Absorption vs Adsorption: Definitions and Examples
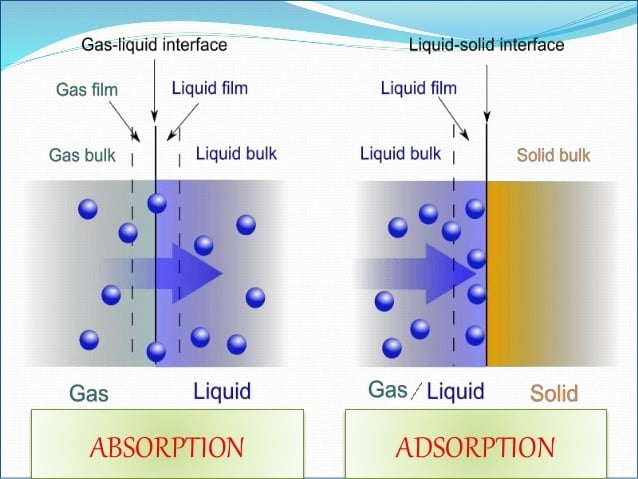
The process of absorbing something involves allowing it to diffuse or osmotically permeate tissues or onto a surface like a cell. The fluid (absorbate) permeates the entire absorbent material in this bulk phenomenon. Endothermic absorption needs energy to take in the particles.
Adsorption is the process by which molecules, atoms, or ions stick to a surface. The surface itself is the adsorbent, and the material adsorbed onto it is known as the adsorbate. It’s a surface phenomenon in which particles adhere to a material’s outermost layer. When the adsorbate binds to the adsorbent, the process of adsorption is exothermic, releasing energy.
Table of Contents
Absorption vs Adsorption
The differentiation of Absorption vs Adsorption are as follows:
| S.N | Absorption | S.N | Adsorption |
| 1) | The process by which one material is absorbed into the interior of another is called absorption. | 1) | Adsorption is the process through which molecules of one material stick to the surface of another. |
| 2) | Absorption is a bulk phenomenon that takes up the absorbent’s whole volume. | 2) | Adsorption is a surface phenomenon that only affects the adsorbent’s surface. |
| 3) | Absorption usually happens across the material at a constant rate. | 3) | Adsorption is quick at first, but as the surface gets saturated, it slows down. |
| 4) | Endothermic processes typically see an increase in temperature. | 4) | Adsorption usually becomes less as temperature rises (exothermic). |
| 5) | It is used in procedures such as gas absorption in liquids and liquid-liquid extraction. | 5) | It is used in water filters, air purifiers, and catalysis, among other applications. |
| 6) | When the concentration is constant throughout the absorbent, it reaches equilibrium. | 6) | When the rate of adsorption and the rate of desorption are equal, equilibrium is reached. |
| 7) | Absorbed materials can be separated into distinct phases. Based on how they interact chemically with the phases | 7) | Adsorbed materials can be separated by introducing a fresh substance onto the adsorbent’s surface. |
| 8) | Without interacting chemically with the absorbent, the absorbed materials stay in the absorbent. | 8) | Van der Wall’s forces or covalent bonds keep the adsorbed materials bonded to the adsorbent. |
| 9) | The nature of the particle and the amount of space available cause substances to be absorbed into an absorbent. | 9) | The reason substances are adsorbed onto an adsorbent’s surface is because the adsorbent contains open spaces that encourage particle adhesion. |
| 10) | Examples of absorption includes: A sponge absorbing water, the digestive system’s absorption of medications, absorption of nutrients, a piece of fabric absorbing gasoline etc. | 10) | Examples of adsorption includes: Gases or contaminants are absorbed by activated charcoal, contaminants adsorbing onto activated charcoal, glass and silver sticking together to create a mirror surface, non-stick coatings on pans etc. |
In Addition:
Adsorption vs Absorption are two different processes. Adsorption is a bulk phenomenon, like when water is soaked into a sponge, where molecules are absorbed throughout the volume of a material. Adsorption, on the other hand, is a surface phenomenon in which molecules only stick to a material’s surface; activated charcoal is a good example of this, as it traps impurities on its surface. The primary distinction of Adsorption vs Absorption is that whereas adsorption is limited to the surface layer, absorption involves the entire material volume.
Frequently Asked Questions:
What is the main difference between absorption and adsorption?
The process of a substance being absorbed into the volume (bulk) of another substance is known as absorption. Molecules attach to the surface of another substance through a process known as adsorption.
What effects on environmental science do absorption and adsorption have?
Absorption: Critical for activities such as soil or plant absorption of pollutants.
Adsorption: Essential for eliminating pollutants from water and air with adsorbent materials such as activated carbon.
What are some common examples of absorption and adsorption?
Absorption: The way a sponge absorbs water and how the lungs’ blood absorbs oxygen.
Adsorption: Silica gel absorbs moisture, while activated charcoal absorbs gases.
Related Articles: