What is Arboreal?

“Arboreal” describes anything having to do with trees or living among trees. It can refer to any living entity related to tree environments, including plants that grow on trees and animals that reside in them. The phrase can also be used to describe traits or adaptations unique to organisms that live in trees.
Table of Contents
Arboreal Definition
Anything having to do with trees is considered arboreal. Everything that is considered “arboreal” includes the creatures that live there as well as any architecture or chandeliers that have a branching shape akin to a tree. The word “arboreus” is derived from the Latin and means “pertaining to or relating to trees.” It particularly refers to living things that move within or around trees in a biological environment.
Biomechanics of Trees

The structure and mechanical operation of trees are studied in the field of biomechanics. Trees are amazing creatures that have developed a variety of adaptations to sustain their enormous growth, endure environmental stress, and move sugars, nutrients, and water through their structures with efficiency. The following are some essential elements of tree biomechanics:
Trunk and Branch Architecture
Trees are supported and stabilized by their main trunk. Extending from the trunk are branches that sustain the structure and increase the surface area available for photosynthesis. The distribution of weight and wind resistance are influenced by the angle and arrangement of branches.
Wood Formation
Wood is made by trees and is mainly made up of cellulose fibers that are encased in lignin. Trees can grow tall because of the structural support that wood gives them. The densities and compositions of the wood in different tree species affect the flexibility and strength of the wood.
Root Systems

Trees are anchored in the earth by their roots, which also take up water and nutrients from the surrounding soil. Different tree species have different root system structures and depths, which are governed by things like water availability and soil type. While some trees have deep taproots, others have shallow, spreading roots.
Flexibility and Elasticity
Trees are able to bend in reaction to wind and other external pressures because of their elasticity and flexibility. Because of their flexibility, trees can sway without falling over. This helps minimize breaking.
Bark
Trees are protected from physical harm, diseases, and high temperatures by their bark, which acts as an exterior covering. The thickness and texture of bark can range significantly between different types of trees.
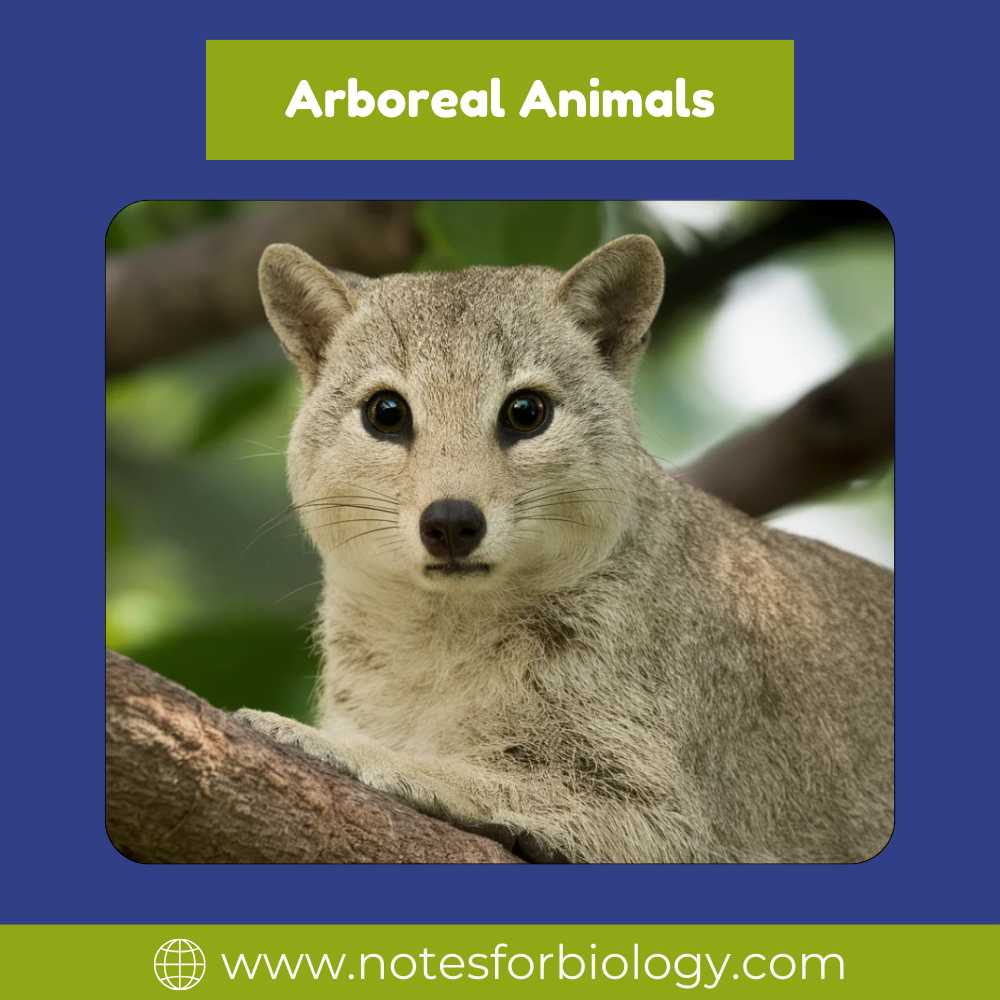
Arboreal Adaptions
The unique characteristics and behaviors that allow animals to flourish in situations where trees are present are known as arboreal adaptations. Although these adaptations differ greatly between species, they usually fall into a few groups:
Appendages and Limbs
A large number of arboreal creatures possess appendages or limbs that are designed to allow them to grip, cling, or climb branches. These could be prehensile tails, opposable thumbs, or unique feet with sticky pads or sharp claws.
Body Type and Size
To help them glide among the branches, arboreal creatures frequently have streamlined or elongated bodies. Certain species minimize the pressure on branches by being small and light, while others have flattened bodies to lessen wind resistance.
Sensory Adaptations
In order to traverse their three-dimensional environment, arboreal animals could possess specialised senses. This could be sensitive touch receptors in their hands or feet, keen hearing to identify predators or prey, or improved vision for depth perception.
Coloration & Camouflage
Many arboreal creatures have developed patterns and colors that assist them blend in with their environment and reduce their visibility to predators and prey.
Dietary Adaptations
Depending on the resources in their environment, arboreal animals may have unique diets. While some species are carnivores or omnivores and graze on insects, birds, or small mammals, others are herbivores and eat leaves, fruits, or flowers.
In general, arboreal adaptations show the variety of methods that animals have developed to take advantage of the chances and resources that tree habitats offer. Because of these adaptations, which are necessary for surviving in these harsh settings, arboreal species have flourished in forests and jungles all over the world.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the Arboreal Adaptions?
IT describes anything having to do with trees or living among trees. It can refer to any living entity related to tree environments, including plants that grow on trees and animals that reside in them. The phrase can also be used to describe traits or adaptations unique to organisms that live in trees.
What do you mean by Biomechanics of Trees ?
The structure and mechanical operation of trees are studied in the field of biomechanics. Trees are amazing creatures that have developed a variety of adaptations to sustain their enormous growth, endure environmental stress, and move sugars, nutrients, and water through their structures with efficiency.
What are the Arboreal Adaptions?
The Arboreal Adaptions are
1.Appendages and Limbs
2.Body Type and size
3.Dietary Adaptations
Related Articles