Amies transport medium is a crucial tool in healthcare for preserving and transporting clinical specimens, especially swabs, to laboratories for microbial testing. It ensures that microorganisms like bacteria remain alive during transit, enabling accurate diagnosis. Developed by J.R. Amies in 1967, this medium enhanced previous versions by offering better preservation for delicate pathogens. In this summary, we’ll explain the composition, how it’s prepared, and its uses in a clear and easy-to-understand way.

Table of Contents
Composition of Amies Transport Medium
The components of Amies transport medium are carefully selected to keep bacteria alive without encouraging their growth. These include:
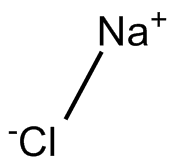
Sodium Chloride (NaCl): This helps maintain the right balance of water in bacterial cells, preventing them from shrinking or swelling.
Potassium Chloride (KCl): Similar to sodium chloride, it contributes to the stability of cells by maintaining ionic balance.
Calcium Chloride (CaCl2): Calcium ions from this ingredient help stabilize bacterial cell membranes, aiding in their survival.
Magnesium Chloride (MgCl2): Magnesium ions support the stability of bacterial enzymes and structures, ensuring better preservation.
Disodium Hydrogen Phosphate (Na2HPO4): This acts as a buffer, maintaining a stable pH to prevent the medium from becoming too acidic or alkaline, which could harm the sample.
Sodium Thioglycolate: This reduces the oxygen levels in the medium, creating a suitable environment for anaerobic bacteria (those that grow in low oxygen conditions).
Charcoal: In some versions of Amies medium, charcoal is added to neutralize toxic substances that could harm the bacteria.
Agar: Provides a semi-solid structure that holds the sample in place while keeping it moist during transport.
Preparation of Amies Transport Medium
The preparation of Amies transport medium is relatively simple and follows these steps:
Collecting Ingredients: The necessary salts and buffers like sodium chloride, potassium chloride, calcium chloride, magnesium chloride, disodium hydrogen phosphate, and sodium thioglycolate are gathered. If charcoal is used, it is added at this stage.
Dissolving: The ingredients are mixed with distilled water in the right proportions.
pH Adjustment: The solution’s pH is adjusted to around 7.2, which ensures the environment is neutral and safe for the microorganisms.
Adding Agar: Once the solution is prepared and the pH is corrected, agar is added to create the semi-solid consistency.
Sterilization: The mixture is sterilized, often using an autoclave (a machine that uses high-pressure steam) to kill any unwanted organisms that could contaminate the medium.
Storage: After cooling, the medium is poured into sterile tubes and sealed for future use. These tubes can be stored at room temperature until needed.
Uses of Amies Transport Medium
Collecting Microbial Samples
Amies medium is primarily used for transporting swabs from clinical samples. This includes specimens from areas like the throat, nose, wounds, and urethra, where the preservation of bacteria is crucial.
Maintaining Bacterial Viability
The primary role of Amies medium is to keep bacteria alive without allowing them to multiply, which is especially important for delicate organisms such as Neisseria gonorrhoeae (causing gonorrhea) and Haemophilus influenzae.
Public Health Investigations
The medium is used extensively in public health to collect samples during outbreak investigations. Whether it’s tracking down sources of infections like Staphylococcus aureus (staph infections) or more severe diseases like meningitis, Amies medium ensures the samples remain viable until they can be tested in the lab.
Veterinary Applications
In animal health, this medium is used to transport samples for the diagnosis of diseases in animals, making it a vital tool for veterinarians.
Infection Control
Hospitals and clinics rely on Amies medium to transport swab samples from patients with suspected bacterial infections for testing. This allows for accurate identification of the bacteria involved and timely treatment.
Conclusion
Amies transport medium is indispensable in preserving the viability of bacteria in clinical samples during transportation. Its carefully balanced composition ensures that bacteria stay alive without growing, making it perfect for transporting sensitive microorganisms to laboratories for analysis. Whether in human or veterinary medicine, public health, or infection control, Amies medium plays a crucial role in enabling accurate diagnostics and improving health outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQ)
What is Amies transport medium?
Amies transport medium is a crucial tool in healthcare for preserving and transporting clinical specimens, especially swabs, to laboratories for microbial testing. It ensures that microorganisms like bacteria remain alive during transit, enabling accurate diagnosis.
What is Staphylococcus aureus?
Gram-positive, spherically-shaped, Bacillota-affiliated Staphylococcus aureus is a common component of the body’s microbiota and is often found on the skin and in the upper respiratory system.
Realated Articles