Fungi are a unique group of organisms that are different from plants, animals, and bacteria. They belong to their own kingdom called the Kingdom Fungi. These organisms play important roles in nature and have a wide range of uses in medicine, industry, and agriculture. In this article, we will explore the main characteristics of fungi and how they are classified into different groups.

Summary of Fungi
- Fungi are a group of living organisms that include molds, yeasts, and mushrooms, and they do not make their own food like plants.
- They grow by absorbing nutrients from organic matter and play key roles in decomposition, food production, and sometimes cause infections.
- Fungi can be found in many environments and reproduce through spores, either sexually or asexually.
Table of Contents
General Characteristics of Fungi
Fungi share some common features that make them different from other organisms:
1.Eukaryotic Cells
Fungi have complex cells with a nucleus and other parts inside. These are like plant and animal cells, not like bacteria.
2.Cell Wall Made of Chitin
Their outer covering (cell wall) is made of a tough material called chitin, which is also found in the shells of insects. This makes them strong and different from plants, which have cell walls made of cellulose.
3.Cannot Make Their Own Food
Fungi do not have chlorophyll, so they can’t make food using sunlight like plants. Instead, they absorb nutrients from other things, like dead plants, animals, or even living hosts.
4.Feed by Absorption
Fungi release special chemicals (enzymes) into their surroundings to break down food, then they absorb it. This helps them live on dead or decaying things.
5.Made of Hyphae and Mycelium
Most fungi are made of thin thread-like parts called hyphae. Many hyphae together form a big network called mycelium, which helps the fungus absorb nutrients.
6.Reproduce by Spores
Fungi spread and grow using tiny cells called spores. Spores can travel in the air or water and grow into new fungi in the right conditions.
7.Grow in Moist, Warm Places
Fungi love places that are damp and warm, like soil, rotten wood, or old food.
8.Store Energy as Glycogen
Like animals, fungi store energy in the form of glycogen (a type of sugar), not starch like plants.
Modes of Nutrition in Fungi
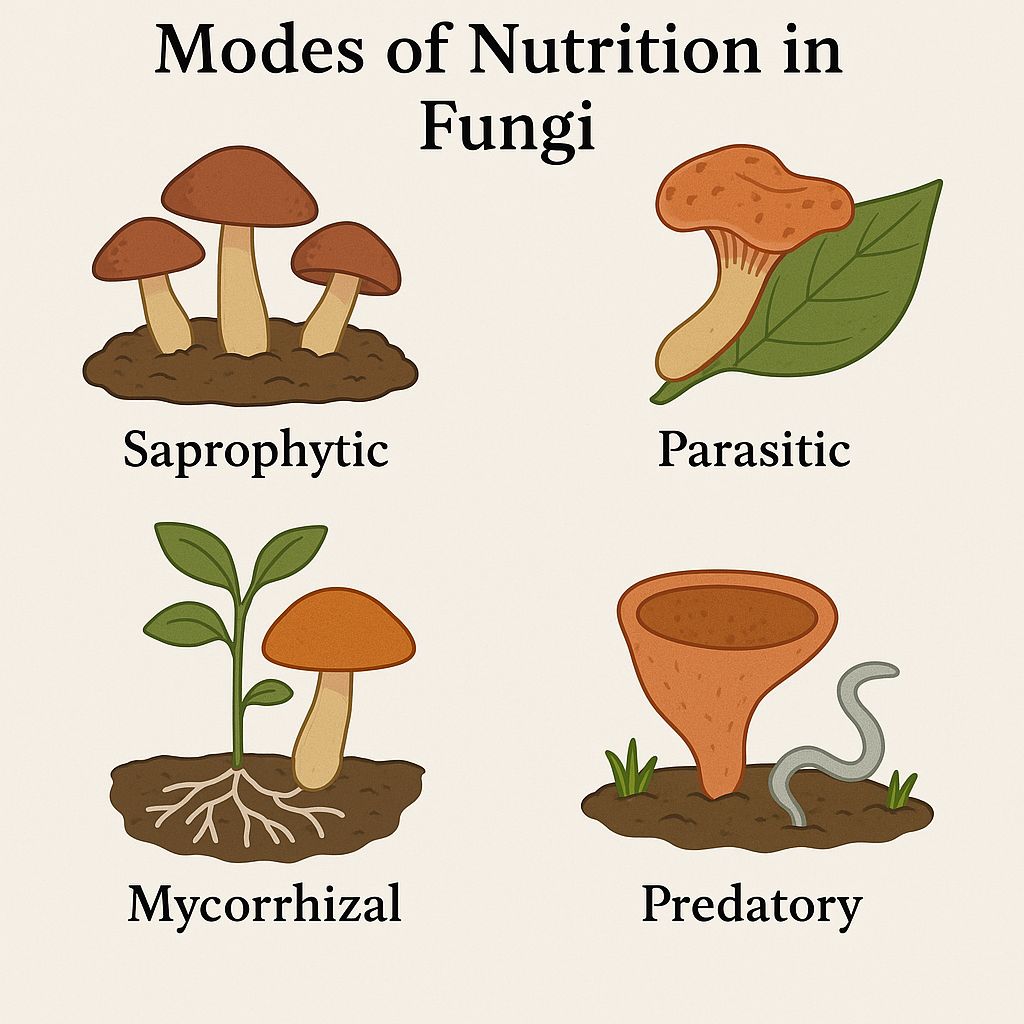
Fungi use different methods to obtain food:
Saprophytic fungi feed on dead and decaying organic matter. They are essential in ecosystems because they help decompose and recycle nutrients back into the soil. A common example is Rhizopus, which grows on stale bread. Parasitic fungi obtain their nutrients from living organisms. They often harm their host, causing diseases in plants, animals, and humans. Examples include Candida, which can infect humans, and Puccinia, which causes rust disease in wheat. Symbiotic fungi live in a mutual relationship with other organisms. Mycorrhizal fungi, for example, form associations with plant roots, helping the plant absorb minerals and water while receiving food in return. Lichens are another example where fungi live together with algae or cyanobacteria, both benefiting from the relationship
Reproduction in Fungi

Fungi reproduce in various ways:
Asexual reproduction in fungi involves only one parent and typically results in genetically identical offspring. This can occur through the formation of spores, which are lightweight and easily dispersed, allowing the fungus to colonize new areas quickly. Some fungi, like yeast, reproduce asexually through a process called budding, where a new cell grows out of the parent cell. Others can reproduce by fragmentation, where a piece of the fungal body breaks off and grows into a new organism.
Sexual reproduction involves the fusion of two different mating types, resulting in genetic variation. This process leads to the formation of sexual spores, such as zygospores, ascospores, and basidiospores, depending on the fungal group. Sexual reproduction usually occurs under unfavorable environmental conditions, giving rise to more resilient offspring.
Classification of Fungi
Fungi are classified into several major groups based on their structure, mode of reproduction, and other features. The main classes of fungi include:
1. Zygomycota (Zygomycetes)
Zygomycota are fungi known for forming sexual spores called zygospores, which develop when two compatible hyphae fuse together. Asexually, they reproduce through sporangiospores, which are produced inside a sporangium at the tip of the hyphae. Most zygomycetes are saprophytic, meaning they feed on dead and decaying organic matter. A common example is Rhizopus stolonifer, known as black bread mold, which is often seen growing on spoiled bread.
2. Ascomycota (Sac Fungi)
Ascomycota, also called sac fungi, represent the largest group of fungi. They are named for their characteristic sac-like structure called an ascus, where sexual spores called ascospores are formed. These fungi can also reproduce asexually using conidiospores, which are formed externally on specialized hyphae. Ascomycetes can be either unicellular, like yeast, or multicellular, like molds. Examples include Saccharomyces cerevisiae (used in baking and brewing), Penicillium (used to produce antibiotics), and Aspergillus (used in food production and fermentation).
3. Basidiomycota (Club Fungi)
Basidiomycota are known as club fungi because they produce sexual spores called basidiospores on a club-shaped structure called a basidium. These fungi include many of the common mushrooms, puffballs, and bracket fungi seen in forests. While some are edible, others can be toxic or cause diseases in plants. For example, Agaricus bisporus is the common edible mushroom, while Puccinia species are responsible for rust diseases in crops.
4. Deuteromycota (Imperfect Fungi)
Deuteromycota are called imperfect fungi because their sexual stage of reproduction has not been observed. They reproduce only asexually through conidia. This group includes many fungi that are medically and agriculturally important. For example, Candida albicans can cause infections in humans, and Trichophyton causes skin diseases like athlete’s foot and ringworm.
5. Chytridiomycota (Chytrids)
Chytridiomycota are considered the most primitive type of fungi. They produce motile, flagellated spores called zoospores, which allow them to move in water. These fungi are mostly found in aquatic or very moist environments. Some chytrids are harmless, while others, like Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis, are known to infect amphibians and contribute to the decline in frog population
Importance of Fungi
Fungi are very important in both natural ecosystems and human life. Here are some of their key roles:
As decomposers, fungi help break down dead plants, animals, and organic materials, returning essential nutrients to the soil. This makes them crucial for maintaining healthy ecosystems. In food production, fungi such as yeast are used to make bread, beer, and wine, while molds like Penicillium are involved in cheese-making. Edible mushrooms are also a source of nutrition.
In medicine, fungi have given us important antibiotics, such as penicillin, and are used to produce various drugs, enzymes, and hormones. In agriculture, mycorrhizal fungi improve plant growth by enhancing nutrient absorption, and some fungi act as natural pesticides, helping to control harmful pests.
Importance of Fungi
While many fungi are helpful, some can be harmful:
Fungi can act as plant pathogens, causing diseases like rust, smut, and mildew, which reduce crop yields and affect food supply. In humans, certain fungi cause infections such as ringworm, candidiasis, and respiratory problems. Molds can spoil food and produce toxic substances like aflatoxins, which are harmful if ingested. Additionally, some fungi break down wood and other building materials, leading to structural damage in homes and buildings.
Symbiotic Relationships
Fungi often form close partnerships with other organisms:
Lichens are a symbiotic association between a fungus and an alga or cyanobacterium. The fungus provides protection and structure, while the alga performs photosynthesis to make food. Lichens can grow on rocks, trees, and soil and are useful as indicators of air pollution.
Mycorrhizae are partnerships between fungi and plant roots. The fungus increases the root’s ability to absorb water and nutrients, especially phosphorus, while the plant supplies sugars and other nutrients to the fungus. This relationship is beneficial for both and is found in the majority of plant species.
Fungi vs Plants
Though fungi were once classified as plants, they are quite different:
| Feature | Fungi | Plants |
|---|---|---|
| Cell Wall | Chitin | Cellulose |
| Nutrition | Heterotrophic (absorption) | Autotrophic (photosynthesis) |
| Chlorophyll | Absent | Present |
| Storage Product | Glycogen | Starch |
| Body Structure | Hyphae and Mycelium | Roots, stems, leaves |
Conclusion
Fungi are fascinating organisms that play many important roles in our world. From helping decompose waste to producing medicines and food, their benefits are vast. At the same time, they can also be harmful as disease-causing agents. Understanding their characteristics and classification helps us appreciate their diversity and importance. As research continues, fungi may offer even more valuable uses in science, medicine, and industry.
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
What is fungi?
Fungi are a group of living organisms that are distinct from plants, animals, and bacteria. They form their own biological kingdom called Fungi.
What is the importance of fungi?
Fungi are essential organisms that decompose organic matter, support plant growth, produce food and medicine, and play vital roles in ecological balance and biotechnology.
What are the harmful effects of fungi?
Fungi can cause harmful effects such as infections in humans and animals, spoilage of food, and diseases in plants that reduce agricultural productivity.
Related Articles