Aspergillus flavus is a species of fungus belonging to the genus Aspergillus. It is widely known for its ability to produce aflatoxins, which are highly toxic and carcinogenic secondary metabolites. This fungus can infect both plants and animals, including humans, and is commonly found in soil, decaying vegetation, grains, and nuts. One species of fungus in the Aspergillus genus is Aspergillus flavus. It is well-known for its capacity to create aflatoxins, which are strong poisons and carcinogens. This is a thorough synopsis of Aspergillus flavus.
Table of Contents
Aspergillus flavus
Classification
Kingdom: Fungi
Phylum: Ascomycota
Class: Eurotiomycetes
Order: Eurotiales
Family: Trichocomaceae
Genus: Aspergillus
Species: A. flavus
Key Characteristics
Morphology
Hyphae: The fungus possesses translucent, hyaline (cross-walled) hyphae.
Conidiophores: Stems that stand upright and are unbranched, ending in a vesicle coated in phialides that give rise to conidia.
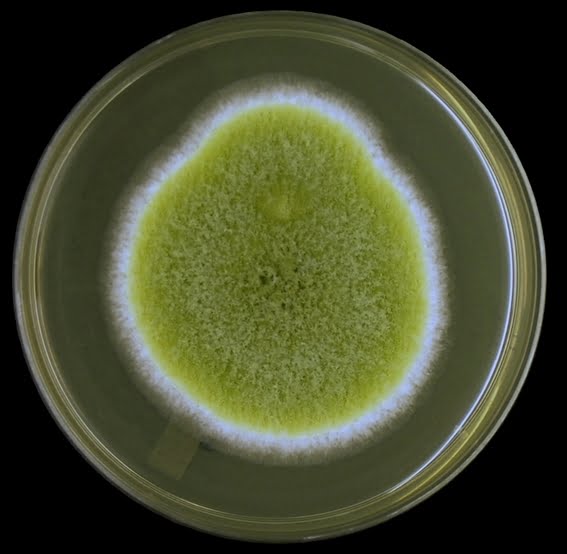
Conidia: The round, greenish-yellow spores that give colonies their distinctive powdery look.
Habitat
Natural Habitat: Decomposing vegetation, grains, seeds, and soil are frequently home to A. flavus. It grows best in warm, humid climates.
Ecological Role : Its role in the environment is that of a saprophyte, breaking down organic matter and assisting in the cycling of nutrients.
Pathogenicity
Human Health
- Aspergillosis can be brought on by A. flavus, particularly in people with weakened immune systems. This covers cutaneous aspergillosis, allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis, and invasive aspergillosis.
- Symptoms include fever, chest pain, respiratory problems, and, in extreme situations, potentially fatal systemic infections.
Plant Pathogen
Crops Affected: Corn, peanuts, cottonseed, and tree nuts.
Disease: Causes ear rot in corn and can infect seeds, leading to pre-harvest and post-harvest contamination.
Toxin Production
Disease: Causes ear rot in corn and can infect seeds, leading to pre-harvest and post-harvest contamination.
Aflatoxins: One of the most dangerous known naturally occurring carcinogens is aflatoxins, which are produced by A. flavus. The two most prevalent forms of aflatoxins that this fungus produces are B1 and B2.
Effect on Health: Acute aflatoxicosis, immunological suppression, and liver cancer can result from eating food infected with aflatoxin.
Regulation: To reduce aflatoxin levels in food and feed, several nations have strict laws and monitoring in place.
Industrial and Environmental Impact
Food Spoilage: A. flavus, especially in stored grains and nuts, is a major source of food spoilage.
Biotechnology: In biotechnology, some strains are utilized to produce organic acids and enzymes.
Control and Prevention
Agricultural Practices
Crop rotation: Assists in lowering A. flavus’s soil inoculum.
Resistant Varieties: Crop cultivars that are resistant to fungus infestation should be developed and planted.
Biocontrol Agents: Utilizing non-toxic strains of A. flavus to outcompete and suppress the number of toxic strains is known as biocontrol agentry.
Post-Harvest Management
- Proper Drying and Storage: Ensuring that crops are sufficiently dried and kept in an environment that inhibits the establishment of fungi is known as proper drying and storage.
- Frequent surveillance: Examining food items for aflatoxin contamination.
Health Measures
Protective gear: To avoid spore inhalation, personnel handling contaminated materials should wear it.
Medical Care: Aspergillosis should be treated with antifungal drugs as soon as possible.
Conclusion
Due to its twin roles as a pathogen and a generator of toxins, Aspergillus flavus is an important fungus. Because of its effects on agriculture, human health, and food safety, it must be carefully monitored and managed to lessen its negative consequences. Its biology, ecology, and growth-promoting environments may all be understood to assist create efficient control measures.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQ)
Define Aspergillus flavus ?
Aspergillus flavus is a species of fungus belonging to the genus Aspergillus. It is widely known for its ability to produce aflatoxins, which are highly toxic and carcinogenic secondary metabolites.
In which family Aspergillus flavus belongs to?
Aspergillus flavus belongs to Trichocomaceae.
Define Aflatoxins ?
One of the most dangerous known naturally occurring carcinogens is aflatoxins, which are produced by Aspergillus flavus.
Define Conidia ?
The round, greenish-yellow spores that give colonies their distinctive powdery look.
Related Article