Within the range of human health situations are two separate categories: Acute disease vs Chronic disease . Acute illnesses are defined by their abrupt onset and frequently severe symptoms that appear quickly. Most of these illnesses have a short course and clear up rather quickly. On the other hand, chronic illnesses endure for a long time, perhaps for a lifetime. They usually appear gradually, and the intensity of the symptoms may change over time.
Table of Contents
What is Acute disease?
An acute disease is a type of illness that usually manifests itself quickly, lasts very briefly, and frequently has noticeable symptoms. These illnesses typically develop suddenly and spread swiftly, but they normally go away in a few days or weeks thanks to medical intervention or the body’s own healing mechanisms. Acute illnesses include strep throat, acute appendicitis, influenza, and the common cold.
What is Chronic disease?
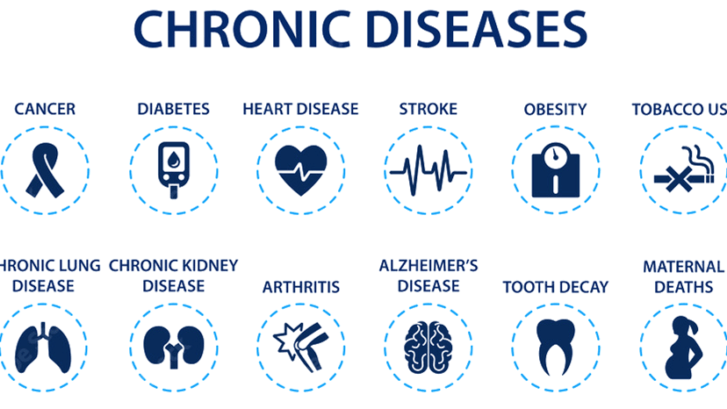
An protracted period of time, usually three months or longer, is what is referred to as a chronic disease. Chronic illnesses, in contrast to acute ones, frequently progress gradually and may experience flare-ups as well as remissions. A person’s quality of life may be greatly impacted by these illnesses, which may necessitate continuous care and therapy to manage symptoms and avoid complications. Diabetes, hypertension, asthma, arthritis, and cardiovascular conditions like coronary artery disease are a few examples of chronic diseases.
Difference between Acute disease vs Chronic disease
What distinguishes acute illnesses from chronic illnesses:
| S.N | Aspect | Acute Disease | Chronic Disease |
| 1. | Definition | An acute disease is a type of illness that usually manifests itself quickly, lasts very briefly, and frequently has noticeable symptoms | A chronic disease is a long-lasting medical condition that persists over an extended period, often for months to years, requiring ongoing management to control symptoms and prevent complications. |
| 2. | Duration | Its last for short-term ( days to weeks). | Its lasts for long-term( months to years). |
| 3. | Onset | Its has Sudden onset. | Its has Gradual onset. |
| 4. | Progression | Acute disease has rapid progression. | Chronic disease has slow progression. |
| 5. | Management | Short-term treatment to alleviate symptoms and promote recovery. | Ongoing management to control symptoms and prevent complications |
| 6. | Response to treatment | frequently reacts favourably to particular therapies, and full recovery is typical | May need lifetime care with sporadic modifications to treatment regimens |
| 7. | Prevention | Prevention of Acute disease focus on avoiding exposure to pathogens or injuries | Prevention of Chronic disease often involves lifestyle modifications |
| 8. | Health Utilization | Acute disease typically involves acute care settings such as emergency departments or urgent care clinics | Chronic disease often requires long-term care involving primary care providers, specialists, and allied health professionals |
| 9. | Economic impact | Acute disease can result in immediate but short-lived economic burden. | Chronic disease contribute significantly to long-term healthcare costs, productivity losses and disability. |
| 10. | Psychological Impact | Acute disease may cause temporary stress and anxiety but don’t lead to long term psychological effects. | Chronic diseases profound psychological impact, leading to depression, anxiety, and adjustment difficulties. |
| 11. | Nature of symptoms | In Acute disease, symptoms are often severe and intense, with rapid onset. | In Chronic disease symptoms may be mild initially and gradually worsen over time. |
| 12. | Impact on Quality of Life | Acute disease temporarily disturb daily life also it resolve quickly. | Chronic disease can significantly impact daily functioning and quality of life over the long term. |
| 13. | Example | Common cold, influenza, gastroenteritis, appendicitis | Diabetes, hypertension, asthma, arthritis, cardiovascular diseases |

Frequently Asked Questions(FAQ)
What are the examples of Acute disease?
The examples of Acute disease are Common cold, influenza, gastroenteritis, appendicitis….etc
Define Acute disease?
An acute disease is a type of illness that usually manifests itself quickly, lasts very briefly, and frequently has noticeable symptoms. These illnesses typically develop suddenly and spread swiftly, but they normally go away in a few days or weeks thanks to medical intervention or the body’s own healing mechanisms.
How does Chronic disease impact on quality of life?
Chronic disease can significantly impact daily functioning and quality of life over the long term.
Related Articles