What do you mean by Tinea corporis?
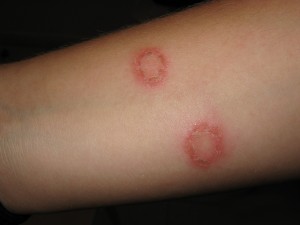
Tinea corporis, commonly referred to as ringworm, is a typical skin fungal infection. Despite the unsettling moniker, dermatophytes, a type of fungus, are the source of the condition. These microscopic creatures feed on the keratin found in human skin, hair, and nails and flourish in warm, humid conditions. Tinea corporis is not fatal, but it can be very unpleasant, generating scaly, itchy patches that are hard to remove.
Table of Contents
The Aetiology of the Source of Itch
When dermatophytes get on your skin, tinea corporis occurs. Direct contact with an infected person or animal, sharing personal items like towels or clothing, or even coming into contact with contaminated soil are all easy ways for these fungus to spread.
Below is a summary of the most frequent offenders:
Trichophyton: The predominant causative agent, accountable for the majority of instances of tinea corporis.
Microsporum: Particularly in young patients, this fungus can lead to more serious infections.
Epidermophyton: It can also result in tinea corporis. It is frequently linked to tinea pedis (athlete’s foot) and tinea cruris (jock itch).
The Clinical Manifestations of the Signs and Symptoms
Although tinea corporis can appear with a range of symptoms, the ring-shaped rash is the most distinctive feature. Let’s take a deeper look:
Oval or round patches: These frequently have a distinct centre surrounded by an elevated, scaly border. Usually, the outside border is itchy, red, and swollen.
The impacted region may be dry, flaky, and covered in microscopic scales that are easily removed with a scraper.
Itching: This is a typical complaint that can range from little annoyance to excruciating itching that keeps you up at night.
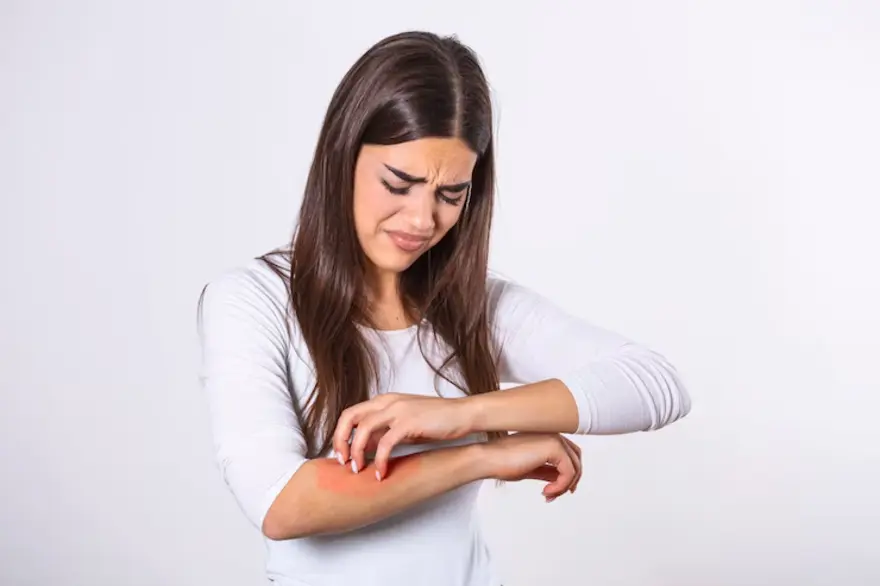

Pain: Although it’s not usually felt, some people may feel as though something is burning or stinging, particularly if the infection is severe or if a secondary bacterial infection appears.
Location: Although tinea corporis can develop anywhere on the body, the arms, legs, chest, and belly are the most common places.
Shape and size: The patches might take the form of tiny, coin-sized lesions or bigger, spreading regions that cover a sizable amount of the skin.
Finding the Offender: Evaluation
Tinea corporis is usually easy to diagnose, based on a combination of:
Clinical examination
A physician will look at the skin lesions and record their location, size, form, and appearance.
Microscopic analysis
An afflicted area’s skin scraping is collected and analysed under a microscope. This makes it possible to identify the hyphae and fungal spores, validating the diagnosis.
Culture
To help identify the precise type of dermatophyte causing the infection, a sample of the skin scraping may be cultured to grow the fungus in a laboratory setting.
It’s crucial to remember that tinea corporis might resemble other skin disorders. A medical professional’s comprehensive examination is essential to rule out other potential causes, such as psoriasis, eczema, or allergic responses.
Eliminating the Fungus: Management
The goals of treating tinea corporis include symptom management and fungal infection eradication.
Treatment with topical antifungal medicines is the cornerstone. By directly applying these creams, lotions, or solutions to the afflicted area, the fungi are killed. Typical instances consist of:
- Clotrimazole
- Miconazole
- Ketoconazole Terbinafine
In cases where topical treatment is ineffective or the infection is severe, a prescription for oral antifungal medicine may be necessary. These drugs function by preventing the fungus from spreading throughout the body. As examples, consider:
- Fluconazole
- Terbinafine Itraconazole
For a satisfactory outcome, general care and management are essential:
Maintain the afflicted region dry and clean by giving it a gentle wash with soap and water. Especially in the spaces between the fingers and toes, give it a vigorous pat to dry.
Refrain from scratching: Despite the allure, scratching can exacerbate the infection and raise the possibility of developing secondary bacterial infections.
Refrain from sharing personal goods: Clothes, towels, and other materials that are intimate can transfer the fungus.
Wear clothing that breathes: Natural fibres that fit loosely allow the skin to breathe and reduce the buildup of sweat.
Wasj towles and bed lines: Regularly wash towels and bed linens in hot water with detergent to get rid of any remaining fungus.
Treat underlying illnesses: eople who have compromised immune systems or undiagnosed medical conditions may need specialised care and treatment plans.
The key is prevention
Maintain proper hygiene by avoiding close contact with sick people and washing your hands frequently.
Maintain a dry skin tone: If you work out, change out of your wet clothes right away, and stay away from wearing anything too tight.
Make use of distinct washcloths and towels: Keep personal hygiene products apart from other people.
Refrain from touching animals: If you have pets, make sure they are clear of fungus and stay away from stray animals in close proximity.
When to Get Medical Help
Even though tinea corporis is typically treatable, you should consult a physician if:
Either a serious or widespread illness exists.
Over-the-counter medication does not work to treat the illness.
It may be more challenging to treat the infection if you have underlying medical issues.
You have a fever, discomfort, or other unsettling symptoms.
Treatment for tinea corporis is simple and involves taking the right medication and maintaining proper cleanliness. You may reduce your risk of infection and have clear, healthy skin by being aware of its causes, identifying its symptoms, and taking the appropriate precautions.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQ)
What do you mean by Tinea corporis?
Tinea corporis, commonly referred to as ringworm, is a typical skin fungal infection. Despite the unsettling moniker, dermatophytes, a type of fungus, are the source of the condition. These microscopic creatures feed on the keratin found in human skin, hair, and nails and flourish in warm, humid conditions. Tinea corporis is not fatal, but it can be very unpleasant, generating scaly, itchy patches that are hard to remove.
What do you mean by Fungus?
Eukaryotic organisms, or fungi, are microorganisms that include moulds, mushrooms, and yeasts. These organisms fall into the category of fungus. The creatures that make up Kingdom fungus are ubiquitous and have cell walls. They fall under the category of heterotrophs in the kingdom of living things.
Related Articles