Cells are the fundamental units of life, and their survival depends upon the continuous exchange of substances between their internal environment and the surrounding extracellular fluid. This exchange process is meticulously regulated by the plasma membrane, a selectively permeable barrier that controls the entry and exit of molecules. The membrane transport system comprises various mechanisms by which substances move across the cell membrane, either passively without the expenditure of energy or actively requiring cellular energy.
This content aims to provide a comprehensive explanation of the membrane transport system, with particular emphasis on passive and active transport mechanisms.
Summary of Membrane transport
- Membrane transport regulates the movement of substances in and out of cells through the plasma membrane, ensuring cellular homeostasis.
- It is classified into passive transport (without energy, along the concentration gradient) and active transport (requiring energy, against the concentration gradient).
- Key processes include diffusion, osmosis, and filtration in passive transport, and carrier-mediated pumps, endocytosis, and exocytosis in active transport.
Table of Contents
Definition of Membrane Transport System
The membrane transport system refers to the collection of processes that facilitate the movement of substances such as ions, nutrients, gases, and waste products across the plasma membrane. This system ensures the maintenance of cellular homeostasis by regulating the internal composition of the cell in response to external environmental conditions.
Transport mechanisms are generally classified into two major types based on the requirement of metabolic energy: passive transport, which occurs without the use of energy, and active transport, which requires energy expenditure by the cell.
Structure of the Plasma Membrane
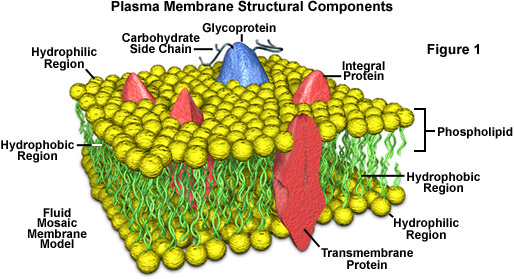
The plasma membrane is composed of a phospholipid bilayer interspersed with proteins, cholesterol, and carbohydrates. The amphipathic nature of phospholipids, with hydrophilic heads and hydrophobic tails, forms a semi-permeable barrier that permits the selective passage of substances. Proteins embedded within the membrane serve as transport channels, carriers, receptors, and enzymes, thereby playing a crucial role in membrane transport.
The structural organization of the plasma membrane provides both fluidity and selectivity, enabling the regulation of material movement in and out of the cell.
Types of Membrane Transport
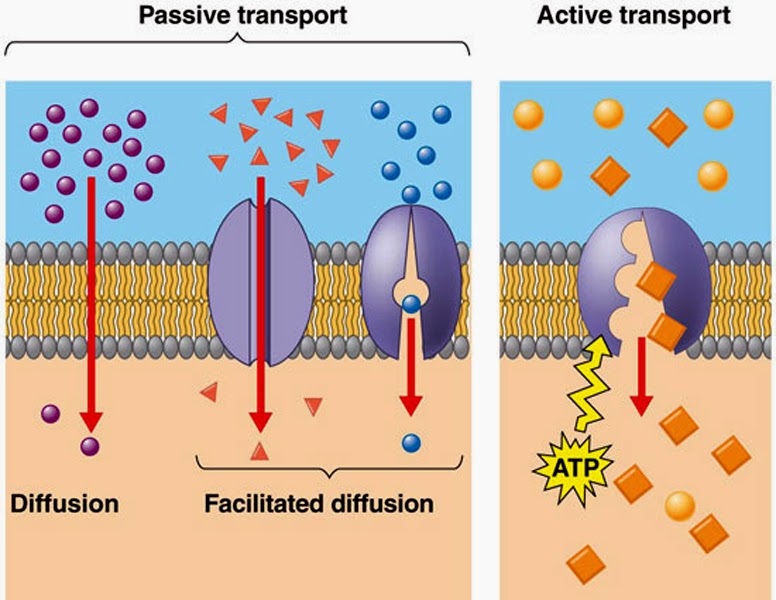
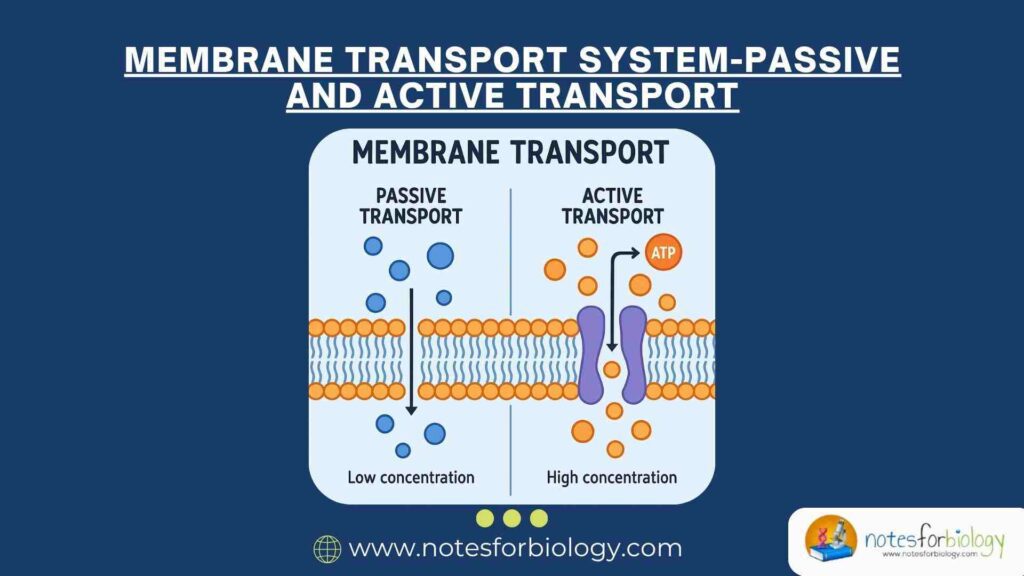
Membrane transport is broadly categorized into passive transport and active transport, based on whether or not cellular energy is consumed during the process.
Passive Transport
Passive transport is the movement of molecules across the cell membrane without the expenditure of cellular energy. This process occurs along the concentration or electrochemical gradient, from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration, until equilibrium is achieved.
Simple Diffusion
Simple diffusion is the unassisted movement of small, non-polar, or lipid-soluble molecules across the phospholipid bilayer. Gases such as oxygen and carbon dioxide, as well as certain lipid-soluble substances like steroids and alcohol, readily diffuse through the membrane without the involvement of transport proteins. This movement occurs due to the kinetic energy of the molecules and continues until an equilibrium is established.
Facilitated Diffusion
Facilitated diffusion involves the transport of larger, polar, or charged molecules that cannot freely diffuse through the lipid bilayer. This process requires the assistance of specific membrane proteins, such as carrier proteins or channel proteins. Carrier proteins bind to the molecule, undergo a conformational change, and release it on the other side of the membrane. Channel proteins form hydrophilic pores through which ions and water-soluble substances can pass.
Despite involving specialized proteins, facilitated diffusion remains a passive process, as the movement occurs down the concentration gradient without energy expenditure.
Osmosis
Osmosis is a specialized form of passive transport involving the movement of water molecules across a selectively permeable membrane. Water moves from a region of higher water potential (lower solute concentration) to a region of lower water potential (higher solute concentration) through protein channels known as aquaporins. Osmosis plays a vital role in maintaining the osmotic balance of cells and tissues, ensuring that cells neither shrink nor swell excessively.
Filtration
Filtration is the passive movement of water and solutes through a membrane due to hydrostatic pressure. This process occurs in tissues where differences in pressure forces fluid and small solutes across capillary walls. A physiological example of filtration is the glomerular filtration in the kidneys, where blood pressure forces water and dissolved substances out of the blood into the renal tubules.
Active Transport
Active transport is the movement of substances across the cell membrane against their concentration or electrochemical gradient, from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration. This process requires the expenditure of metabolic energy, usually in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), and involves specific carrier proteins.
Primary Active Transport
In primary active transport, energy derived directly from the hydrolysis of ATP is used to transport molecules across the membrane. One of the most significant examples is the sodium-potassium pump (Na⁺/K⁺-ATPase). This carrier protein actively transports three sodium ions out of the cell and two potassium ions into the cell against their respective concentration gradients, maintaining essential electrochemical gradients for various cellular functions.
Secondary Active Transport
Secondary active transport, also known as coupled transport, utilizes the energy stored in the form of ion gradients established by primary active transport processes. This energy is harnessed to transport other molecules against their concentration gradients.
In this mechanism, the movement of one molecule down its gradient provides the energy for the simultaneous transport of another molecule against its gradient. Depending on the direction of the coupled transport, it is classified into symport and antiport. In symport, both molecules move in the same direction, while in antiport, they move in opposite directions. An example of symport is the sodium-glucose transport in the intestinal epithelium, where the inward movement of sodium drives the uptake of glucose.
Endocytosis
Endocytosis is an active transport process by which large molecules, particulate matter, or fluids are engulfed by the cell through invagination of the plasma membrane, forming vesicles. Endocytosis can be further classified into phagocytosis, pinocytosis, and receptor-mediated endocytosis. In phagocytosis, the cell engulfs large particles such as bacteria or cellular debris. In pinocytosis, the cell takes in extracellular fluid containing dissolved substances. Receptor-mediated endocytosis involves the selective uptake of specific molecules through receptor binding.
Exocytosis
Exocytosis is the process by which materials stored in vesicles within the cell are expelled to the extracellular environment. This is achieved by the fusion of the vesicle membrane with the plasma membrane, releasing the vesicle’s contents outside the cell. Exocytosis is vital for the secretion of hormones, neurotransmitters, and digestive enzymes.
Factors Affecting Membrane Transport
Concentration Gradient
The concentration difference across the membrane influences the rate and direction of transport. Passive transport relies heavily on this gradient, with substances moving from regions of high to low concentration.
Membrane Permeability
The permeability of the plasma membrane to specific molecules determines their ability to pass through it. Non-polar and small molecules permeate more easily than large or charged molecules.
Temperature
An increase in temperature enhances the kinetic energy of molecules, thereby increasing the rate of diffusion and other passive transport processes.
Surface Area
A larger surface area of the membrane provides more sites for transport to occur, thus accelerating the overall rate of movement of substances.
Molecular Size
Smaller molecules diffuse more rapidly through the membrane compared to larger molecules, which may require facilitated diffusion or active transport.
Comparison of Passive and Active Transport
Cells constantly exchange materials with their environment to maintain homeostasis, obtain nutrients, and expel waste products. This movement of substances across the cell membrane occurs through two primary processes: passive transport and active transport. While both are vital for cellular function, they differ significantly in their energy requirements, mechanisms, and direction of molecular movement.
Energy Requirement
A major distinction between passive and active transport lies in their dependence on cellular energy. Passive transport occurs naturally without the use of cellular energy (ATP). It relies on the inherent kinetic energy of molecules and proceeds along the concentration gradient, from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. In contrast, active transport requires energy, usually derived from ATP, because it involves the movement of substances against their concentration gradient — from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration
Direction of Movement
In passive transport, the movement of molecules is always along the concentration gradient. This means that substances move from a region where they are more concentrated to where they are less concentrated, continuing until equilibrium is reached. On the other hand, active transport involves the movement of molecules against the concentration gradient. This type of movement is essential when a cell needs to accumulate substances in high concentrations inside or outside the cell, even when the concentration in the surrounding environment is lower.
Types of Transport
Passive transport can be further divided into processes such as simple diffusion, where molecules move freely across the membrane without assistance; facilitated diffusion, where specific carrier or channel proteins aid in the movement of larger or charged molecules; and osmosis, the diffusion of water molecules through a selectively permeable membrane. In comparison, active transport is categorized into primary active transport, which directly uses energy from ATP to move molecules, and secondary active transport, which uses energy stored in the form of an electrochemical gradient established by primary active transport.
Role of Carrier Proteins
While both transport mechanisms may involve proteins, their roles differ. In passive transport, proteins function as channels or carriers that facilitate the movement of molecules without the use of energy. These proteins assist substances like ions and glucose to pass through the membrane via facilitated diffusion. In active transport, specific carrier proteins known as pumps are essential. These proteins utilize energy to change their shape and actively move molecules against their concentration gradient, ensuring the desired intracellular or extracellular concentrations are maintained.
Examples
Examples help illustrate these differences clearly. In passive transport, gases like oxygen and carbon dioxide diffuse across cell membranes naturally as part of cellular respiration and photosynthesis. Water moves by osmosis to balance solute concentrations on either side of a membrane. In active transport, processes like the sodium-potassium pump (Na⁺/K⁺ pump) in animal cells actively maintain ion gradients necessary for nerve impulse transmission and muscle contraction. Another example is the proton pump in plant cells, which helps in nutrient absorption and maintaining cell turgidity.
Importance of Membrane Transport
Membrane transport is the process by which substances move across the cell membrane. It is essential for maintaining cellular homeostasis, enabling nutrient uptake, waste removal, and communication between cells and their environment. The importance of membrane transport can be understood under the following points:
Maintenance of Cellular Homeostasis
Membrane transport helps maintain a stable internal environment by controlling the entry and exit of ions, nutrients, and water. This balance is crucial for proper cellular functioning and survival.
Nutrient Uptake
Cells require essential nutrients such as glucose, amino acids, and minerals for energy and growth. Membrane transport mechanisms like facilitated diffusion and active transport ensure these nutrients enter the cell efficiently.
Removal of Waste Products
As cells perform various metabolic activities, waste products like carbon dioxide, ammonia, and urea are produced. Membrane transport allows these toxic substances to be expelled from the cell, preventing damage and maintaining cell health.
Regulation of Ion Concentration
Membrane transport systems regulate the concentration of important ions like sodium, potassium, calcium, and chloride. This regulation is vital for processes such as nerve impulse transmission, muscle contraction, and maintaining osmotic balance.
Communication and Signal Transmission
Transport proteins and receptors embedded in the cell membrane help in cell-to-cell communication by transmitting chemical signals. This is essential for coordinating various biological processes like immune responses and hormonal signaling.
Energy Production
In processes like cellular respiration and photosynthesis, membrane transport of protons and electrons across membranes (such as in mitochondria and chloroplasts) is vital for the synthesis of ATP, the energy currency of the cell.
Protection Against Harmful Substances
Membrane transport selectively allows the entry of beneficial substances while preventing harmful or toxic materials from entering the cell. This selective permeability is crucial for protecting the cell from environmental hazards.
Physiological Importance of Membrane Transport
Membrane transport mechanisms are indispensable for the survival and functioning of cells. They maintain the appropriate intracellular and extracellular composition necessary for vital biochemical processes. Through passive transport, cells exchange gases and small nutrients efficiently. Active transport mechanisms preserve essential ion gradients, regulate pH, and enable nutrient uptake in environments where diffusion alone would be insufficient.
Furthermore, processes like endocytosis and exocytosis facilitate intercellular communication, immune responses, and the secretion of substances necessary for bodily functions. Disruptions in membrane transport can lead to pathological conditions such as cystic fibrosis, hypertension, and neurological disorders.
Conclusion
The membrane transport system is a complex yet elegantly coordinated network of processes that regulate the movement of molecules across the cell membrane. It ensures cellular homeostasis by facilitating the uptake of nutrients, elimination of waste, and maintenance of electrochemical gradients. Passive transport mechanisms, including diffusion, osmosis, and filtration, occur without energy expenditure, while active transport requires metabolic energy to move substances against their gradients.
Understanding these transport mechanisms is fundamental to comprehending various physiological and pathological processes, as membrane transport is essential for maintaining life at the cellular and systemic levels.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the main difference between passive and active transport?
Passive transport moves substances across the cell membrane without using energy, along the concentration gradient (from high to low concentration). Active transport requires energy (usually ATP) to move substances against the concentration gradient (from low to high concentration).
What are examples of passive transport in cells?
Examples of passive transport include simple diffusion (like oxygen and carbon dioxide movement), facilitated diffusion (such as glucose transport through carrier proteins), osmosis (movement of water), and filtration (as seen in kidney filtration).
Why is the sodium-potassium pump important for cells?
The sodium-potassium pump maintains the essential electrochemical gradient across the cell membrane by actively transporting sodium ions out and potassium ions into the cell. This gradient is crucial for nerve impulses, muscle contractions, and regulating cell volume.
Related Contents
Classification of Bacteria – Importance , Basis and Historical Development