What is Alpha Oxidation?
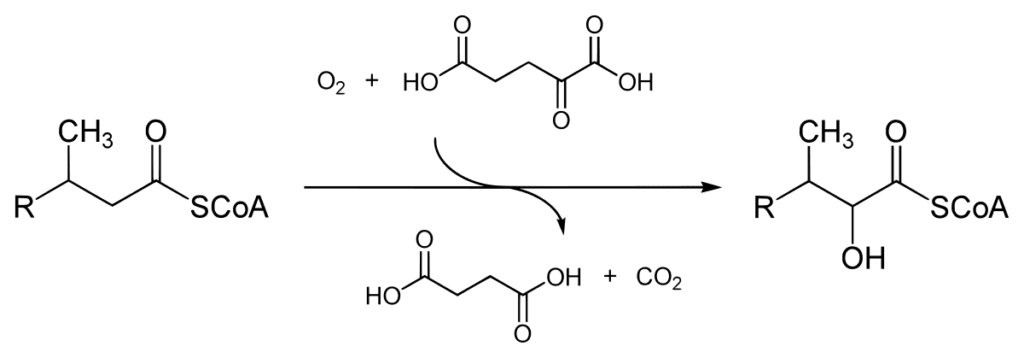
A metabolic process mainly takes place in the liver and kidneys and involves the breakdown of branched-chain fatty acids, especially those that have a methyl group joined to the carbon atom close to the carboxyl group. This is not the same as beta oxidation, which is the main process that breaks down straight-chain fatty acids.
Table of Contents
Location
Peroxisomes are membrane-bound organelles that are predominantly located in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells and are the site of alpha oxidation. Peroxisomes are essential for several metabolic functions, including as the alpha oxidation process that breaks down fatty acids.
Alpha-hydroxy acid oxidase and alpha-hydroxy acid dehydrogenase are two alpha oxidation-related enzymes found in peroxisomes that catalyze the subsequent processes in alpha oxidation.
IT is compartmentalized within peroxisomes for a number of reasons, such as:
Isolation of Reactive Intermediates:
By offering a regulated setting for the oxidation processes, peroxisomes reduce the risk of reactive oxygen species and intermediates produced during fatty acid oxidation causing harm to other cellular constituents.
Spatial Organization
The alpha pathway functions more efficiently when enzymes and substrates are concentrated inside peroxisomes, which makes the subsequent enzymatic reactions easier to carry out.
Regulation
It can be regulated independently of other cellular processes thanks to certain enzymes found within peroxisomes. This flexibility in response to metabolic demands is made possible.
All things considered, alpha oxidation’s placement within peroxisomes guarantees the effective and regulated breakdown of branched-chain fatty acids, supporting metabolic equilibrium and cellular energy metabolism.
Pathway
Initial step
The fatty acid molecule’s alpha carbon atom and its associated methyl group are removed at the start of the process. The fatty acid is changed into an alpha-hydroxy fatty acid by the enzyme alpha-hydroxy acid oxidase, which catalyses this process.
Conversion to alpha-keto acid
The alpha-hydroxy acid dehydrogenase enzyme further breaks down the alpha-hydroxy fatty acid to produce an alpha-keto acid.
Decarboxylation
This phase involves the decarboxylation of the alpha-keto acid, which eliminates a carboxyl group and forms a shorter fatty acid molecule.
Additional processing
The reduced fatty acid molecule can go through additional metabolism, such as being incorporated into other metabolic pathways or transformed into acetyl-CoA for the production of energy.
Steps
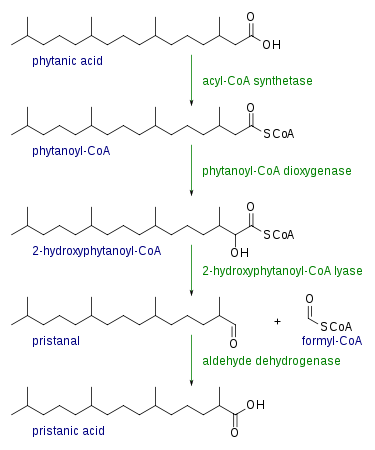
Branching-chain fatty acids—especially those with a methyl group bonded to the carbon atom adjacent to the carboxyl group—are transformed into shorter fatty acid molecules through the processes of alpha oxidation. The following are the main phases in alpha oxidation:
Hydroxylation
The hydroxylation of the fatty acid at the alpha carbon atom is the first stage of alpha oxidation. The alpha-hydroxy acid oxidase enzyme catalyzes this process by introducing a hydroxyl group (-OH) to the alpha carbon atom, resulting in the formation of an alpha-hydroxy fatty acid.
Dehydrogenation
After that, the alpha-hydroxy fatty acid undergoes dehydrogenation, which converts the alpha-hydroxyl group into a keto group (-C=O). Alpha-hydroxy acid dehydrogenase is the enzyme that catalyzes this process, which produces an alpha-keto fatty acid.
Decarboxylation
This stage involves the removal of a carboxyl group (-COOH) from the alpha-keto fatty acid by a process known as decarboxylation. Under healthy settings, this process usually happens on its own and results in the creation of a shorter fatty acid molecule.
Further Metabolism
The fatty acid molecule that is shortened as a result of alpha oxidation can be further metabolized. It could be further degraded by alternative routes or by more rounds of alpha oxidation. As an alternative, it can undergo beta-oxidation or other metabolic processes to become acetyl-CoA, a crucial molecule in the metabolism of cellular energy.
Together, these actions promote energy production and metabolic equilibrium in the cell by aiding in the breakdown of branched-chain fatty acids. Peroxisomes are specialized organelles engaged in a variety of metabolic processes, including the breakdown of fatty acids, where alpha oxidation predominantly takes place.
Significance
Certain types of fatty acids, especially those with methyl-branched structures that cannot be metabolised by beta oxidation, require alpha oxidation in order to be broken down.
It assists in clearing the body of extra branched-chain fatty acids, reducing their build-up that may result in metabolic problems.
Through the manufacture of acetyl-CoA, which can enter the citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle) for ATP synthesis, alpha oxidation contributes to the production of energy.
Alpha oxidation abnormalities, like peroxisomal disorders, can cause harmful metabolites and fatty acid accumulation, which can result in metabolic diseases with a range of symptoms and consequences.
Frequently Asked Questions
What do you mean by Alpha Oxidation?
A metabolic process mainly takes place in the liver and kidneys and involves the breakdown of branched-chain fatty acids, especially those that have a methyl group joined to the carbon atom close to the carboxyl group. This is not the same as beta oxidation, which is the main process that breaks down straight-chain fatty acids.
What are the significance of Alpha Oxidations?
The significance of Alpha Oxidation are as mentioned below,
It assists in clearing the body of extra branched-chain fatty acids, reducing their build-up that may result in metabolic problems.
Through the manufacture of acetyl-CoA, which can enter the citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle) for ATP synthesis, alpha oxidation contributes to the production of energy.
What are the steps of Alpha Oxidation?
The steps of Alpha Oxidation are
1.Hydroxylation
2.Dehydrogenation
3.Decarboxylation
4.Further Metabolism
Related Articles