What is acetamide?
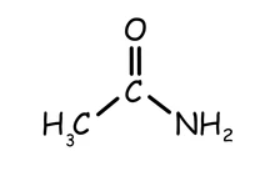
Acetamide comes from the acid acetic. The chemical formula for acetamide, also known by its systematic name, ethanamide, is CH₃CONH₂
Table of Contents
Acetamide Utilizations Test
The Acetamide Utilization Test is a biochemical test used in microbiology to assess an organism’s capacity to employ deamidation to use acetamide for bacterial growth and metabolism.
Principle of Acetamide utilization test
- The only carbon source in the medium is acetamide, while the only nitrogen source is inorganic ammonium salts.
- A positive test result for acetamide utilization is growth.
- The ammonium salts are converted to ammonia by the bacterium’s acylamidase during the enzymatic metabolization of acetamide, which raises alkalinity.
- A positive test result is indicated when the medium’s bromthymol blue indicator changes from green to blue due to a PH shift.
Procedure of Acetamide utilization test
A biochemical test called the acetamide utilization test is used in microbiology to assess an organism’s capacity to use acetamide as its only source of carbon and nitrogen. The general protocol for doing the acetamide utilization test is as follows:
Preparation of Media
As the only source of nitrogen, prepare a minimal salts agar medium supplemented with acetamide. To track the use of acetamide, the medium’s composition usually consists of salts, trace elements, and a pH indicator.
Inoculation
Introduce the test organism into the liquid. This can be accomplished by either inoculating the medium with a standardised inoculum or by streaking the organism onto the agar’s surface using a sterile loop.
Incubation
Place the inoculation plates in an incubator with the right parameters (pH, temperature, etc.) to support the organism’s growth. Depending on the microorganism under examination, there can be variations in the temperature and length of incubation.
Observation
Periodically check the plates for growth and pH indicator changes. The organism will thrive on the medium and create acid as a byproduct of metabolism if it is able to use acetamide. The pH indicator’s color will change as a result of this acid generation, indicating a drop in PH .
Interpretation
Check the plates frequently for changes in pH indicator and growth. If the organism is able to use acetamide, it will flourish on the medium and produce acid as a byproduct of metabolism. This acid creation will cause the pH indicator’s colour to shift, indicating a pH decrease.
Controls
To validate the test results, always include the relevant positive and negative controls.
Reporting
Note the test’s outcomes, including the organism’s name, growth parameters, and the acetamide utilisation test’s interpretation.
It’s crucial to remember that differences in the medium’s composition and incubation conditions can have an impact on the test’s outcomes, therefore it’s critical to adhere to a consistent procedure and apply the right controls to ensure proper interpretation.
Result of Acetamide utilization test
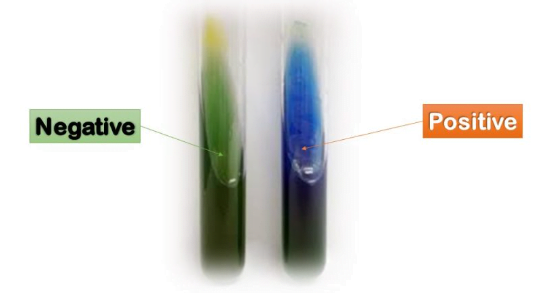
Positive
Acetamide is deamined, giving it a blue tint.
Negative
No yellow color development or shift in hue.
Uses of Acetamide utilization test
The Acetamide utilization test has multiple uses in microbiology and other related domains:
Identification of Microorganisms
The ability of microorganisms to use acetamide as their only source of carbon and nitrogen can help distinguish and identify them. The ability of different species or strains to use acetamide may vary, offering important information for taxonomic categorization.
Characterization of Microbial Communities
The test can be used to describe the microbial communities in a variety of settings, including water, soil, and medical samples. Researchers can learn more about the metabolic capacities and ecological roles of various microorganisms in a sample by evaluating their acetamide utilization profiles.
Screening for Biodegradation Potential
tests microorganisms for their capacity to break down industrial chemicals containing acetamide or similar compounds, environmental contaminants, or both can be done using acetamide utilization tests. Acetamide-using microorganisms can be used in bioremediation procedures to break down pollutants and lessen environmental contamination.
Quality Control in Microbiology Laboratories
The test can be used to evaluate the effectiveness of microbial culture media and spot any possible impurities or variations from expected outcomes. It can be included into microbiology lab quality control protocols.
Research and Biotechnology Applications
Microbial physiology, metabolism, and environmental adaption can all be studied by researchers using the acetamide utilization test. It can also be used in biotechnological applications, such the engineering of metabolic pathways for the synthesis of valuable substances or the generation of microbial strains for bioproduction processes.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQ)
What is Acetamide?
Acetamide comes from the acid acetic. The chemical formula for acetamide, also known by its systematic name, ethanamide, is CH₃CONH₂.
What is the systematic name for acetamide ?
Acetamide comes from the acid acetic. The chemical formula for acetamide, also known by its systematic name, ethanamide, is CH₃CONH₂.
What are the uses of Acetamide utilization test?
The uses of Acetamide utilization test are
1.Identification of Microorganisms
2.Quality Control in Microbiology Laboratories
3.Screening for Biodegradation Potential
Related Articles