The conducting system of the heart is a group of specialized muscle cells that generate and carry electrical signals to control the heartbeat. This system ensures that the heart beats in a coordinated and rhythmic way, allowing the atria and ventricles to contract in proper sequence and pump blood efficiently throughout the body.

SUMMARY OF HEARTBEAT
Initiation: The heartbeat starts at the SA node (sinoatrial node), which generates electrical impulses that cause the atria to contract.
Coordination: The impulse reaches the AV node, then travels through the Bundle of His, bundle branches, and Purkinje fibers, ensuring the ventricles contract in a coordinated manner.
Regulation: The heartbeat is automatic but is influenced by the nervous system to speed up or slow down based on the body’s needs (like rest or activity).
Table of Contents
Why is it important?
Every heartbeat must be carefully timed. If the chambers of the heart contract out of sync, blood will not flow properly, and oxygen may not reach vital organs. The conducting system makes sure that the heart beats regularly, even without input from the brain.
Main Parts of the Conducting System
The system consists of the following parts:
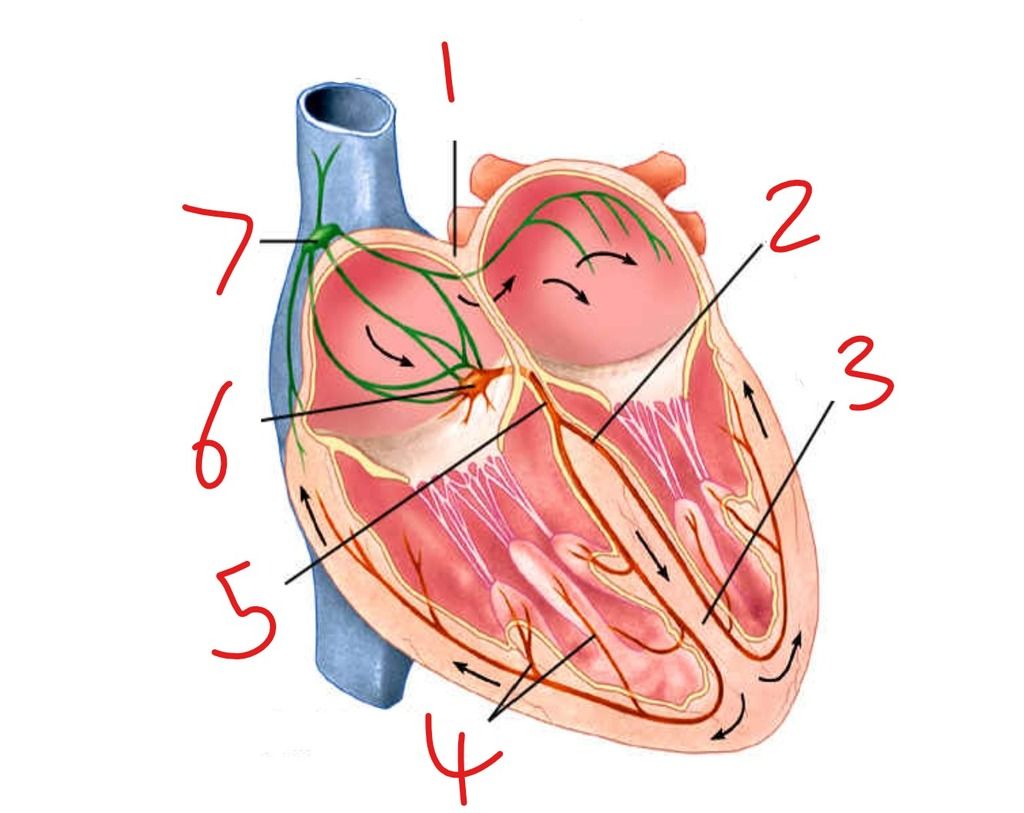
- Sinoatrial (SA) Node
- Atrioventricular (AV) Node
- Bundle of His
- Right and Left Bundle Branches
- Purkinje Fibers
1. SA Node – The Natural Pacemaker
- Located in the right atrium.
- Produces electrical impulses that start each heartbeat.
- These impulses spread across both atria, causing them to contract and push blood into the ventricles.
- The SA node sets the pace, usually 60–100 beats per minute.
2. AV Node – The Delay Gate
- Found between the atria and ventricles.
- Delays the electrical signal slightly to let the atria finish contracting before the ventricles begin.
- This delay ensures the ventricles are filled before they pump blood out.
3. Bundle of His
- A pathway that carries the impulse from the AV node down to the ventricles.
- Located in the interventricular septum.
- It divides into two branches.
4. Right and Left Bundle Branches
- These run down the right and left sides of the ventricular septum.
- They carry signals to both ventricles, ensuring they contract at the same time.
5. Purkinje Fibers
- Thin fibers that spread through the walls of the ventricles.
- They quickly send the signal to the ventricular muscle cells, causing a strong contraction that pushes blood out of the heart.
How a Heartbeat Happens (Cardiac Cycle)
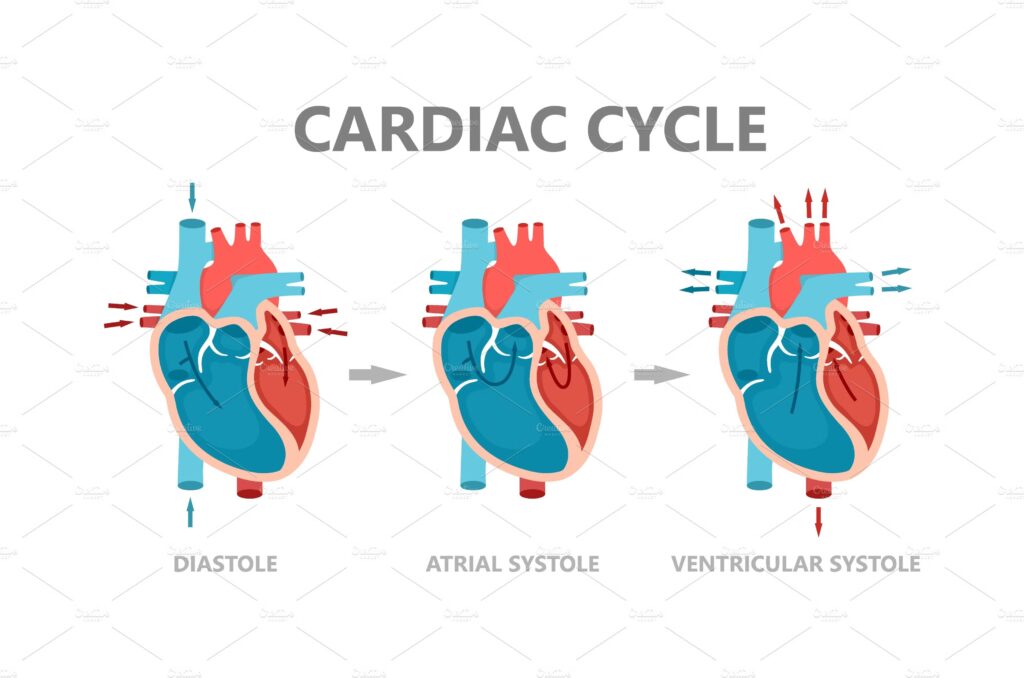
- SA node fires → Atria contract.
- Signal reaches AV node → Brief pause.
- Signal moves through Bundle of His.
- Signal travels down bundle branches.
- Signal reaches Purkinje fibers → Ventricles contract.
This process repeats every second, forming your heartbeat.
Automaticity and Control
- The heart beats on its own due to automatic signals from the SA node.
- The nervous system (brain and nerves) can speed up or slow down the rate as needed:
- Sympathetic nerves increase heart rate (e.g., during exercise).
- Parasympathetic nerves (via the vagus nerve) slow it down (e.g., during rest).
Disorders of the Conducting System
Problems with this system can cause irregular heartbeats (arrhythmias):
- Bradycardia: Slow heart rate.
- Tachycardia: Fast heart rate.
- Heart block: Delayed or blocked signals.
- Fibrillation: Irregular, fast, uncoordinated beating (especially dangerous in ventricles).
Diagnosis and Treatment
- ECG (Electrocardiogram): Measures the electrical activity of the heart.
- Pacemaker: A device that helps maintain proper rhythm.
- Defibrillator: Delivers a shock to correct dangerous rhythms.
Importance in Daily Life
- Keeps blood and oxygen flowing properly.
- Helps the body respond to stress, exercise, or rest.
- Maintains life-sustaining rhythms without conscious effort.
Conclusion
The conducting system of the heart is a beautifully designed natural system that ensures our heart beats correctly and rhythmically, keeping us alive and healthy. It is automatic, yet adaptable, and is one of the most essential systems in the body.
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
What is the conducting system of heartbeat ?
The conducting system of the heartbeat is a network of special muscle cells in the heart that create and carry electrical signals. These signals control the rhythmic contraction of the heart’s chambers, ensuring that the atria contract first, followed by the ventricles, to pump blood efficiently. This system includes the SA node, AV node, Bundle of His, bundle branches, and Purkinje fibers.
Why is it important?
The conducting system of the heart is important because it ensures that the heart beats in a regular and coordinated way. It controls the timing of atrial and ventricular contractions, making sure blood flows properly through the heart and to the rest of the body. Without it, the heart would beat irregularly, leading to poor blood circulation and possibly life-threatening conditions.
What are the disorders of the Conducting System ?
Disorders of the conducting system of the heart, such as bradycardia, tachycardia, heart block, and fibrillation, cause abnormal heart rhythms that can affect blood circulation and may require medical treatment like pacemakers or medication.
Related Articles