What is Living?
Living organisms are those that exhibit characteristics such as cellular organization, metabolism, growth, reproduction, response to stimuli, homeostasis, adaptation, and consciousness, which distinguish them from non-living things.
A living thing is any organism that can grow, reproduce, respond to its environment, and carry out life processes like breathing and digesting food.
Summary of Living Organisms
- Living organisms are defined by unique characteristics like growth, metabolism, reproduction, and response to stimuli.
- Biodiversity represents the variety of life on Earth, which is essential for ecological balance and human survival.
- Classification helps organize the vast diversity of life, making it easier to study, understand, and conserve living organisms.
Table of Contents
1. Characteristics of Living Organisms
Living organisms are unique because they show specific features that are not found in non-living things. According to the NCERT Class 11 Biology book, these characteristics help us understand what makes something truly alive. These features include cellular structure, metabolism, growth, reproduction, response to stimuli, homeostasis, adaptation, and consciousness.
1.1 Cellular Organization
All living organisms are made up of cells. A cell is the basic structural and functional unit of life. Some organisms, like bacteria and protozoa, are made up of just one cell and are called unicellular organisms. Others, like humans, trees, and animals, are made up of many cells and are known as multicellular organisms. Each cell performs specific functions that are essential for the survival of the organism.
1.2 Metabolism
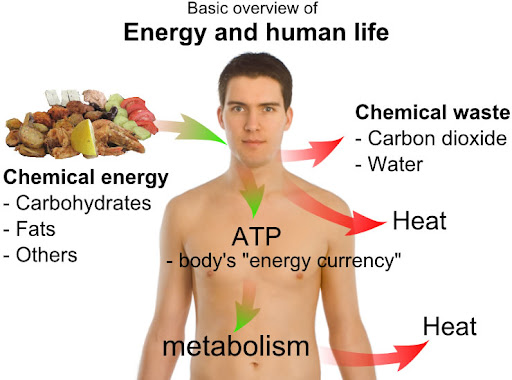
Metabolism refers to all the chemical reactions that take place inside a living organism’s body. These reactions help in breaking down food to release energy and also in building up new substances. These are categorized as anabolic (building up) and catabolic (breaking down) reactions. Only living things have metabolism. If any substance shows metabolic reactions, it is considered to be alive.
1.3 Growth
Growth means an increase in size and mass. In living organisms, growth happens by increasing the number of cells through cell division. In plants, growth continues throughout life. In animals, growth happens only up to a certain age. Unicellular organisms grow by increasing in size and then dividing into two new cells. Some non-living things like crystals can grow by accumulating material, but that is not real biological growth.
1.4 Reproduction
Reproduction is the process by which living organisms produce new individuals of their own kind. It is essential for the survival of the species. Organisms can reproduce in two ways: asexually and sexually. Asexual reproduction does not involve gametes and occurs in single-celled organisms through methods like binary fission. Sexual reproduction involves the fusion of male and female gametes. However, reproduction is not always a necessary feature to define life, as some living organisms like sterile worker bees or mules do not reproduce.
1.5 Response to Stimuli
All living organisms can sense changes in their environment and respond to them. This ability is known as responsiveness. Plants respond to sunlight by growing towards it. Animals respond to sound, light, touch, and temperature. Even simple organisms like bacteria respond to chemicals in their environment. This ability to react is one of the key features of life.
1.6 Homeostasis

Homeostasis is the ability of living organisms to maintain a stable internal environment. For example, humans maintain a constant body temperature and water balance in the body even when the outside environment changes. This is done through various control systems inside the body. Non-living things cannot maintain homeostasis.
1.7 Adaptation and Evolution
Living organisms change gradually over generations to better survive in their environment. These changes are called adaptations. Over time, these adaptations can lead to the evolution of new species. Evolution shows that all living organisms are related to each other and have changed over time from common ancestors.
1.8 Consciousness
Consciousness means being aware of the surroundings and responding to them. It is one of the most advanced features of life. All living beings have some level of consciousness. In humans, it is highly developed, allowing us to think, learn, and make decisions.
Biodiversity
1. Introduction to Biodiversity
Biodiversity means the variety of life forms on Earth. It includes different types of plants, animals, fungi, and microorganisms. Biodiversity is found everywhere from forests and oceans to deserts and mountains. It includes three levels: genetic diversity, species diversity, and ecosystem diversity.
1.1 Global Biodiversity

Scientists have identified around 1.7 to 1.8 million species so far, but many more are still unknown. Biodiversity is not the same in all parts of the world. It is highest in tropical regions like rainforests and lowest in polar regions. India is one of the 12 mega-diverse countries in the world.
1.2 Types of Biodiversity
- Genetic Diversity: This is the variety of genes within a species. It allows species to adapt to changes and resist diseases.
- Species Diversity: This refers to the number of different species in a particular area. For example, a forest has many types of trees, birds, and insects.
- Ecosystem Diversity: This includes the variety of ecosystems in a region, such as forests, rivers, grasslands, and wetlands.
2. Importance of Biodiversity
Biodiversity is important for the health of the planet and the well-being of all living beings.
2.1 Ecological Balance
Every organism plays a role in nature. Plants produce food, herbivores eat plants, and carnivores control herbivore numbers. Microorganisms decompose dead matter and recycle nutrients. This balance keeps ecosystems stable.
2.2 Economic Value
Biodiversity provides us with food like fruits, vegetables, grains, and fish. It also gives us medicines, fuel, fiber, and other resources. Many industries depend on natural products.
2.3 Cultural and Recreational Value
Biodiversity has religious, cultural, and aesthetic importance. People enjoy activities like bird watching, wildlife photography, and eco-tourism. Many plants and animals are part of traditional beliefs and customs.
3. Threats and Conservation of Biodiversity
3.1 Causes of Biodiversity Loss
- Habitat Destruction: Cutting forests and building cities destroy the homes of many species.
- Pollution: Air, water, and soil pollution harm living organisms.
- Climate Change: Rising temperatures and changing rainfall patterns affect ecosystems.
- Overexploitation: Excessive hunting, fishing, and use of natural resources reduce populations.
- Invasive Species: Non-native species introduced to new areas can harm local species.
3.2 Conservation Strategies
- In-situ Conservation: Protecting species in their natural habitats. Examples include national parks, wildlife sanctuaries, and biosphere reserves.
- Ex-situ Conservation: Conserving species outside their natural habitats. This includes zoos, botanical gardens, seed banks, and gene banks.
Need for Classification
1. Purpose of Classification
Classification is a method of organizing the vast number of living organisms into groups based on similarities and differences. It helps scientists study organisms, understand relationships among them, and predict characteristics. Without classification, studying millions of species would be confusing and difficult.
1.1 Early Classification Systems
In ancient times, organisms were classified based on simple characteristics like use or appearance. Aristotle divided animals into those with blood and those without. Later, Carolus Linnaeus introduced a scientific classification system based on physical characteristics.
2. Binomial Nomenclature
2.1 Naming Organisms
Linnaeus introduced the system of binomial nomenclature. Each organism is given a two-part name: the first part is the genus, and the second is the species. For example, in Mangifera indica, “Mangifera” is the genus, and “indica” is the species.
2.2 Rules of Nomenclature
- The scientific name is written in italics.
- The genus name starts with a capital letter, and the species name with a small letter.
- If handwritten, the name should be underlined.
3. Hierarchical Classification
3.1 Taxonomic Categories
Organisms are classified in a hierarchy of ranks: Kingdom, Phylum (or Division in plants), Class, Order, Family, Genus, and Species. As we go higher in the hierarchy, the number of shared characteristics decreases.
3.2 Importance of Hierarchy
The hierarchy helps to understand how closely or distantly related different organisms are. It shows evolutionary relationships and makes the study of biology more systematic.
4. Taxonomic Aids
4.1 Keys
Keys help in identifying organisms based on contrasting characteristics. They are very useful in fieldwork.
4.2 Herbarium
A herbarium is a collection of dried, pressed plant specimens mounted on sheets. Each sheet contains information about the plant, such as its name, place of collection, and date.
4.3 Museums and Parks
Museums preserve animal specimens, skeletons, and fossils. Botanical gardens grow living plants for study and conservation. Zoological parks house live animals in conditions similar to their natural habitats.
5. Significance of Classification
Classification helps in:
- Identifying and naming organisms.
- Understanding evolutionary connections.
- Predicting traits of organisms.
- Organizing biological knowledge.
- Promoting conservation efforts.
Conclusion
The study of biology begins with a fundamental understanding of what constitutes life. Living organisms, unlike non-living objects, exhibit a set of shared characteristics that include cellular structure, metabolism, growth, reproduction, response to environmental stimuli, homeostasis, adaptation, and consciousness. These features help us identify and distinguish living beings in the natural world. Without these biological processes working in harmony, life as we know it would not be possible.
One of the most striking features of life is its immense variety, also known as biodiversity. Biodiversity refers to the richness of life forms at genetic, species, and ecosystem levels. It plays a crucial role in maintaining ecological balance and providing resources that are essential for human survival, such as food, medicine, and raw materials. However, biodiversity is facing serious threats due to human activities, and this makes its conservation a top priority for ensuring sustainability and the survival of future generations.
To manage and study this vast diversity of life, scientists use classification systems. Classification brings order to the complexity of life by organizing organisms into groups based on shared characteristics and evolutionary relationships. It allows us to understand similarities and differences among organisms, trace their evolutionary history, and systematically name and categorize them using binomial nomenclature and taxonomic ranks.
The importance of classification extends beyond academic learning; it is essential for practical applications like medicine, agriculture, and conservation biology. Tools such as herbaria, museums, and botanical gardens help in the documentation and preservation of species.
In summary, understanding what is living, recognizing biodiversity, and appreciating the need for classification forms the foundation of biology. These concepts not only enhance our knowledge of life but also encourage responsible behavior towards nature. As our knowledge advances through research and technology, these foundational ideas continue to evolve and shape the way we explore and protect the living world.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What defines a living organism?
Living organisms show traits like cellular structure, metabolism, growth, reproduction, response to stimuli, homeostasis, adaptation, and consciousness, distinguishing them from non-living entities.
Why is biodiversity important?
Biodiversity refers to the variety of life on Earth at genetic, species, and ecosystem levels. It’s vital for ecological balance, food supply, medicine, climate regulation, and cultural values.
What are the types of biodiversity?
There are three types:
– Genetic diversity: variation within a species
– Species diversity: variety of species in an area
– Ecosystem diversity: range of habitats like forests, wetlands, and deserts
Related Articles