Bacillus cereus is a Gram-positive, rod-shaped, facultatively anaerobic, motile bacterium well known for its capacity to produce heat-resistant endospores. It is widely distributed in soil, food, and the environment. B. cereus is a significant disease and spoiling bacterium in food products. It is capable of causing both foodborne diseases and opportunistic infections in people.
Table of Contents
What is Bacillus cereus?
Bacillus cereus is a Gram-positive, rod-shaped bacteria that is extensively found in nature. It is an important species because of its involvement in foodborne illnesses and capacity to induce opportunistic infections in people. Bacillus cereus is a Gram-positive, rod-shaped, facultatively anaerobic, motile bacterium well known for its capacity to produce heat-resistant endospores. It is widely distributed in soil, food, and the environment. B. cereus is a significant disease and spoiling bacterium in food products. It is capable of causing both foodborne diseases and opportunistic infections in people.
Biochemical Test of Bacillus cereus
Gram staining
Definition: A staining technique that differentiates bacteria depending on the structure of their cell walls.
B. cereus appears as a purple (Gram-positive) rod-shaped bacteria.
Endospore Staining
Definition: A staining method for detecting endospores in bacteria.
B. cereus. Endospores stain green, whereas vegetative cells stain red/pink
Catalase Test
Definition: A test for the presence of the enzyme catalase, which converts hydrogen peroxide to water and oxygen.
B. cereus. The application of hydrogen peroxide produced a positive result, as seen by bubbling.
Hemolysis of Blood Agar
Definition: A test to determine bacteria’s ability to lyse red blood cells.
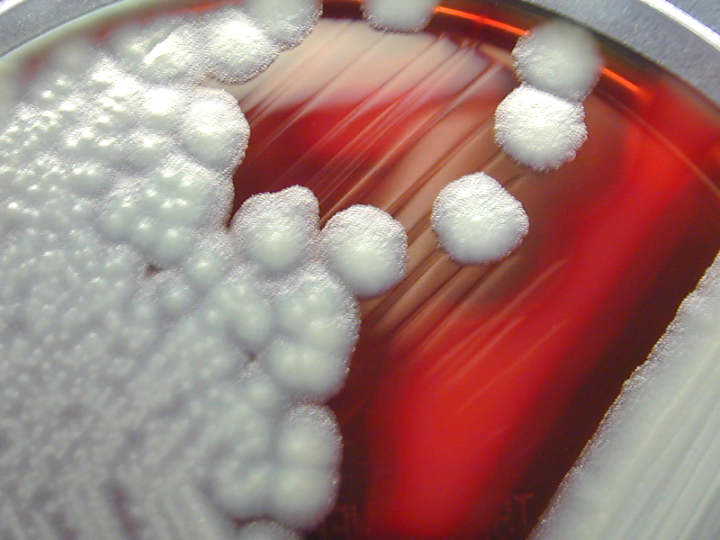
B. cereus. The result is beta-hemolysis, which is defined by a clear zone around the colonies on blood agar.
Motility Test
Definition: A test that determines if germs can migrate.
B. cereus. Positive for motility, as evidenced by the spread of growth from the stab line in semi-solid agar or vigorous movement in a hanging drop preparation.
Lecithinase Production
Definition: A test to detect the enzyme lecithinase, which degrades lecithin.
B. cereus. The result was positive, as demonstrated by an opaque precipitate around colonies on egg yolk agar.
Starch Hydrolysis Test
Definition: A test to assess whether bacteria can hydrolyze starch using the enzyme amylase.
B. cereus. Result: Positive, as evidenced by a clear zone surrounding the colonies following iodine application to starch agar.
Voges-Proskauer (VP) Test
Definition: A test that detects the formation of acetoin during glucose fermentation.
B. cereus. The result is positive, as demonstrated by the red hue after adding Barritt’s reagents.
Nitrate Reduction Test
Definition: A test that determines bacteria’s capacity to convert nitrate to nitrite or other nitrogen molecules.
B. cereus. The result is positive, evidenced by a red hue after adding nitrate reagents, or no color change after adding zinc.
Citrate Utilization Test
Definition: A test that determines bacteria’s capacity to use citrate as their only carbon source.
B. cereus. Positive, as evidenced by a change in color from green to blue on Simmons citrate agar.
Manitol Fermentation Test
Definition: A test to detect bacteria’s capacity to ferment mannitol.
B. cereus. Result: negative, indicated by no color change (remaining red) in mannitol salt agar or phenol red mannitol broth.
Frequently Asked Question
What is Bacillus cereus?
Bacillus cereus is a Gram-positive, rod-shaped bacteria that is extensively found in nature. It is an important species because of its involvement in foodborne illnesses and capacity to induce opportunistic infections in people.
What are the test of Bacillus cereus?
The test of Bacillus cereus are :
1. Gram staining
2. Endospore Staining
3. Catalase Test
4. Hemolysis of Blood Agar
5. Motility Test
6. Lecithinase Production
7. Starch Hydrolysis Test
Related Article