Introduction
In the ever-evolving field of microscopy, the digital microscope has emerged as a revolutionary tool that has changed the way we observe microscopic objects. Unlike traditional microscopes, these microscopes offer enhanced visualization by combining optics and digital technology. They are widely used in scientific research, medical diagnosis, education, industrial inspection, and even forensic analysis. This document presents a comprehensive overview of these microscopes, including their definition, working principle, components, various types, examples, and their wide range of applications.
Table of Contents
Definition
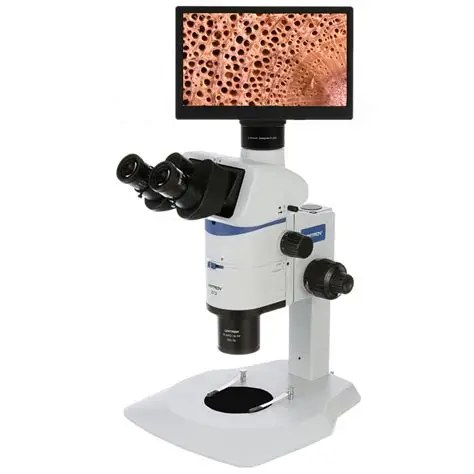
A digital microscope is an advanced form of microscope that uses a digital camera to capture images and videos of the specimen being observed. Instead of using an eyepiece, it displays the magnified image on a computer screen, monitor, or digital display. It enables better visualization, documentation, sharing, and analysis of specimens.
Key Features
- Live digital display of images
- High-resolution image and video capture
- Integrated lighting and magnification controls
- Software for measurements, annotations, and storage
- USB, HDMI, or Wi-Fi connectivity for data sharing
Principle
Working Principle
Digital microscopes operate by capturing light reflected or transmitted from the specimen through optical lenses, which is then focused onto a digital sensor (like a CMOS or CCD sensor). This sensor converts the optical image into a digital format, which is then processed and displayed on a screen. Most digital microscopes use LED lighting to illuminate the specimen for clear visualization.
Optical vs Digital Magnification
- Optical Magnification: Achieved through the lenses of the microscope.
- Digital Magnification: Achieved by enlarging the digital image using software, allowing closer examination without moving the lenses.
Parts of this Microscope
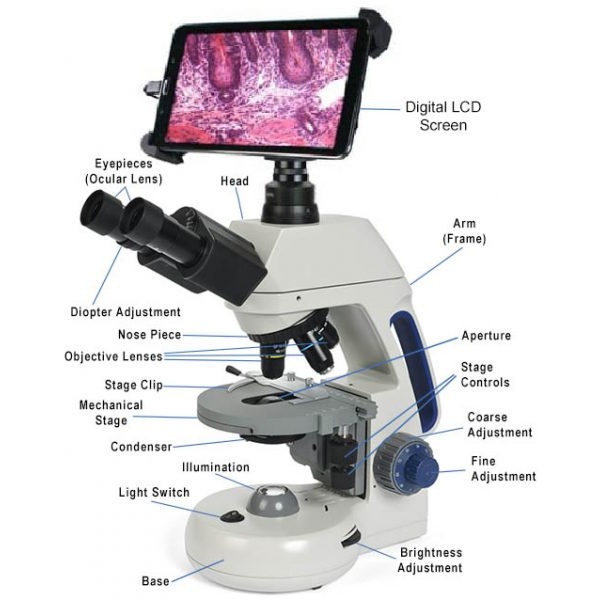
Optical System
- Objective Lenses: Capture the image at a specific magnification level.
- Digital Zoom: Additional magnification by software.
Imaging System
- Digital Camera Sensor: Captures the magnified image.
- Image Processor: Converts and processes the image into digital form.
Display System
LCD Monitor or Computer Screen: Displays the image in real-time.
Illumination System
- LED Light Source: Provides consistent and adjustable lighting.
- Adjustable Brightness Control: For image clarity under varying conditions.
Base and Stage
- Specimen Stage: Platform where the sample is placed.
- Adjustable Base: Allows positioning and focus control.
Software Interface
- Analysis Tools: For measurement, annotation, and image enhancement.
- Storage Options: Save and organize captured data.
- Connectivity: Enables USB, HDMI, or wireless connection.
Types
Based on Functionality

Handheld Digital Microscope
- Portable and easy to use.
- Suitable for field work and quick inspections.
USB Digital Microscope
- Connects to a computer via USB port.
- Offers easy image transfer and storage.
Wireless Digital Microscope
- Uses Wi-Fi or Bluetooth for wireless operation.
- Allows remote viewing and operation.
3D Digital Microscope
- Captures and constructs three-dimensional images.
- Used in industrial and materials science research.
Stereo Digital Microscope
- Provides a 3D view of the sample.
- Useful in dissection and circuit inspection.
Metallurgical Digital Microscope
- Specially designed to view metals and surfaces.
- Common in manufacturing and metallurgy.
Fluorescence Digital Microscope
- Uses fluorescence light to highlight specific structures.
- Widely used in molecular biology and pathology.
Based on Usage
- Educational Microscope: Simple, affordable, and ideal for classrooms.
- Laboratory Microscope: Designed for research and diagnostic labs.
- Industrial Microscope: Built for quality control and manufacturing lines.
- Forensic Microscope: Specialized for criminal investigation.
Examples
Dino-Lite Digital Microscope
- Known for portability and USB connection.
- Used in electronics, dermatology, and entomology.
Celestron Digital Microscope Pro
- Offers 200x magnification with 5MP resolution.
- Suitable for classroom and home laboratories.
Aven Mighty Scope
- High-resolution with measurement features.
- Popular in industrial inspection.
Leica DVM6
- Professional-grade with 3D imaging capabilities.
- Used in material science and engineering.
Omax Digital Biological Microscope
- Combines biological analysis with imaging software.
- Ideal for microbiology and pathology.
Uses
Educational Purposes
- Visual demonstration of microscopic organisms.
- Interactive learning through live image display.
Medical and Clinical Applications
- Diagnosis of diseases from blood, tissues, or body fluids.
- Dental inspection and dermatology.
Industrial and Manufacturing
- Quality control of components and surfaces.
- Semiconductor and circuit board inspection.
Research and Development
- Cell structure analysis.
- Drug testing and development.
Forensic Science
- Examination of hair, fibers, and fingerprints.
- Document and currency verification.
Environmental Studies
- Soil and water sample examination.
- Study of plant and insect microstructures.
Art and Archaeology
- Preservation analysis of artifacts.
- Examination of paintings, documents, and antiques.
Advantages
Enhanced Visualization
- Large, clear display on screens.
- Real-time image observation.
Image and Video Capture
- Store, share, and document findings.
- Create time-lapse videos for analysis.
Easy to Use
- No need for complicated focusing.
- Software guides for adjustments and measurements.
Safe and Non-Invasive
- Non-contact viewing for delicate samples.
- Useful in live biological studies.
Cost-Effective
- Affordable models for home and school use.
- Reduces need for multiple eyepieces or accessories.
Limitations
Resolution Constraints
- Digital zoom can reduce image clarity.
- Limited resolution in low-cost models.
Dependency on Electronics
- Requires computer or screen for operation.
- Susceptible to technical malfunctions.
Not Suitable for All Fields
- Not ideal for deep-tissue microscopy or atomic-level imaging.
- Limited depth perception compared to optical models.
Conclusion
Digital microscopes represent the fusion of optics and modern digital technology, making microscopy more accessible, efficient, and versatile. Their ease of use, ability to capture high-quality images, and capability to share data make them indispensable in many fields. Whether in a classroom, research lab, factory, or forensic lab, digital microscopes offer unmatched advantages over traditional models. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect even more powerful and compact digital microscopes that further expand our ability to observe the microscopic world.
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
What is the main difference between a digital microscope and a traditional microscope?
A digital microscope uses a digital camera and screen instead of eyepieces, allowing for image capture and real-time display.
Can digital microscopes be used for live organisms?
Yes, many digital microscopes are designed for non-invasive observation of living specimens.
Yes, many digital microscopes are designed for non-invasive observation of living specimens.
It can range from 10x to over 1000x depending on the model.
Related Articles