The structure and composition of DNA have long fascinated scientists, especially since it is the molecule responsible for carrying genetic information in all living organisms. Understanding the chemical nature and arrangement of DNA was crucial in laying the groundwork for molecular biology and genetics as scientific disciplines. A key breakthrough in this area came with the discovery of Chargaff’s Rules, which offered important insights into DNA’s molecular architecture and base composition.
This explanation aims to clarify what Chargaff’s Rules are, how they were discovered, and why they remain significant in both historical and modern contexts of genetics and molecular biology.
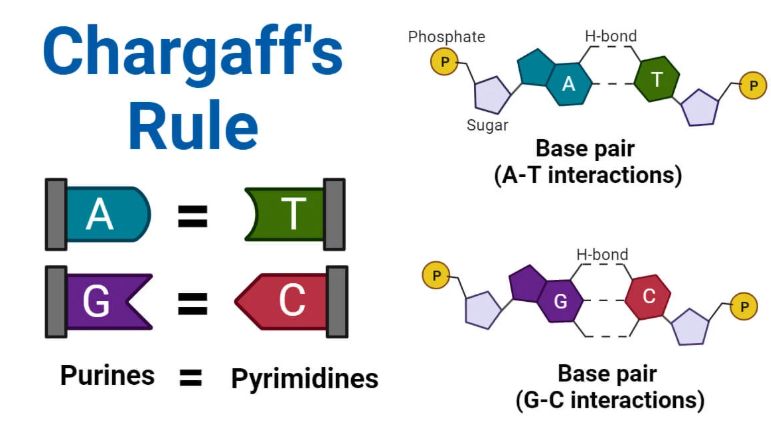
Summary of Chargaff’s Rules
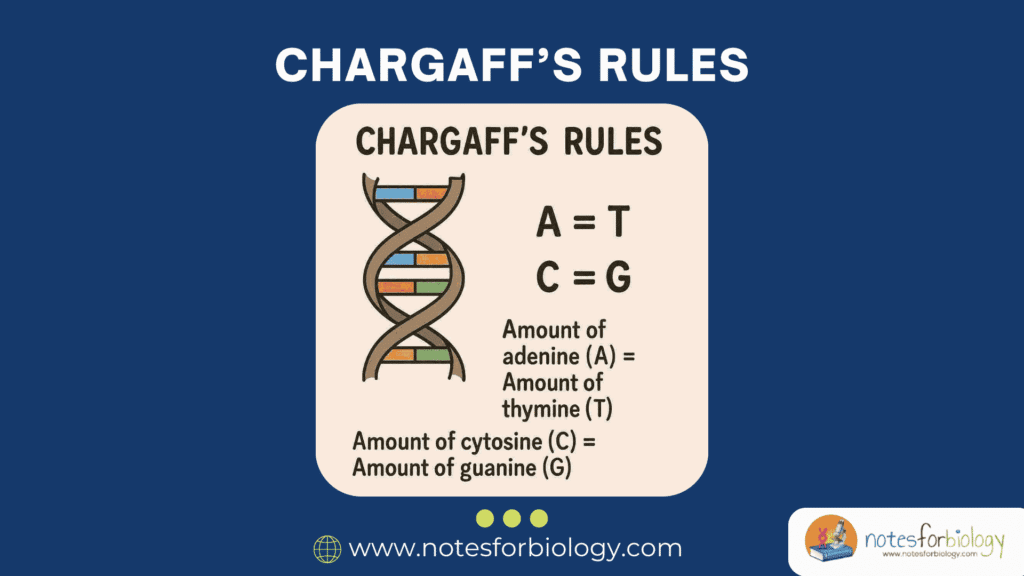
- In double-stranded DNA, the amount of adenine (A) always equals thymine (T), and guanine (G) always equals cytosine (C).
- While base pair ratios are equal within a species, the overall DNA base composition varies between different species.
- These rules provided critical evidence for the DNA double helix structure and the principle of complementary base pairing.
Table of Contents
Importance of Understanding DNA Composition in Molecular Biology
Accurately understanding the composition of DNA is fundamental in molecular biology because it provides a framework for explaining how genetic information is stored, duplicated, and transmitted. Knowing the proportions of different nitrogenous bases in DNA is vital for predicting how the molecule behaves during replication, transcription, and repair.
Without insights into DNA’s base pairing and composition, major developments like gene cloning, DNA sequencing, and genetic engineering would have remained impossible. It is through these compositional studies that scientists were able to decipher the language of life at a molecular level.
Brief Historical Context of DNA Discoveries Leading to Chargaff’s Work
Before Chargaff’s contributions, scientists had established that DNA was composed of four nitrogenous bases: adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine (C). However, it was believed that these bases occurred in equal amounts or random combinations, with little understanding of their significance.
The early 20th century saw discoveries such as Frederick Griffith’s experiment on bacterial transformation and Avery, MacLeod, and McCarty’s identification of DNA as the genetic material. By the 1940s, the scientific community had yet to fully comprehend DNA’s structure. This was the environment in which Erwin Chargaff’s critical findings emerged.
Who Was Erwin Chargaff?
Brief Biography
Erwin Chargaff was an Austrian-born American biochemist born in 1905. He pursued his academic studies in chemistry and later relocated to the United States, where he became a professor of biochemistry at Columbia University in New York.
Chargaff’s scientific career was marked by a strong interest in nucleic acids. His meticulous approach to biochemistry and insistence on careful experimental validation led him to question prevailing assumptions about DNA’s base composition.
Contributions to DNA Research
Chargaff is best remembered for establishing quantitative rules about the base composition of DNA, which later proved essential to understanding DNA’s double-helix structure. His research demonstrated that DNA composition varies between species but exhibits certain consistent patterns within any given organism.
These findings became known as Chargaff’s Rules and directly influenced James Watson and Francis Crick as they constructed their model of the DNA double helix in 1953. Chargaff’s work laid the biochemical foundation for the model of complementary base pairing.
What Are Chargaff’s Rules?
Definition and Overview
Chargaff’s Rules refer to two empirical observations about the composition of nitrogenous bases in DNA. The first rule describes the equality of specific base pairs within a single species, while the second addresses the variability of base composition across different species.
These rules transformed the understanding of DNA from a monotonous, repetitive polymer to a molecule with both regularity and diversity. This duality became a cornerstone of molecular genetics, explaining both the universality and individuality of genetic material.
The Role of Chargaff’s Rules in DNA Structure Discovery
The regularity in base pairing ratios uncovered by Chargaff suggested a structural relationship between bases in DNA. Watson and Crick’s model of the DNA double helix was directly based on this evidence, proposing that adenine pairs with thymine and guanine pairs with cytosine through specific hydrogen bonds.
Without Chargaff’s quantitative data, the concept of base pairing complementarity essential to DNA replication and stability might have remained undiscovered for much longer.
The First Rule of Chargaff
What Does the First Rule State?
The first rule of Chargaff states that in any double-stranded DNA molecule, the number of adenine (A) bases is approximately equal to the number of thymine (T) bases, and the number of guanine (G) bases is approximately equal to the number of cytosine (C) bases. In symbolic terms:
A = T and G = C
This relationship exists because of the specific pairing between bases in the double helix.
Base Pairing Principles: Adenine-Thymine and Guanine-Cytosine
In DNA, adenine forms two hydrogen bonds with thymine, while guanine forms three hydrogen bonds with cytosine. This base pairing is precise and consistent, ensuring DNA’s double-stranded structure remains stable and uniform in width.
These base pairings not only stabilize the double helix but also facilitate accurate DNA replication, as each base can only pair with its complement, minimizing errors during copying.
Experimental Evidence Supporting the First Rule
Chargaff’s meticulous analysis of DNA from various organisms consistently showed equal ratios of adenine to thymine and guanine to cytosine. This was demonstrated using techniques like paper chromatography and ultraviolet absorption, which quantified the different bases in DNA samples.
His results contradicted earlier assumptions that all four bases were present in equal amounts and highlighted a crucial feature of DNA’s composition, paving the way for modern molecular biology.
The Second Rule of Chargaff
What Does the Second Rule State?
The second rule of Chargaff states that although base pairing ratios (A = T and G = C) are equal within a species, the overall base composition — the percentage of purines (A and G) and pyrimidines (T and C) — can vary significantly between species.
This observation revealed that DNA’s composition is species-specific and accounts for genetic diversity among living organisms.
Distribution of Base Pairs Among Different Species
Chargaff demonstrated that while the proportion of adenine to thymine and guanine to cytosine is consistent within a species, the relative abundance of A+T versus G+C differs across species. Some organisms might have a high G+C content, while others might be rich in A+T.
This variation in base composition is now known to influence genome structure, DNA stability, and the regulation of gene expression in different species.
Significance in DNA Composition Variability
The second rule introduced the concept of molecular diversity at the genetic level, proving that DNA is not identical in all organisms. This insight contributed to the fields of evolutionary biology and phylogenetics by offering a molecular basis for comparing genetic material across species.
Today, G+C content is still used to characterize genomes and infer evolutionary relationships between organisms.
Importance of Chargaff’s Rules in Molecular Biology
How the Rules Contributed to Watson and Crick’s DNA Model
Watson and Crick’s groundbreaking model of the DNA double helix was largely dependent on Chargaff’s findings. The equal pairing of A with T and G with C provided a logical explanation for the uniform diameter of the helix and the mechanism for copying genetic information.
Chargaff’s work supplied the biochemical evidence that validated the structural pairing of complementary bases, which is central to the stability and replication of DNA.
Insights into Base Pair Complementarity
Chargaff’s Rules introduced the principle of complementarity, where each base on one strand of DNA pairs with a specific partner on the opposite strand. This principle is crucial not only for DNA structure but also for replication, repair, and transcription.
Complementarity ensures that genetic information is faithfully transmitted from cell to cell and generation to generation.
Practical Applications of Chargaff’s Rules
DNA Fingerprinting and Forensic Science
DNA fingerprinting relies on variations in DNA sequences between individuals. While the overall base pairing rules apply, the unique arrangement of these bases in each person’s genome allows for identity verification and forensic investigation.
Chargaff’s Rules established the molecular consistency necessary for these applications by confirming the predictable pairing of bases.
Genetic Research and Mutation Analysis
Understanding base pair ratios helps researchers identify mutations and genetic anomalies. Deviations from expected base compositions can signal errors, deletions, insertions, or structural variations in DNA sequences.
This knowledge underpins genetic disease studies, diagnostics, and therapeutic research.
Evolutionary Biology and Comparative Genomics
Chargaff’s second rule remains foundational in comparative genomics. Differences in base composition between species offer clues about evolutionary relationships, genome organization, and species-specific adaptations.
By examining G+C content, scientists can infer phylogenetic trees and explore evolutionary history at the molecular level.
Medical Diagnostics and Personalized Medicine
Modern genome sequencing projects and personalized medicine initiatives rely on accurate knowledge of base compositions. Chargaff’s Rules help validate sequencing results and confirm the integrity of DNA samples before clinical interpretation.
Understanding base pairing also guides the development of molecular therapies targeting specific genetic sequences.
Chargaff’s Rules and Modern Genetics
Implications in Genome Sequencing Projects
In large-scale genome sequencing, Chargaff’s Rules are used to verify the accuracy of assembled DNA sequences. Any significant departure from expected base pair ratios may indicate sequencing errors or contamination.
The rules also assist in assembling complementary DNA strands computationally, ensuring sequence fidelity.
DNA Replication and Repair Mechanisms
The principle of base complementarity derived from Chargaff’s Rules is central to DNA replication and repair. Enzymes recognize base pair matches and mismatches, using these rules as a guide to synthesize new strands or correct errors.
This process maintains genetic stability and reduces the likelihood of harmful mutations.
Exceptions and Limitations of Chargaff’s Rules
Mitochondrial DNA and Viral Genomes
Chargaff’s Rules primarily apply to double-stranded nuclear DNA. Mitochondrial DNA and many viral genomes, which are often single-stranded or circular, do not always conform to these rules. Base compositions in these molecules can show significant asymmetry.
This highlights the need for caution when applying Chargaff’s Rules universally.
Non-Double Helical DNA Structures
Certain regions of DNA can form unusual structures, like triple helices or hairpin loops, where base pairing may deviate from standard patterns. In these cases, local base pair ratios may temporarily violate Chargaff’s Rules.
Understanding these exceptions is important in studying non-coding DNA regions and epigenetic regulation.
Conclusion
Erwin Chargaff’s careful biochemical analyses produced two simple yet profound rules about DNA base composition. These rules helped decode DNA’s double-helical structure, laying the groundwork for modern molecular biology.
Chargaff’s contributions continue to shape genetic research, forensic science, medical diagnostics, and evolutionary studies. His findings remind us that careful observation and rigorous experimentation can unlock nature’s most intricate secrets.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the significance of Chargaff’s First Rule?
Chargaff’s First Rule revealed that in any double-stranded DNA molecule, the amount of adenine equals thymine and the amount of guanine equals cytosine. This discovery provided essential biochemical evidence for the base pairing structure of DNA and directly guided Watson and Crick in modeling the double helix.
How did Chargaff’s discoveries influence Watson and Crick?
Chargaff’s findings on equal base pair ratios (A = T and G = C) showed that specific bases pair together in DNA. This evidence helped Watson and Crick realize how complementary base pairing could stabilize the double helix and allow for accurate DNA replication.
Are there exceptions to Chargaff’s Rules?
Yes while Chargaff’s Rules apply to most double-stranded nuclear DNA, exceptions exist in single-stranded DNA, mitochondrial DNA, viral genomes, and certain non-standard DNA structures. In these cases, base pair ratios can be uneven or deviate from the expected patterns.
Related Contents
Centromere- Definition, Structure, Position, Types, Functions