B cells vs T cells are two distinct types of lymphocytes that play pivotal roles in the adaptive immune response, collectively orchestrating the body’s defense against pathogens. Originating from the bone marrow, B cells mature and differentiate therein, whereas T cells undergo maturation in the thymus gland, earning them their respective names.
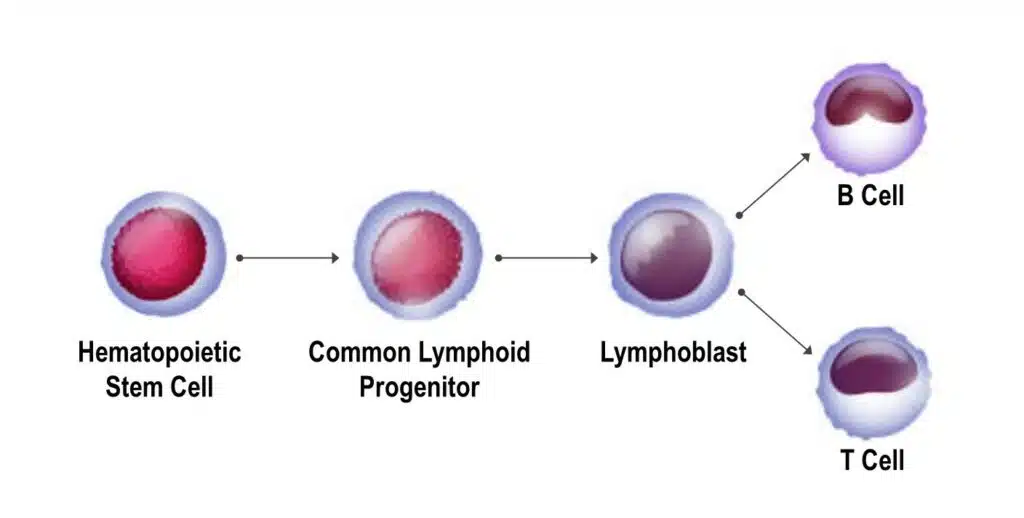
Table of Contents
B Cells vs T Cells
B Cells
One subset of white blood cells called B cells, or B lymphocytes, is essential to the adaptive immune system. Their main job is to produce antibodies, which are proteins that can identify and neutralize harmful substances including viruses, bacteria, and poison.
T Cells
T lymphocytes, another name for T cells, are a subset of white blood cells that are essential to the adaptive immune response. They are named “T” cells because they are made in the bone marrow and develop in the thymus gland.
17 Key Differences Between B Cells vs T Cells
| S.N | T Cells | B Cells |
| 1. | T Cells originate in the bone marrow and mature in the thymus. | B Cells originate and mature in the bone marrow. |
| 2. | Mature cells occur inside the lymph nodes. | Mature cells occur outside the lymph nodes. |
| 3. | T Cells bear TCR receptor. | B Cells bear BCR receptor |
| 4. | Recognize viral antigens on the outside of the infected cells | Recognize antigens on the surface of bacteria and viruses |
| 5. | T Cells have long lifespans. | B Cells have shorter life spans. |
| 6. | Lack surface antigens | Have surface antigens |
| 7. | T Cells Secrete lymphokines | B Cells Secrete antibodies |
| 8. | T Cells involved in the cell mediated immunity | B Cells involved in humoral or antibody-mediated immunity |
| 9. | 80% of the blood are lymphocytes are T cells | 20% of the blood are lymphocytes are B cells |
| 10. | Have three types: helper T cells, cytotoxic T cells, and suppressor T cells | Have two types ,they are plasma cells and memory cells |
| 11. | Move to the site of infection | Does not move to the side of infection |
| 12. | Act against tumor cell or transplants | Do not act against tumor cells or transplants |
| 13. | Have an inhibitory effect on the immune system | Do not have any inhibitory effect on the immunes system |
| 14. | Defend against pathogens including viruses, protists, and fungi that enter the cells in the body. | Defend against bacteria and viruses in the bloodstream or lymph |
| 15. | Primary role in cell mediated | Primary role in humoral immunity |
| 16. | Examples of T Cells are Helper T cells, Cytotoxic T cells,.. | Example of B Cells are Plasma Cells , Plasma Cells,….. |
| 17. | T Cells are effective against intracellular pathogens, such as viruses and intracellular bacteria. | B Cells are effective against extracellular pathogens, such as bacteria and toxins. |
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQ)
What do you mean by B Cells ?
One subset of white blood cells called B cells, or B lymphocytes, is essential to the adaptive immune system. Their main job is to produce antibodies, which are proteins that can identify and neutralize harmful substances including viruses, bacteria, and poison.
What do you mean by T Cells?
T lymphocytes, another name for T cells, are a subset of white blood cells that are essential to the adaptive immune response. They are named “T” cells because they are made in the bone marrow and develop in the thymus gland.
What are two distinct types of lymphocytes ?
The two distinct types of lymphocytes are B Cells vs T Cells.
Related Articles