reagent following inoculation and incubation. A positive outcome is denoted by the colour red, whereas a poor outcome is signified by the colour yellow.
Voges-Proskauer (VP) Test
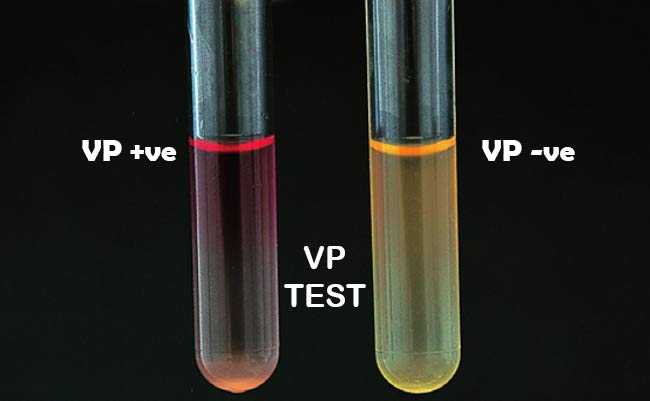

Result: Negative
Method: This test looks for acetoin, a byproduct of the fermentation of glucose. Potassium hydroxide and alpha-naphthol, or VP reagents, are added to the broth after incubation. A pink or red colour denotes a happy outcome, while a yellow colour denotes a poor outcome.
Test of Citrate Utilization
Result: Positive
Method: This test assesses the bacteria’s capacity to use citrate as their only carbon source. A citrate medium with bromthymol blue as a pH indicator is used to inoculate the bacteria. A shift in colour from green to blue, caused by the bacteria’s utilisation of citrate and production of alkaline byproducts, signifies a favourable outcome.
Production of H2S
Outcome: Generally
Positive Method: This test establishes whether the bacteria can synthesise hydrogen sulphide (H2S) from amino acids that contain sulphur. The bacteria are injected into a medium that contains a substance that contains sulphur. A black precipitate caused by ferrous sulphide production indicates a favourable outcome.
Test for Urease
Results: Negative
Method: This test assesses the bacteria’s capacity to hydrolyze urea into carbon dioxide and ammonia. A medium containing urea and a pH indicator is infected with the bacteria. A shift in colour caused by ammonia production indicates a successful outcome.
Ornithine Decarboxylase Test
Procedure: This test assesses the bacteria’s capacity to decarboxylate ornithine; the result is positive. A medium containing ornithine and a pH indicator is used to inoculate the bacteria. A colour shift brought on by putrescine production signifies a successful outcome.
Decarboxylase Test for Lysine
Usually Positive Outcome,This test assesses the bacteria’s capacity to decarboxylate lysine. The bacteria are added to a medium that has lysine and a pH indicator in it. A colour shift brought on by the cadaverine production signifies a successful outcome.
Test of Motility
Result: Positive Method: The mobility of the bacteria is assessed in this test. The medium is semi-solid, and the bacteria are added. A zone of turbidity emanating from the inoculation site indicates a positive outcome.
Important Information
Citrobacter freundii can be identified using the assays mentioned above, but a thorough biochemical profile must be carried out for a precise identification.Test findings for certain strains may vary.For confirmation and additional investigation, it is usually best to speak with a laboratory that specialises in bacterial identification.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQ)
What is Citrobacter freundii ?
Citrobacter freundii is a facultative anaerobic, gram-negative bacterium that is frequently found in both the environment and the human intestine is called Citrobacter freundii.
What are the Biochemical test of Citrobacter freundii ?
The Biochemical test of Citrobacter freundii are
Production of Indoles
Methyl Red Test
Voges-Proskauer (VP) Test
Test of Motility
Decarboxylase Test for Lysine
Write about Methyl Red Test ?
Result: Positive
Method: This test assesses the bacteria’s capacity to ferment glucose to create mixed acids. The broth is supplemented with a few drops of methyl red reagent following inoculation and incubation. A positive outcome is denoted by the colour red, whereas a poor outcome is signified by the colour yellow.
Related Articles